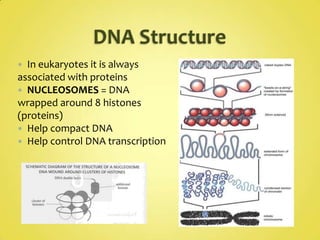
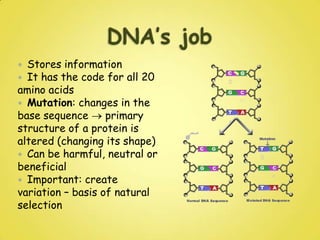
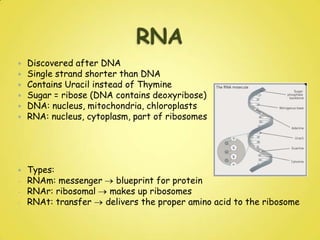
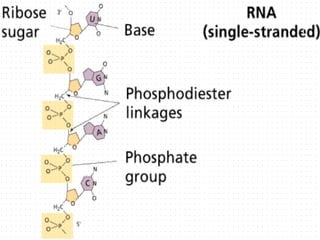
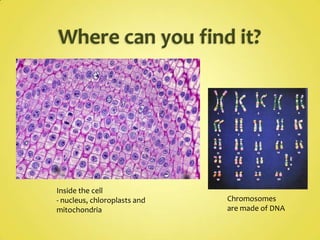
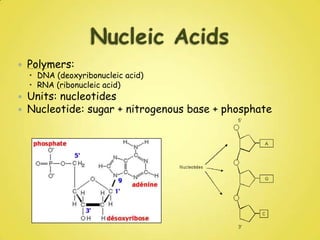
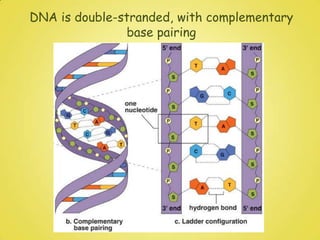
DNA and RNA are nucleic acids that are made up of nucleotides containing a phosphate group, a 5-carbon sugar (ribose in RNA and deoxyribose in DNA), and a nitrogenous base. DNA exists as a double helix containing two anti-parallel strands bound together via hydrogen bonding between complementary nucleotide base pairs of adenine-thymine and cytosine-guanine. RNA is single-stranded and contains the base uracil instead of thymine. DNA stores genetic information in the nucleus, mitochondria, and chloroplasts, while RNA aids in protein synthesis and has various functions in the nucleus and cytoplasm.



![Watson, Crick and Wilkins used unpublished data from Rosalind Franklin’s research obtained without her knowledge and used without her consent. - She was misrepresented and unrecognized - She died of cancer in 1958We know now: DNA is a double helix made of... - 4 nucleotides - A, T, G, C - in 2 polynucleotide strands - strands run antiparallel - [5'-----3'] - held together via weak H-Bonds & complimentary base pairing (A-T and C-G)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3-37-1dnastructure-090907150203-phpapp02/85/3-3-7-1-Dna-Structure-7-320.jpg)