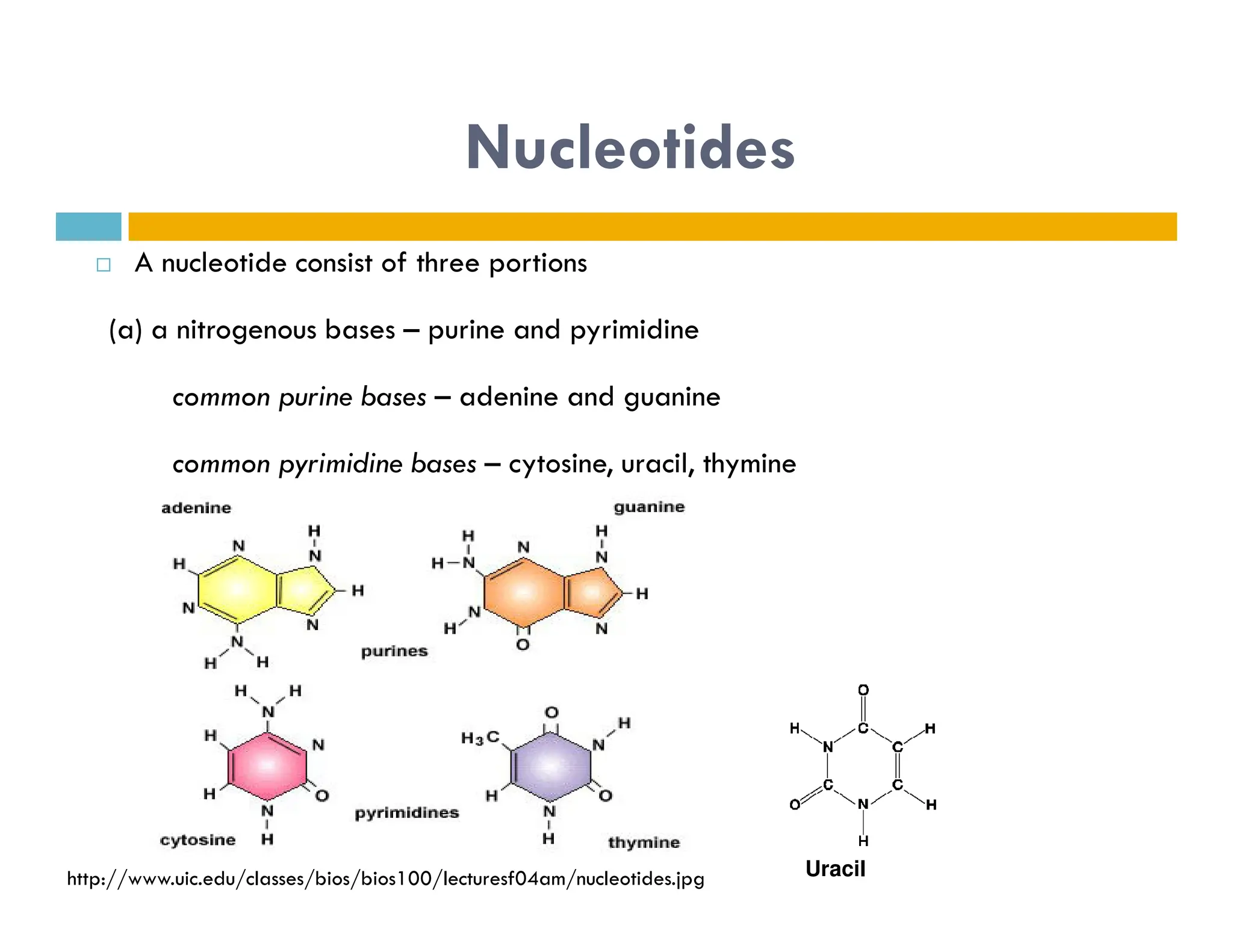
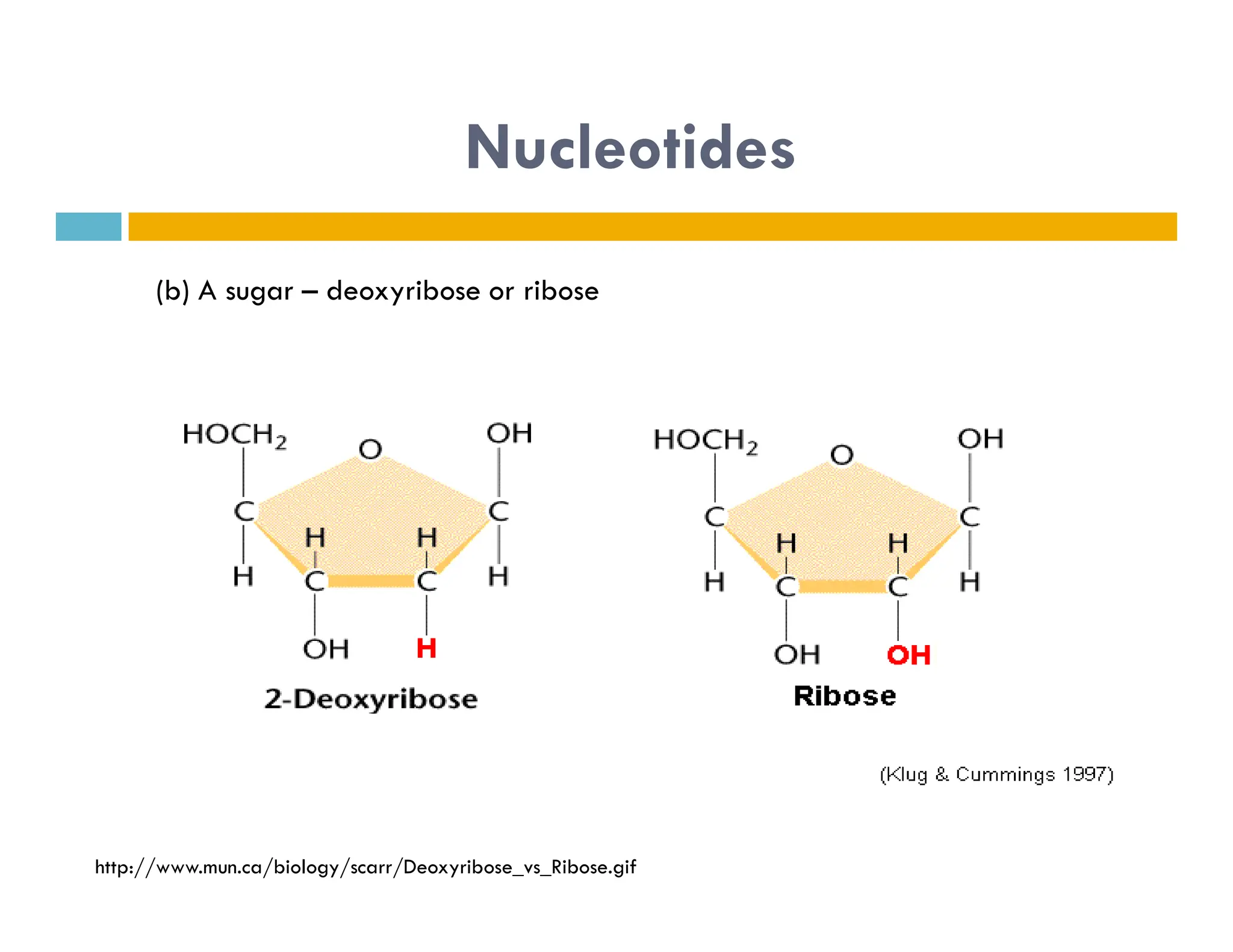
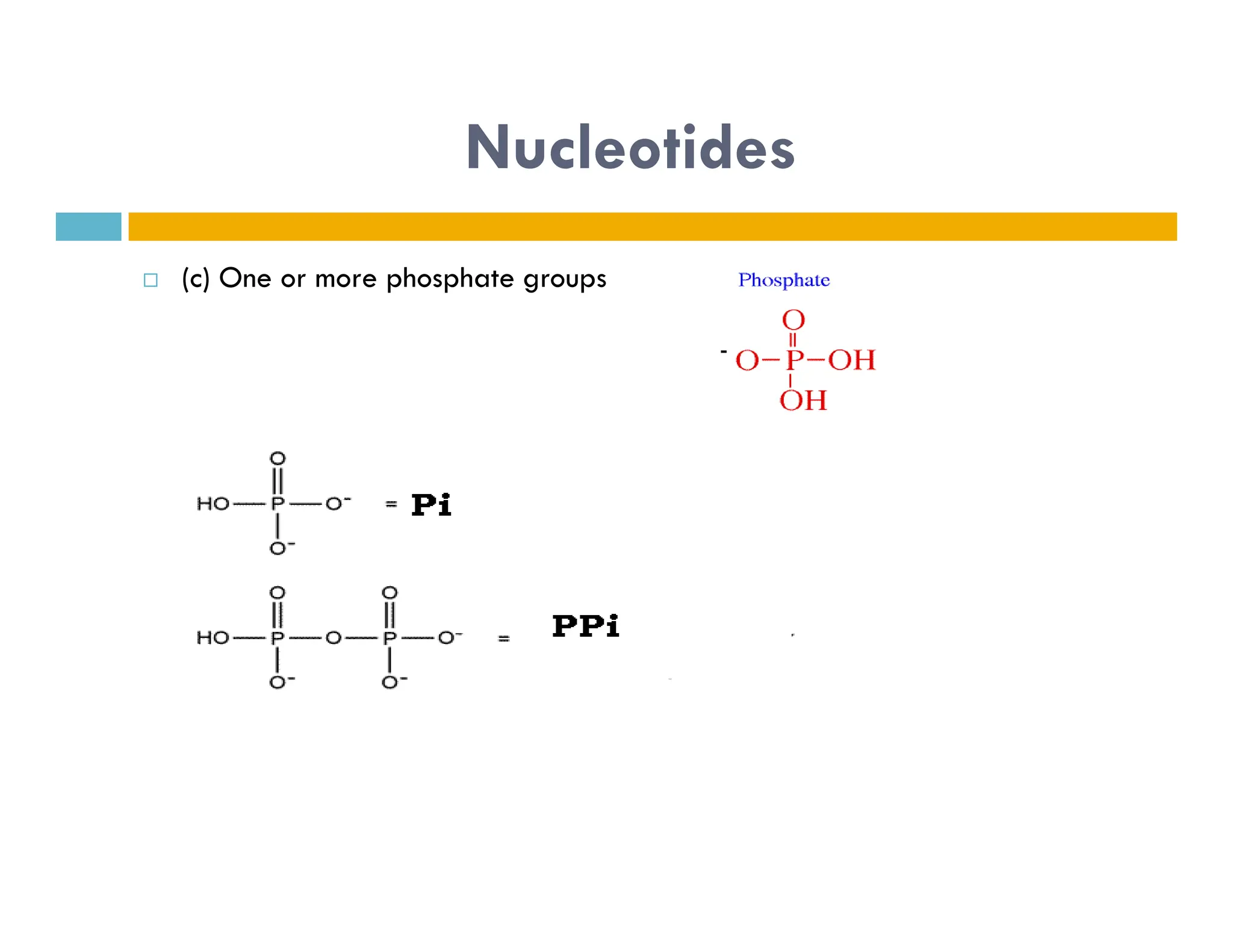
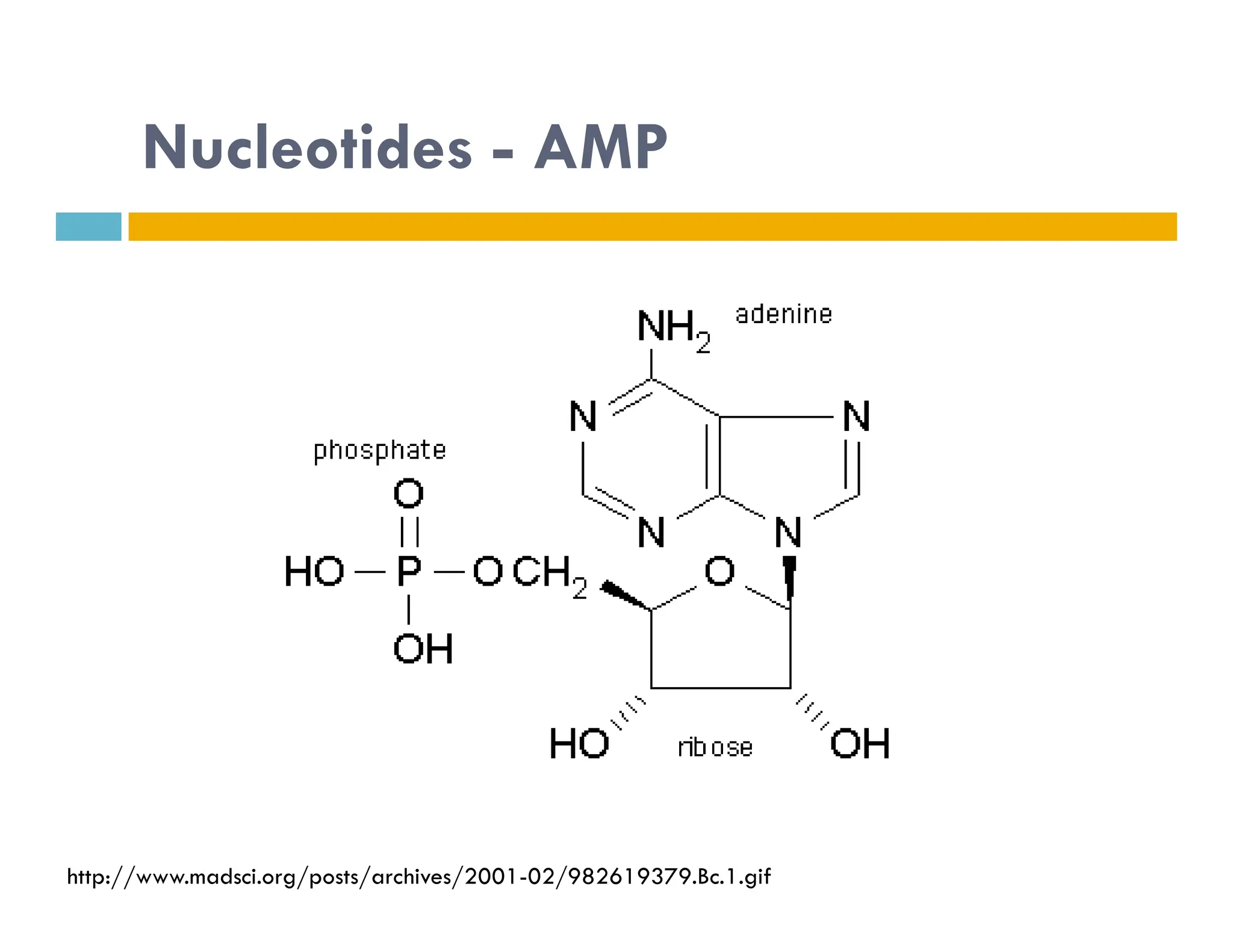
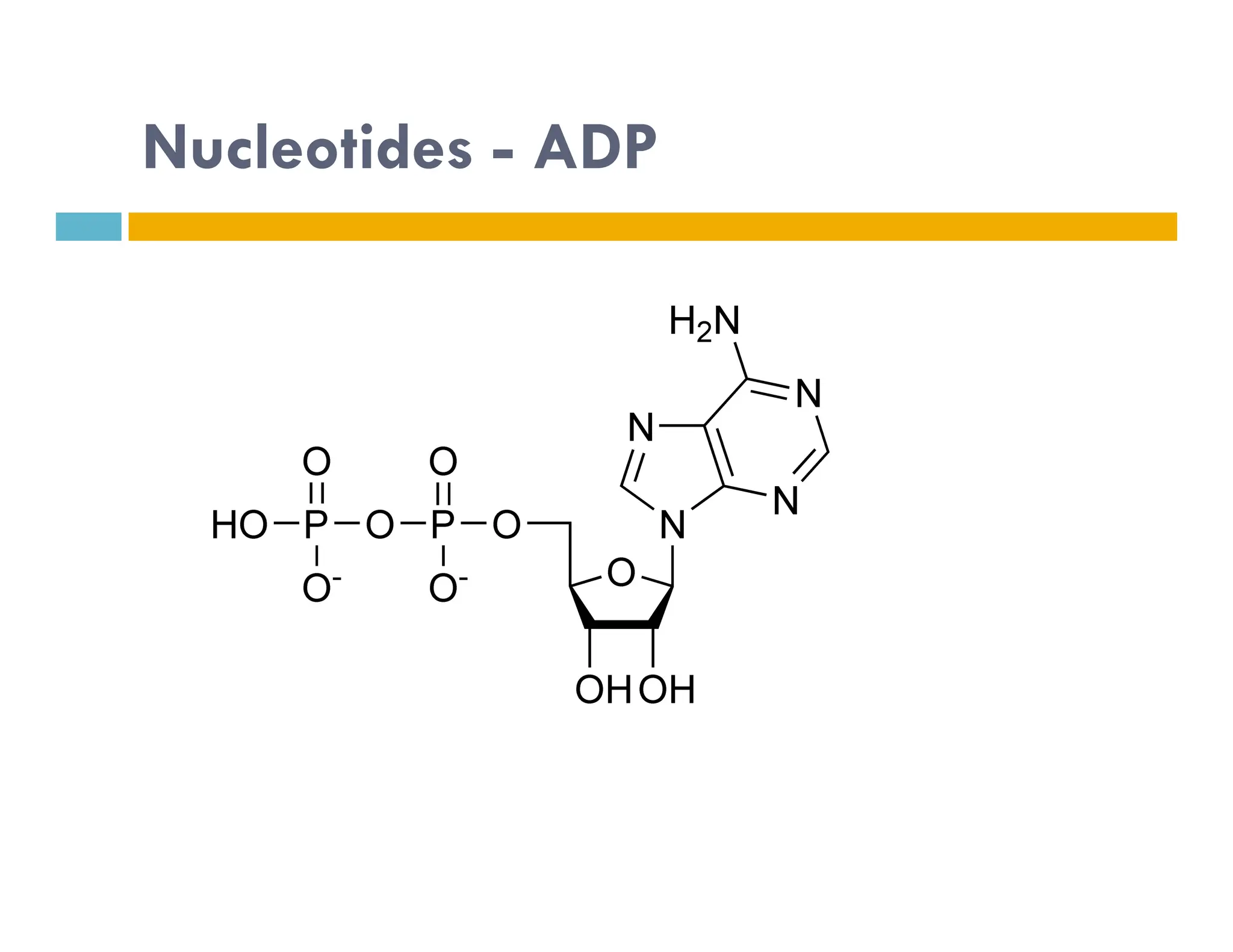
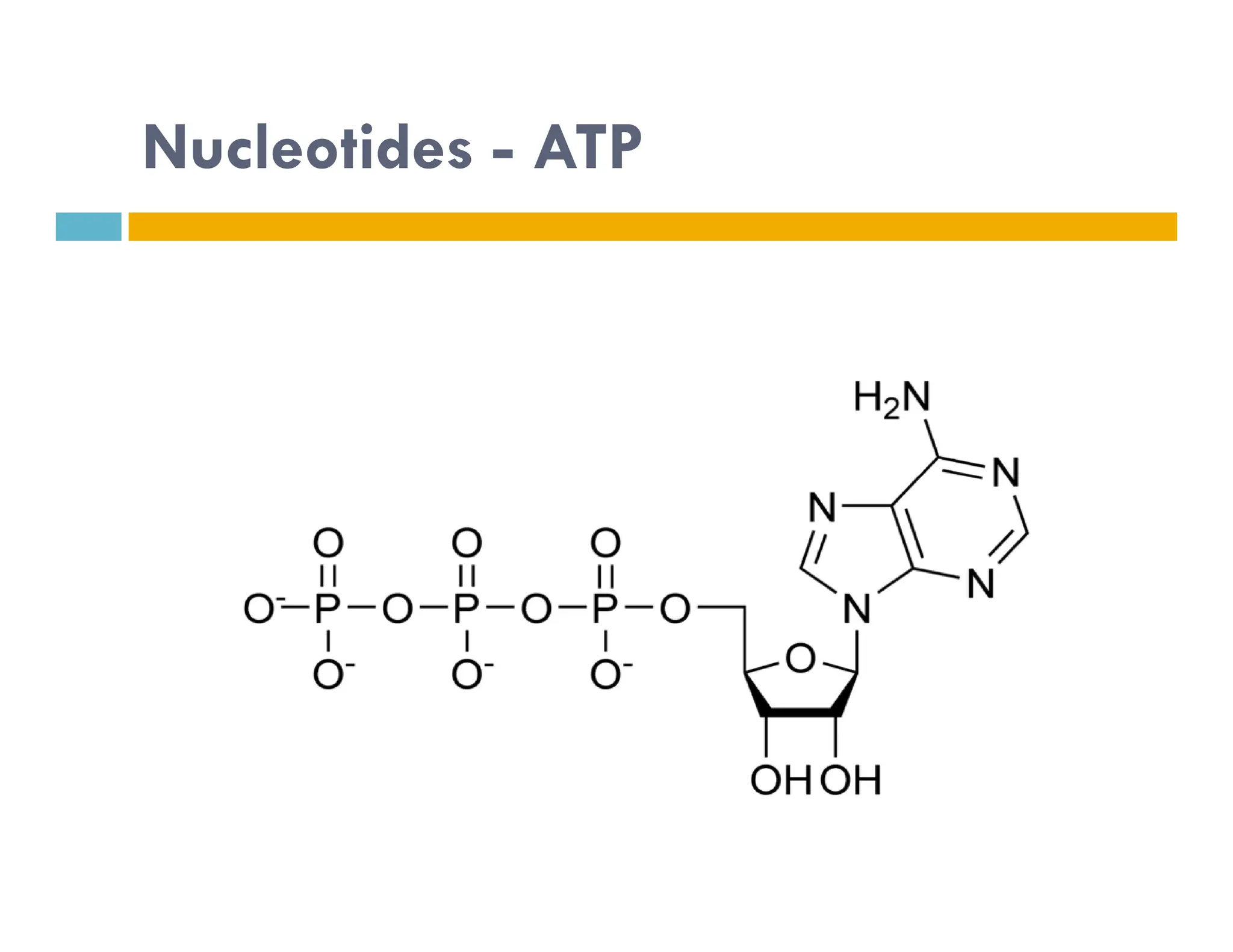
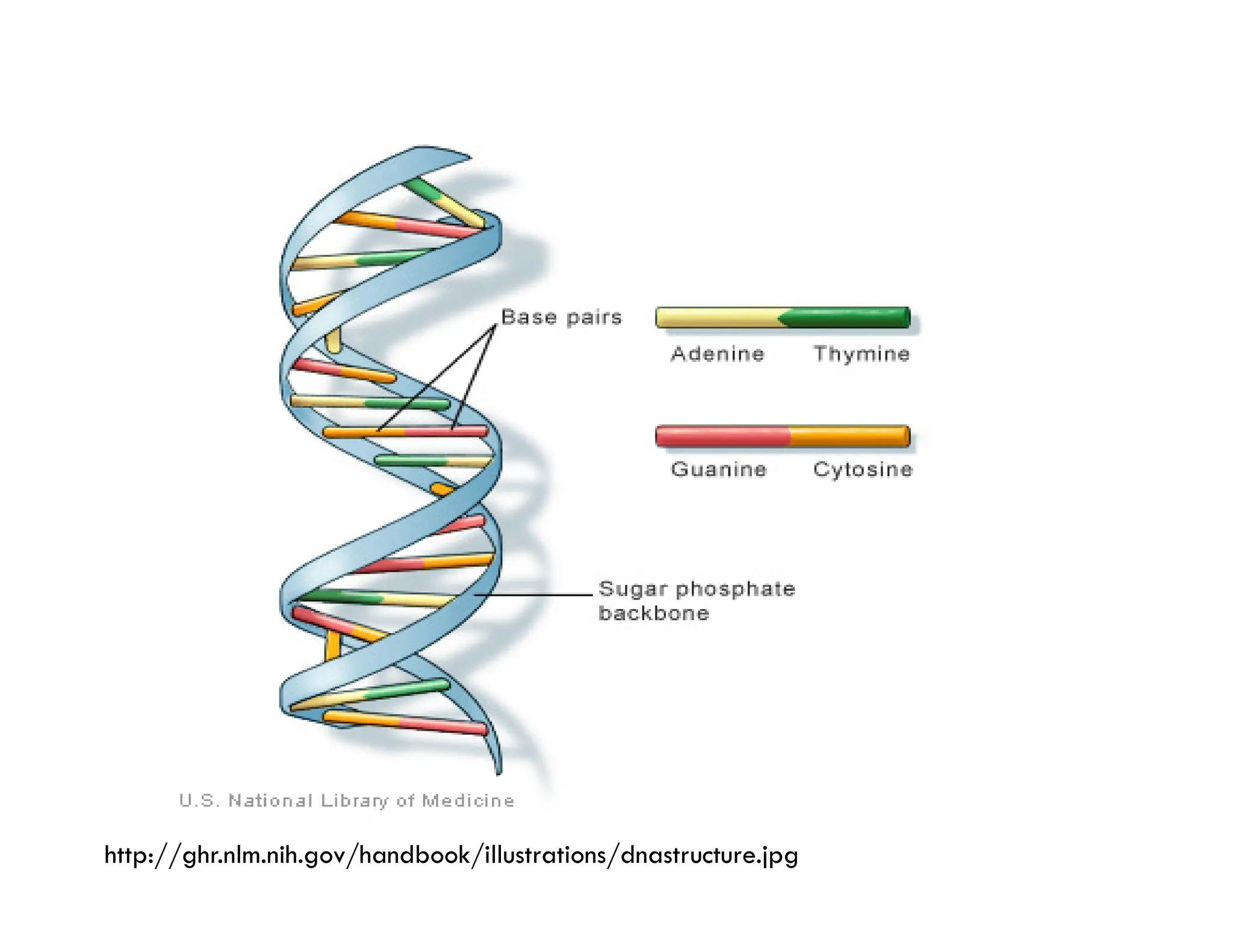
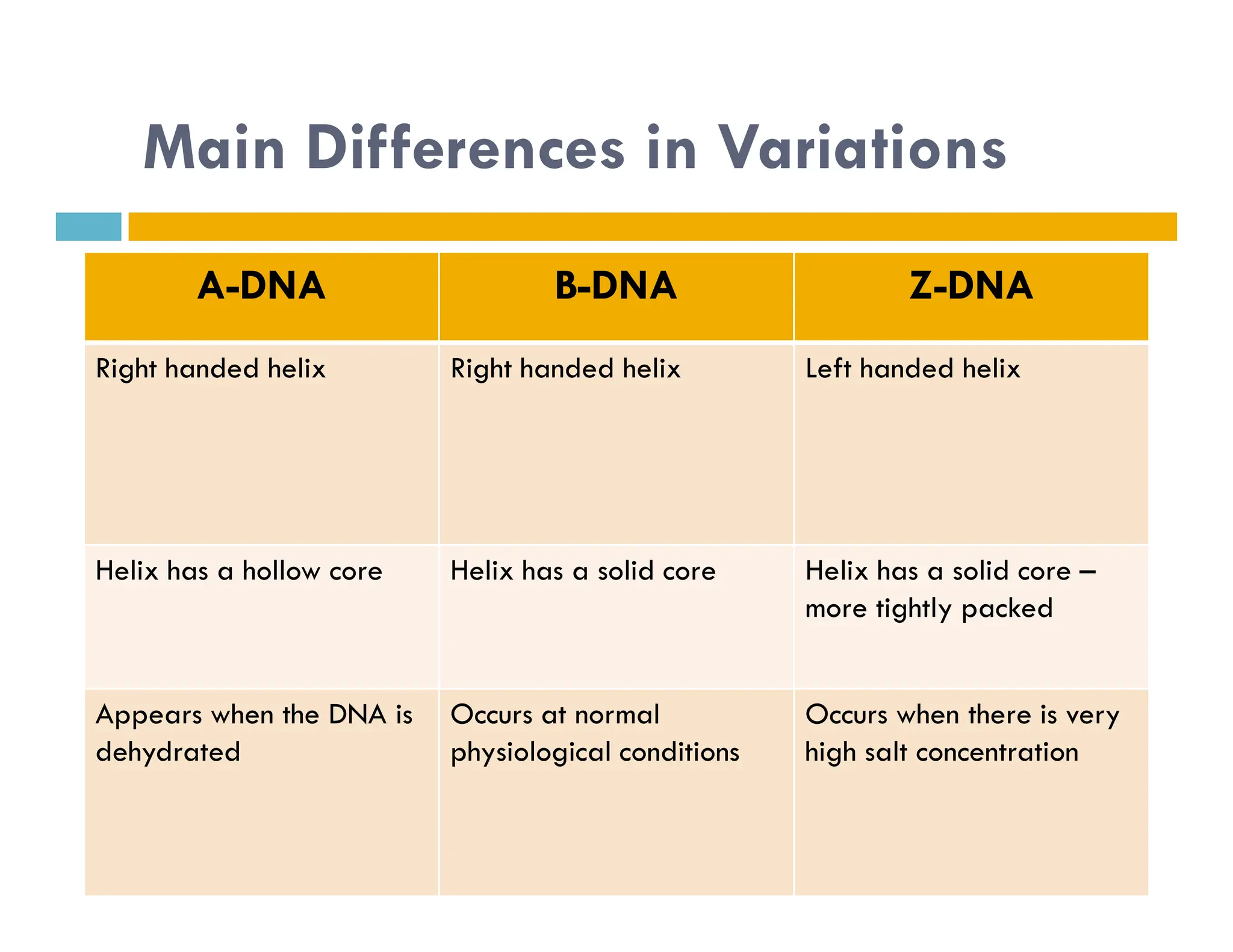
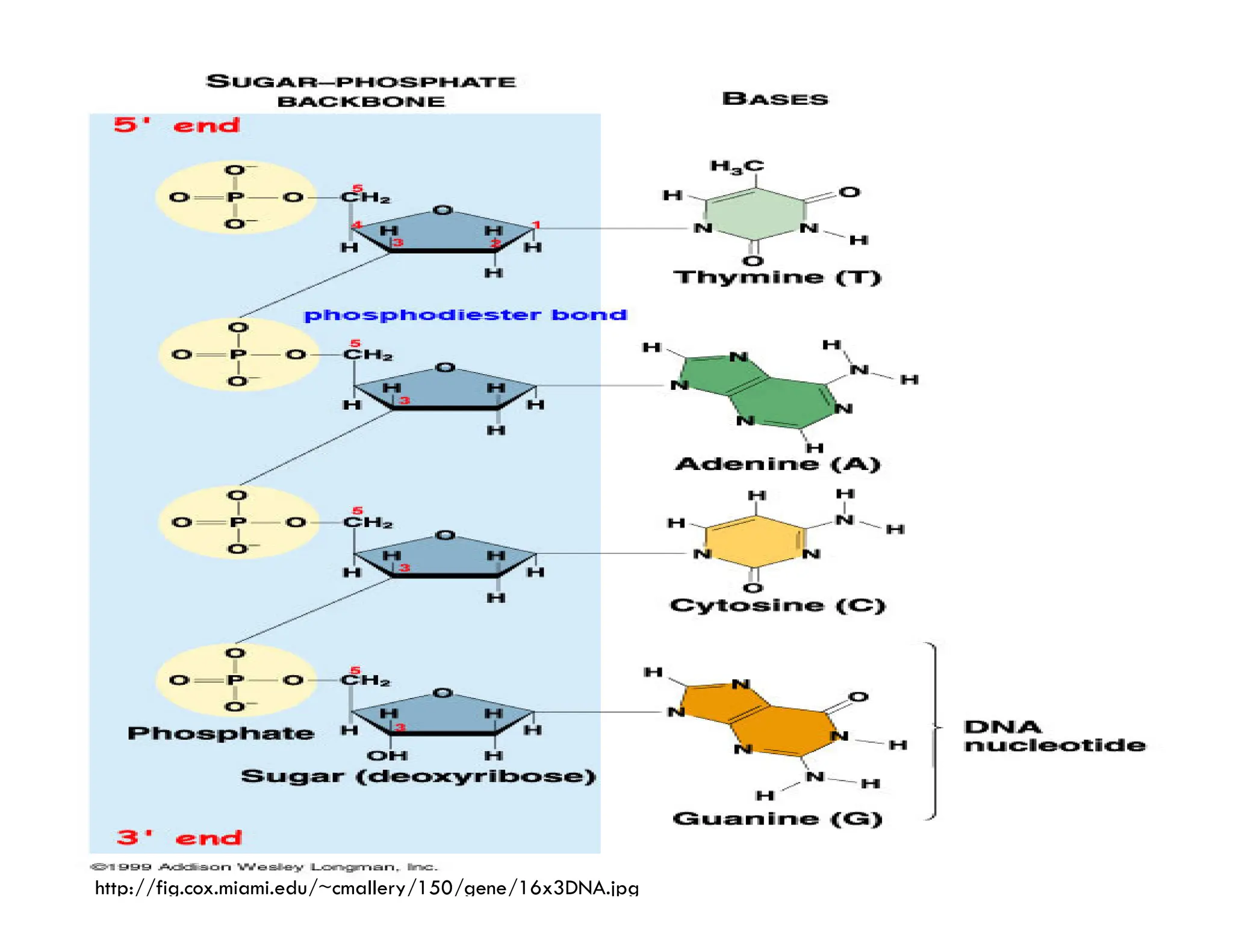
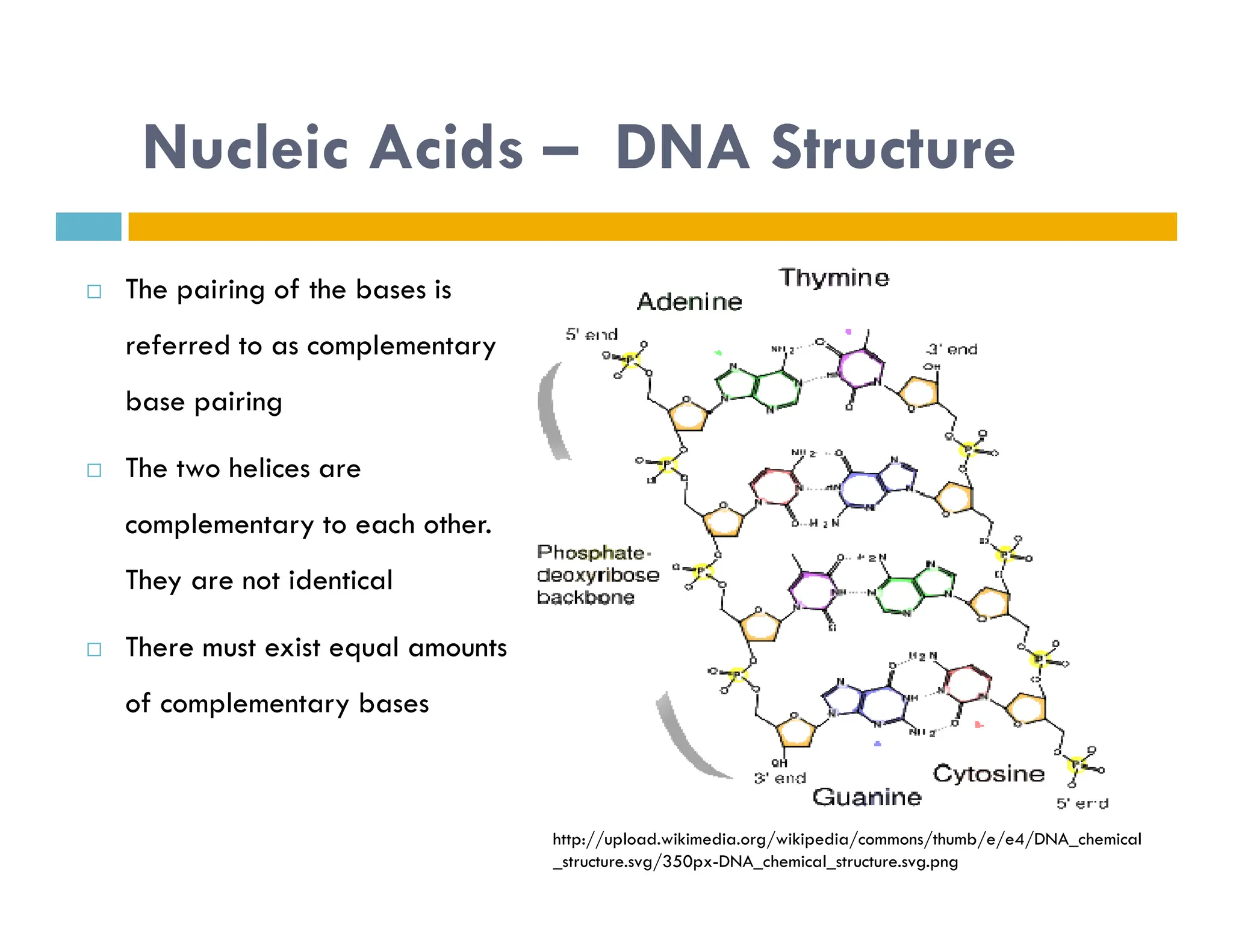
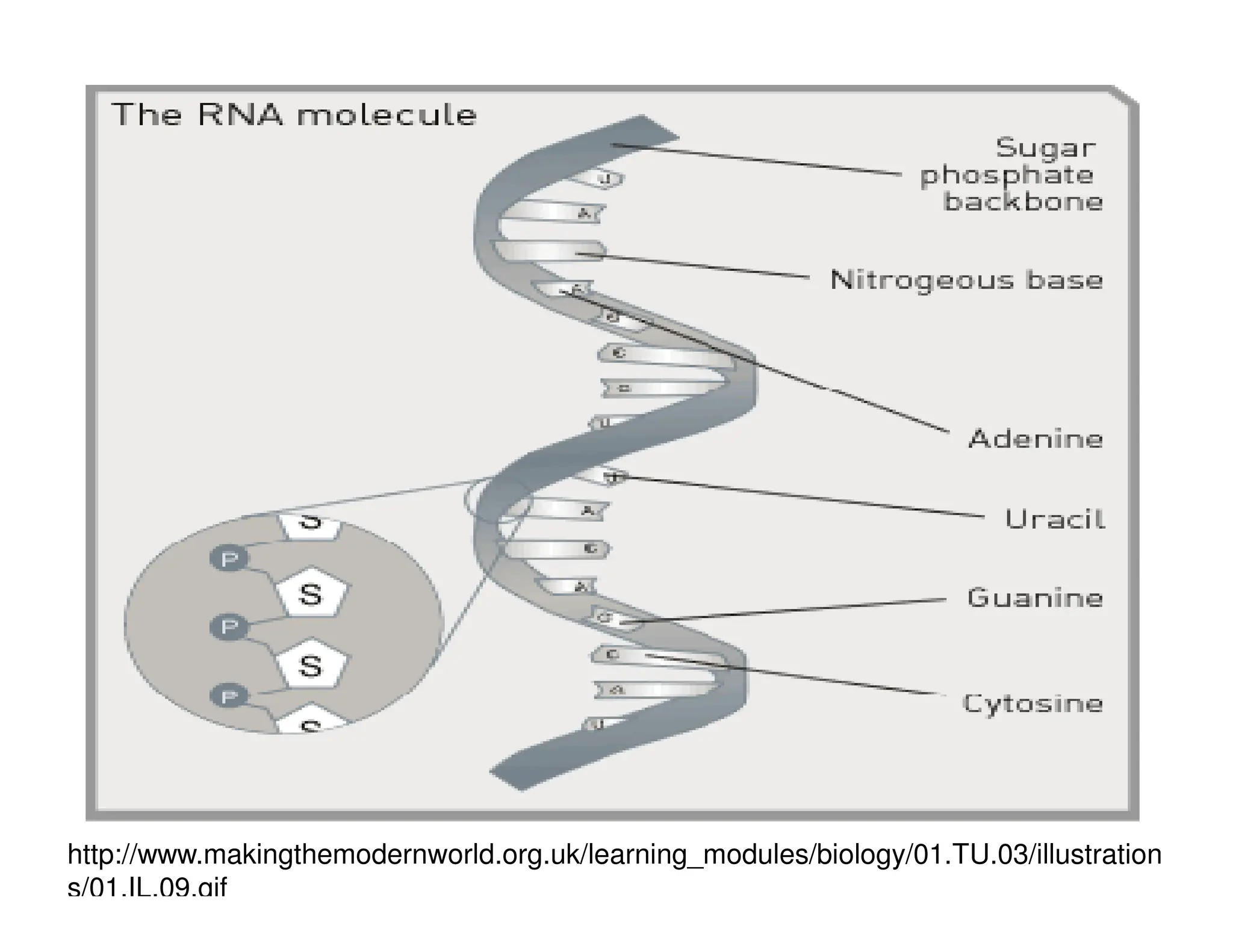
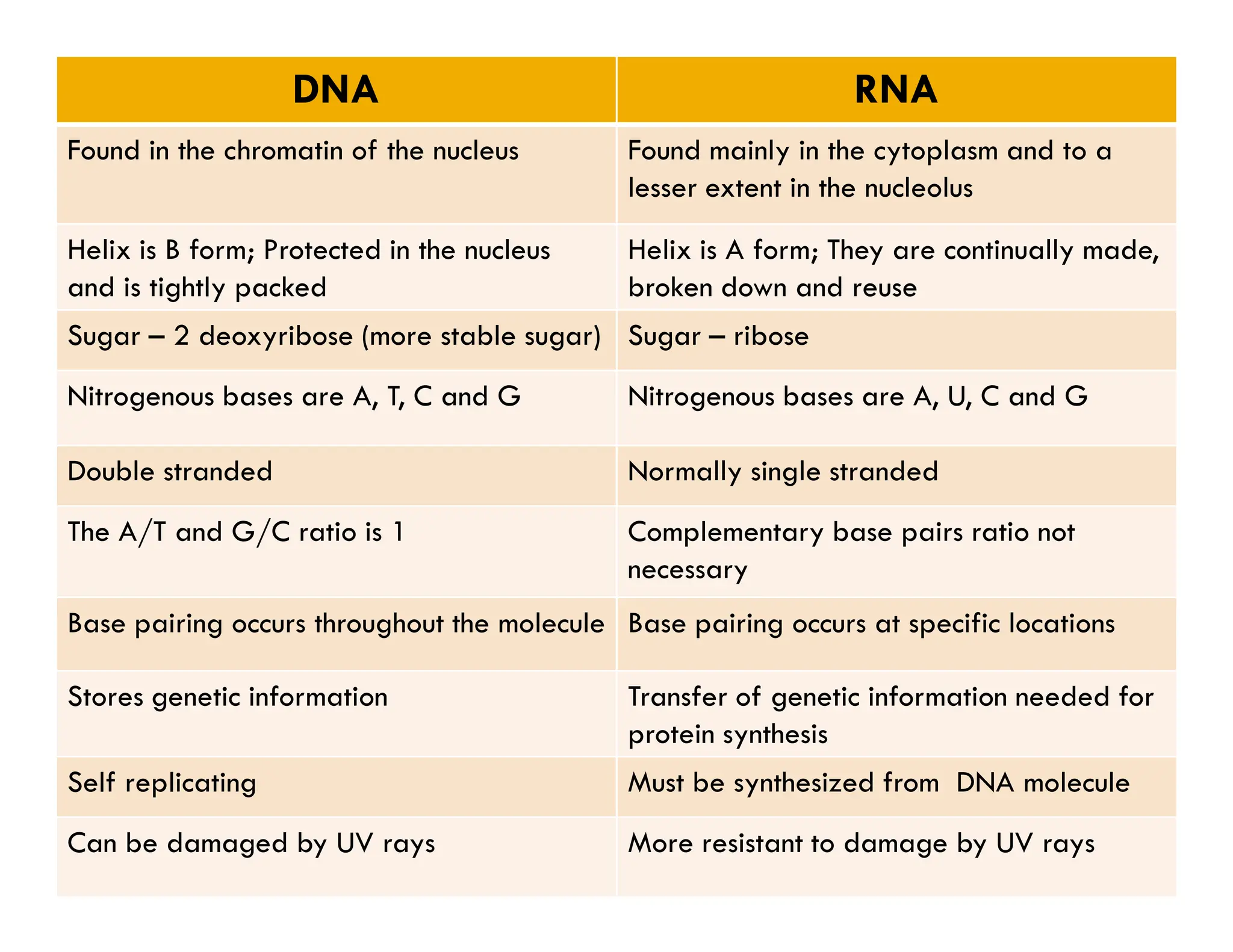
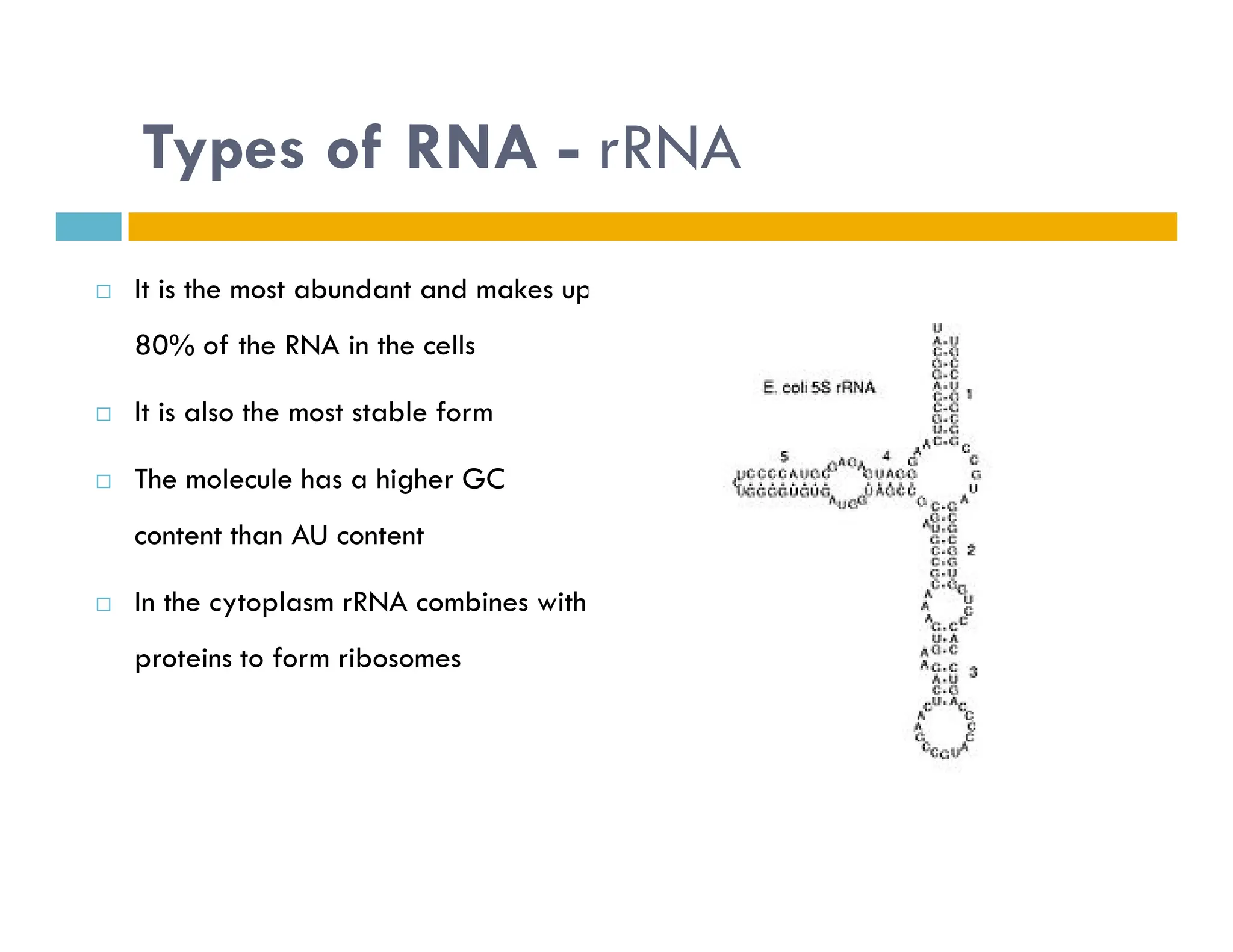
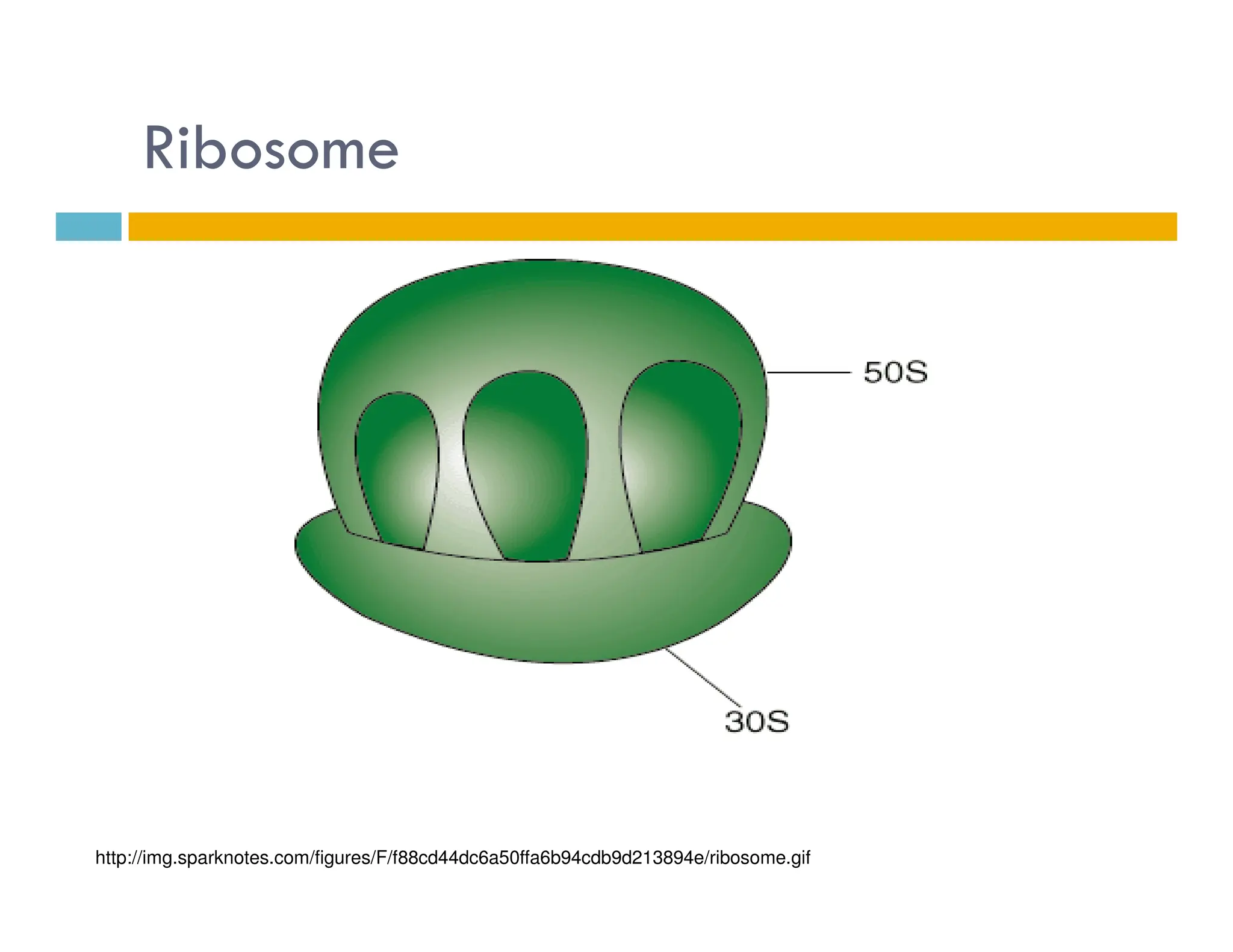
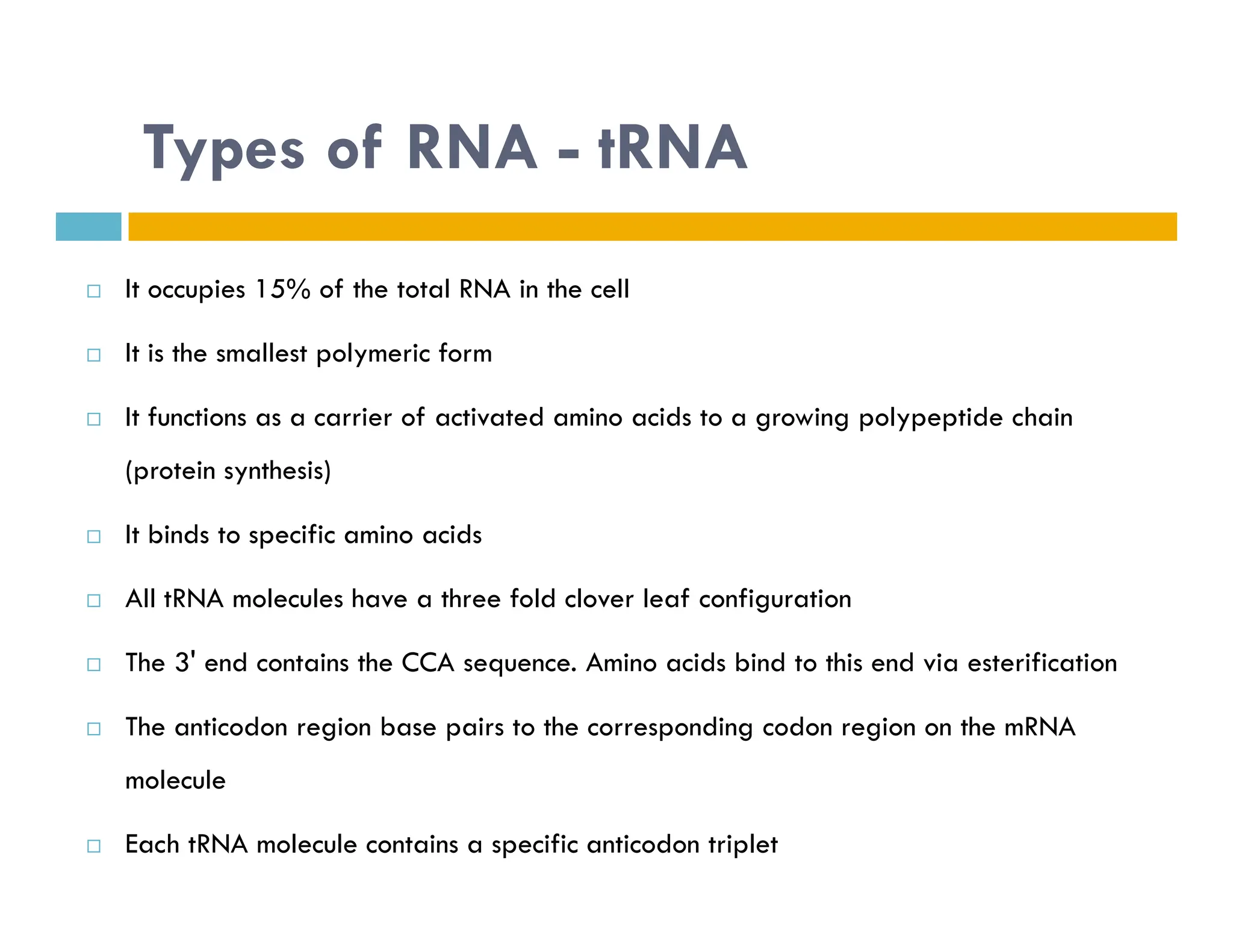
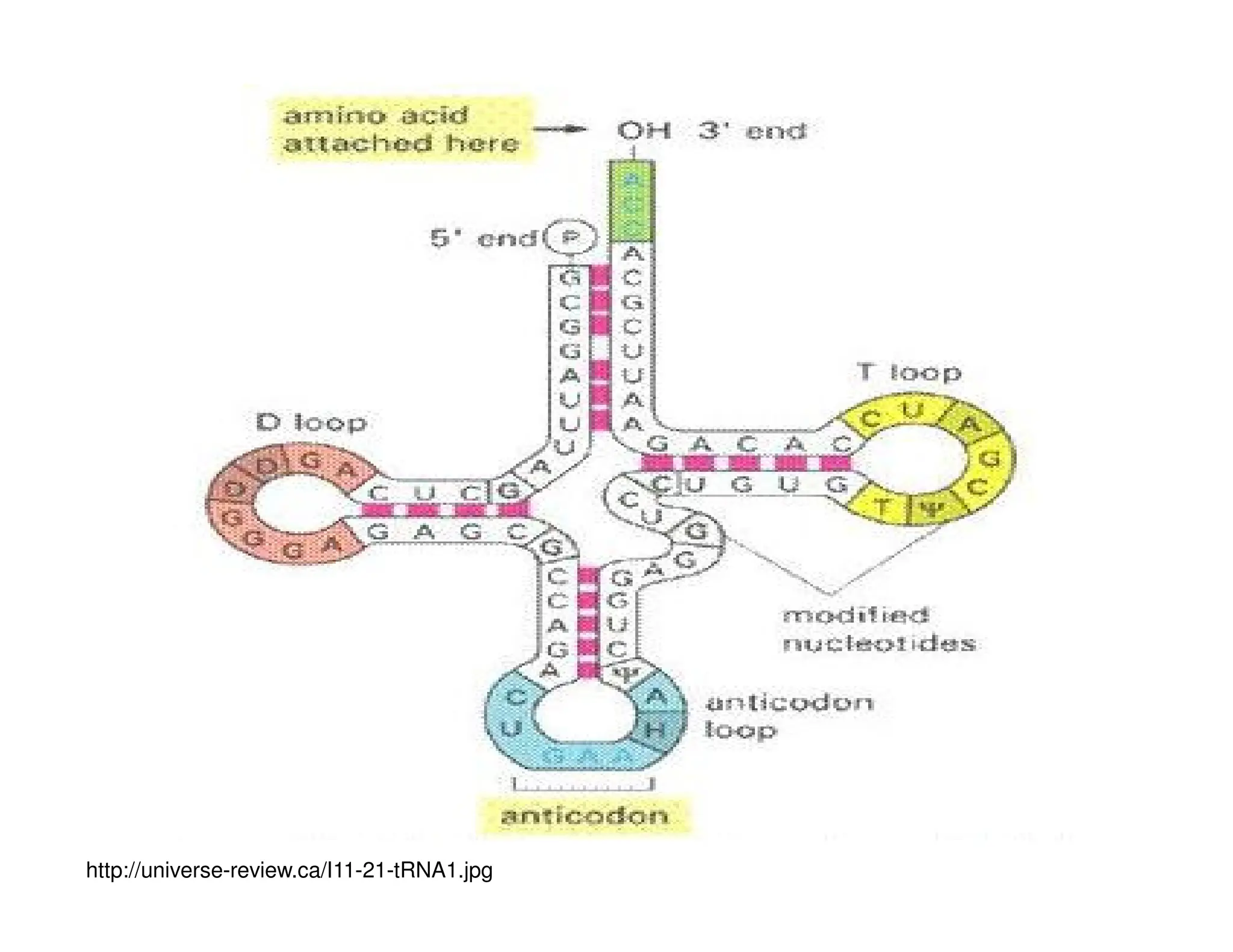
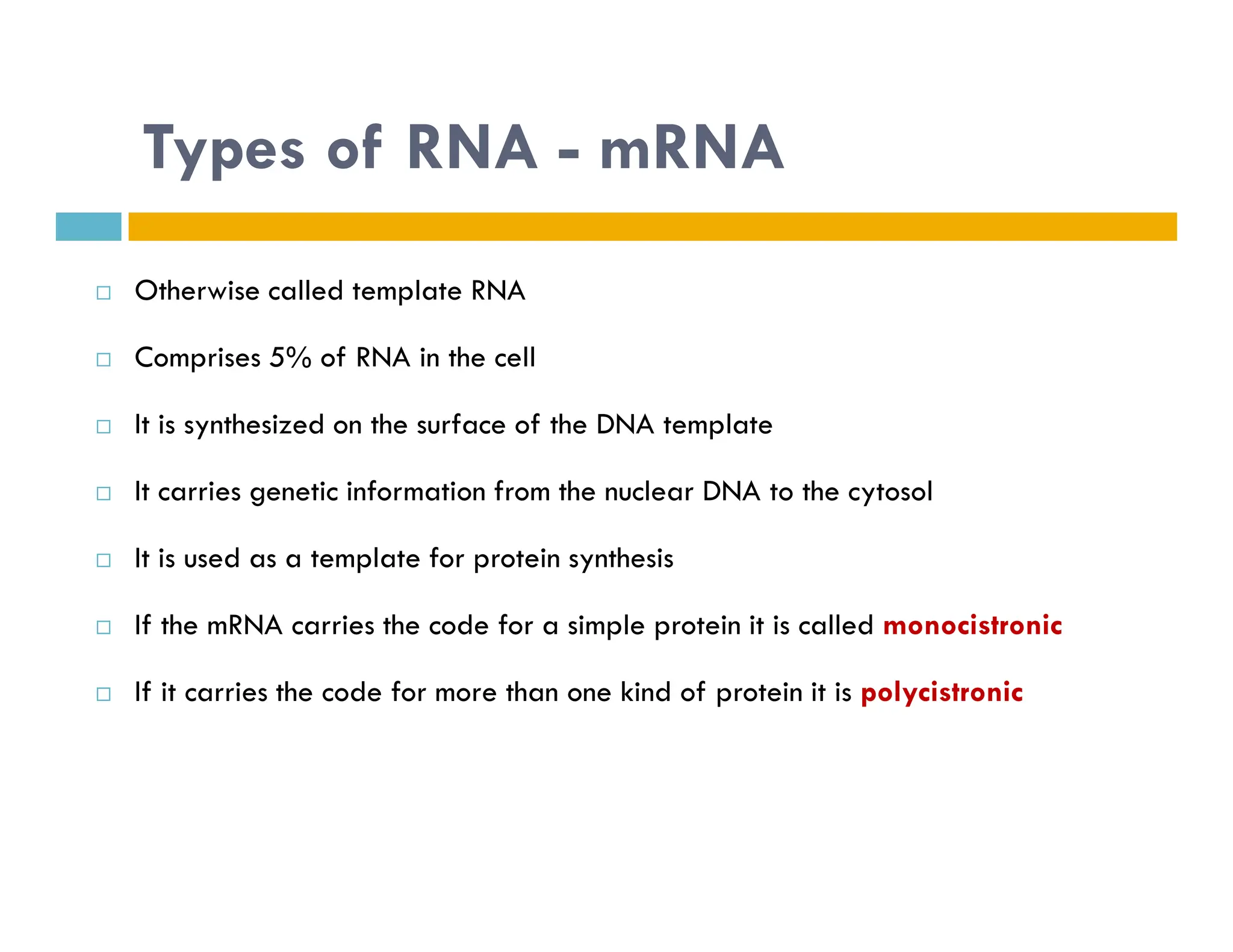
Nucleotides are monomers that make up nucleic acids like DNA and RNA. They consist of a nitrogenous base, a 5-carbon sugar (either deoxyribose or ribose), and phosphate groups. Nucleotides act as energy carriers in cells and are components of coenzymes. There are two main types of nucleic acids: DNA contains the genetic blueprint and is located in the nucleus, while RNA assists in decoding this information and protein synthesis. Both nucleic acids have specific structures like the DNA double helix formed by base pairing between nucleotides on complementary strands.