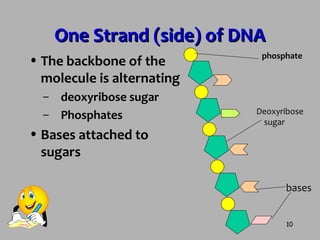
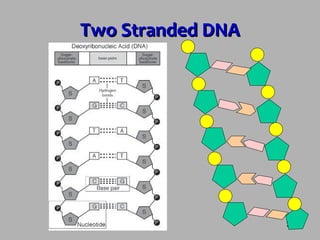
DNA contains the instructions for making proteins and is found in all organisms. It has a double helix shape with nucleotides as subunits. Each nucleotide contains a deoxyribose sugar, phosphate, and one of four nitrogenous bases: adenine, thymine, cytosine, or guanine. The bases bond together in a complementary pairing between strands with adenine bonding to thymine and cytosine bonding to guanine. DNA replication involves the DNA unraveling from histone proteins, being unzipped by the helicase enzyme, and then new complimentary nucleotides being attached to each strand by DNA polymerase to produce two new DNA molecules.