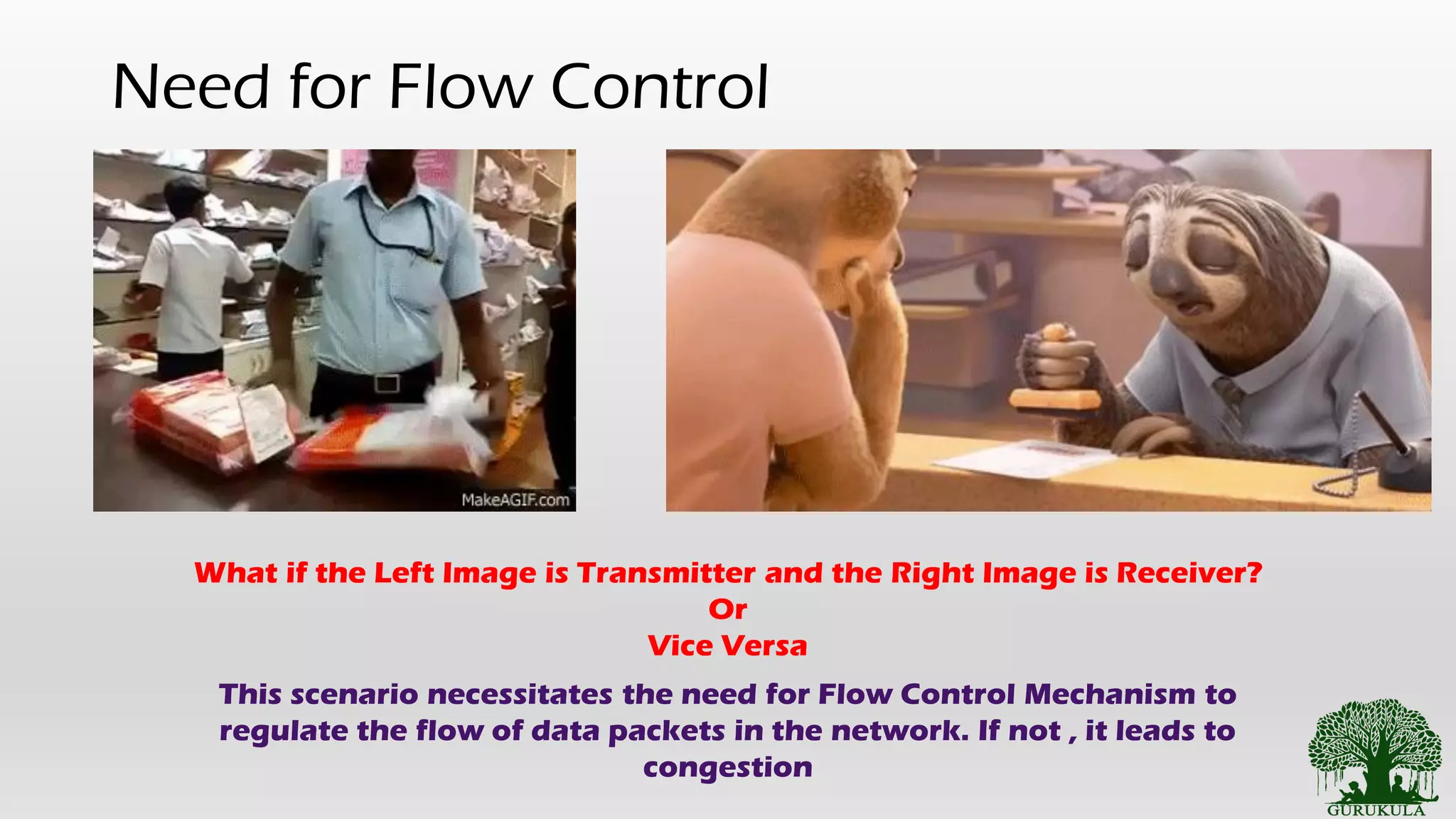
This document discusses flow control in data link layer communication networks. It describes the need for flow control to regulate data packet flow and avoid congestion. The main types of flow control mechanisms are simple protocol, stop and wait protocol, go back N protocol, and selective repeat protocol. Stop and wait protocol is explained, where the sender sends one frame at a time and waits for an acknowledgment before sending the next frame to ensure reliable transmission. The session summary reiterates flow control functions similarly to traffic signals and outlines simple protocol and stop and wait protocol.





![Session Summary
•Flow Control [Similar to traffic control signal]
•Simple Protocol
•Stop and wait protocol
Visit www.youtube.com/GURUKULA for Lecture Videos](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-200802171710/75/2-2-flow-control-8-2048.jpg)
