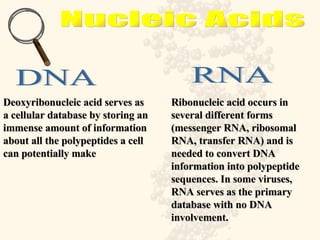
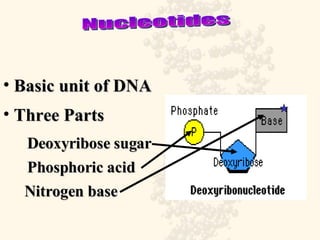
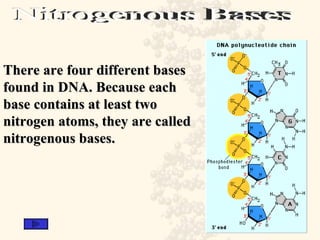
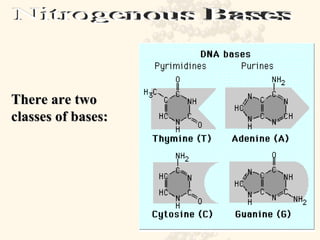
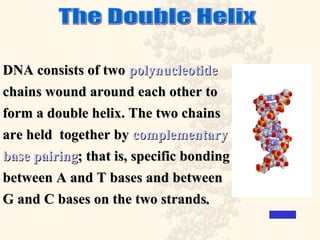
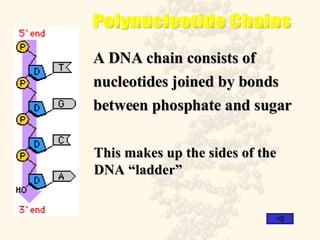
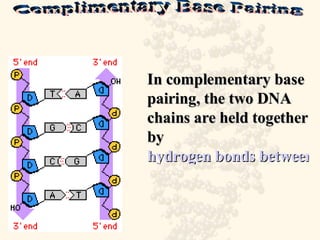
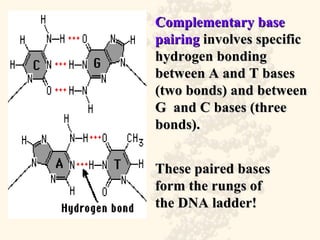
DNA is a long, double-stranded molecule composed of nucleotides that functions to store genetic information. It consists of two polynucleotide chains coiled around each other to form a double helix structure. The two chains are held together by complementary base pairing between adenine (A) and thymine (T), and between guanine (G) and cytosine (C). This complementary base pairing involves hydrogen bonding between the nitrogenous bases and forms the rungs of the DNA ladder.