The document provides an overview of access control in communication networks, focusing on methods used in the data link layer such as framing, flow control, and channelization techniques like FDMA, TDMA, and CDMA. It outlines various access control mechanisms including random and controlled access methods in Ethernet and WLAN environments. Additionally, it references key materials and lecture videos for further learning.
![Communication
Networks
Access Control
in datalink layer
[Channelization Methods]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-200809145201/75/2-5-access-control-channelization-methods-1-2048.jpg)

![Session Summary
• Flow Control [Similar to traffic control signal]
• Simple Protocol
• Stop and wait protocol
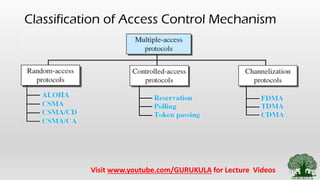
• Access Control [Similar to people accessing the cell tower]
• Random Access Methods [Checks the channel randomly, Idle – Transmit, Busy – Check again]
• ALOHA [Pure ALOHA, Slotted ALOHA]
• CSMA [ 1 Persistent, n Persistent, p Persistent]
• CSMA – CD [widely used in Ethernet]
• CSMA – CA [widely used in WLAN]
• Controlled Access Methods [Following a systematic approach]
• Reservation – Similar to Reserving the seats in Bus or train
• Polling – Similar to Master Slave Concept
• Token Passing – Similar to passing a Mic among the audience in seminar
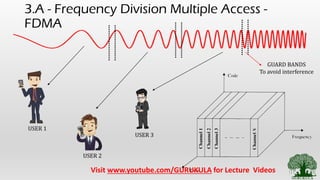
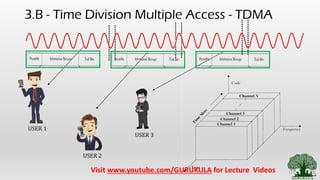
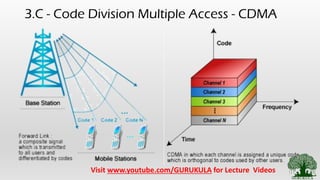
• Channelization Methods [ Similar to Highway Lane separation]
• FDMA – Users are differentiated wrt to Frequency
• TDMA – Users are differentiated wrt to Time
• CDMA – Users are differentiated wrt to Code](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-200809145201/85/2-5-access-control-channelization-methods-7-320.jpg)
