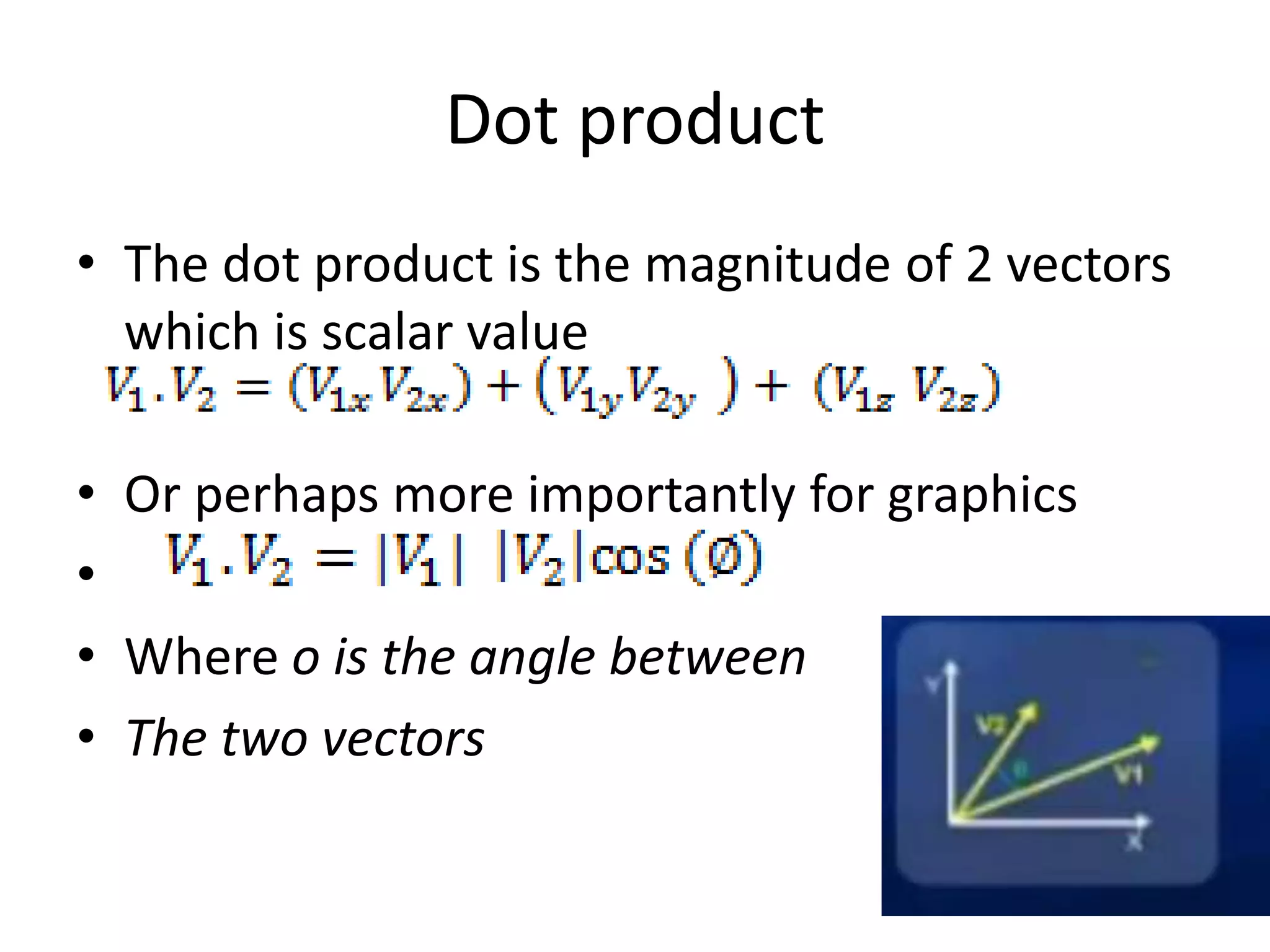
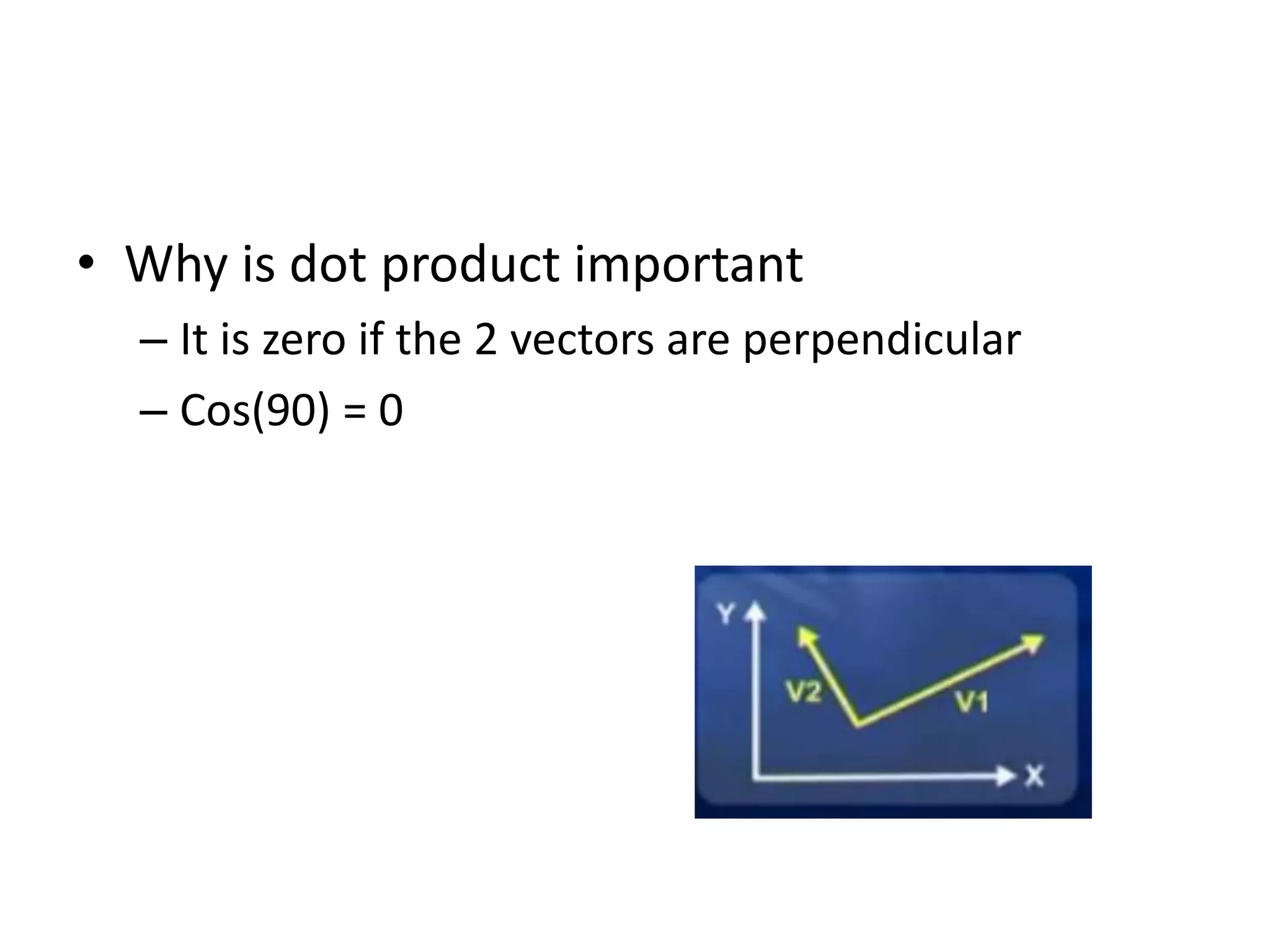
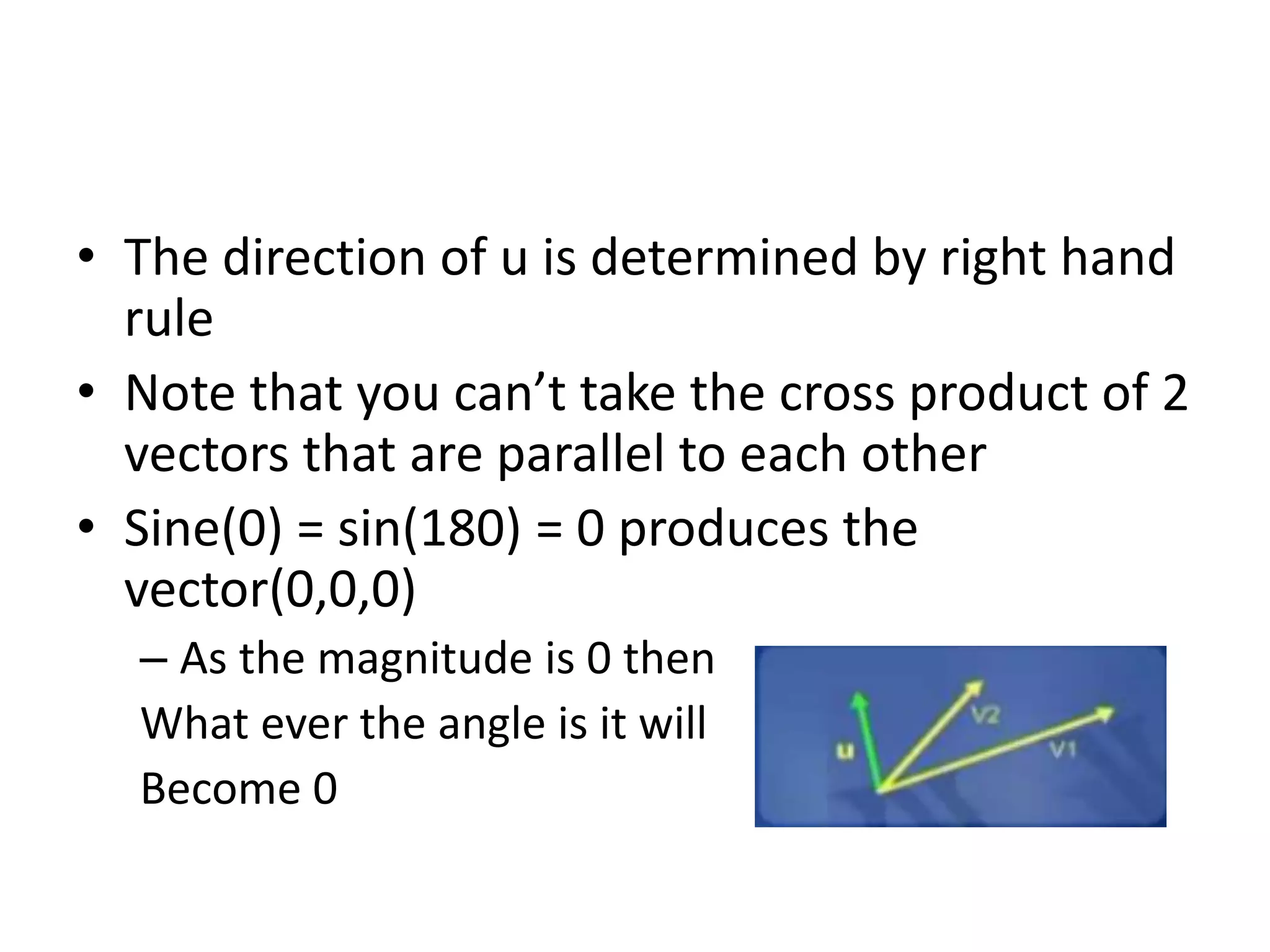
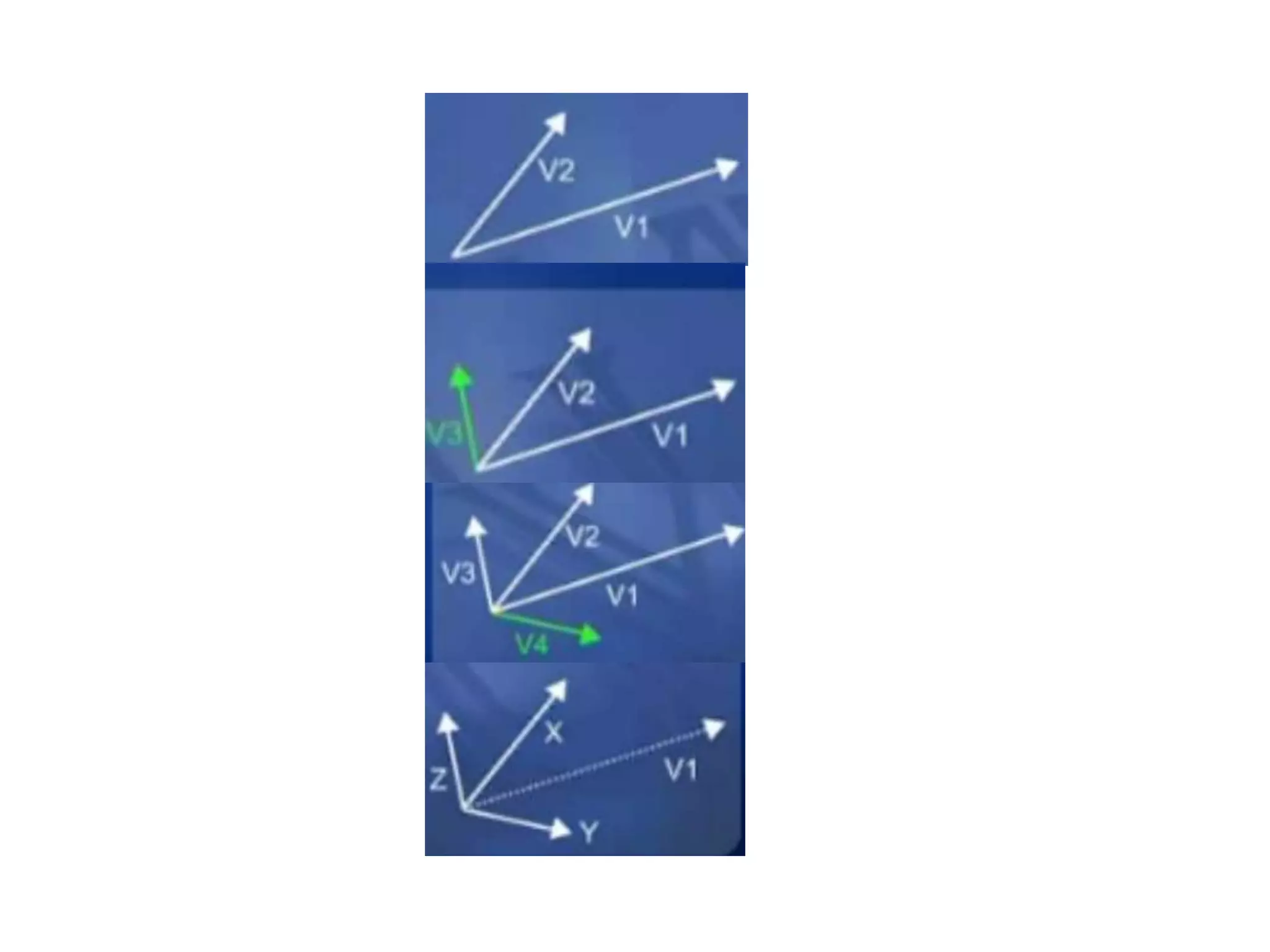
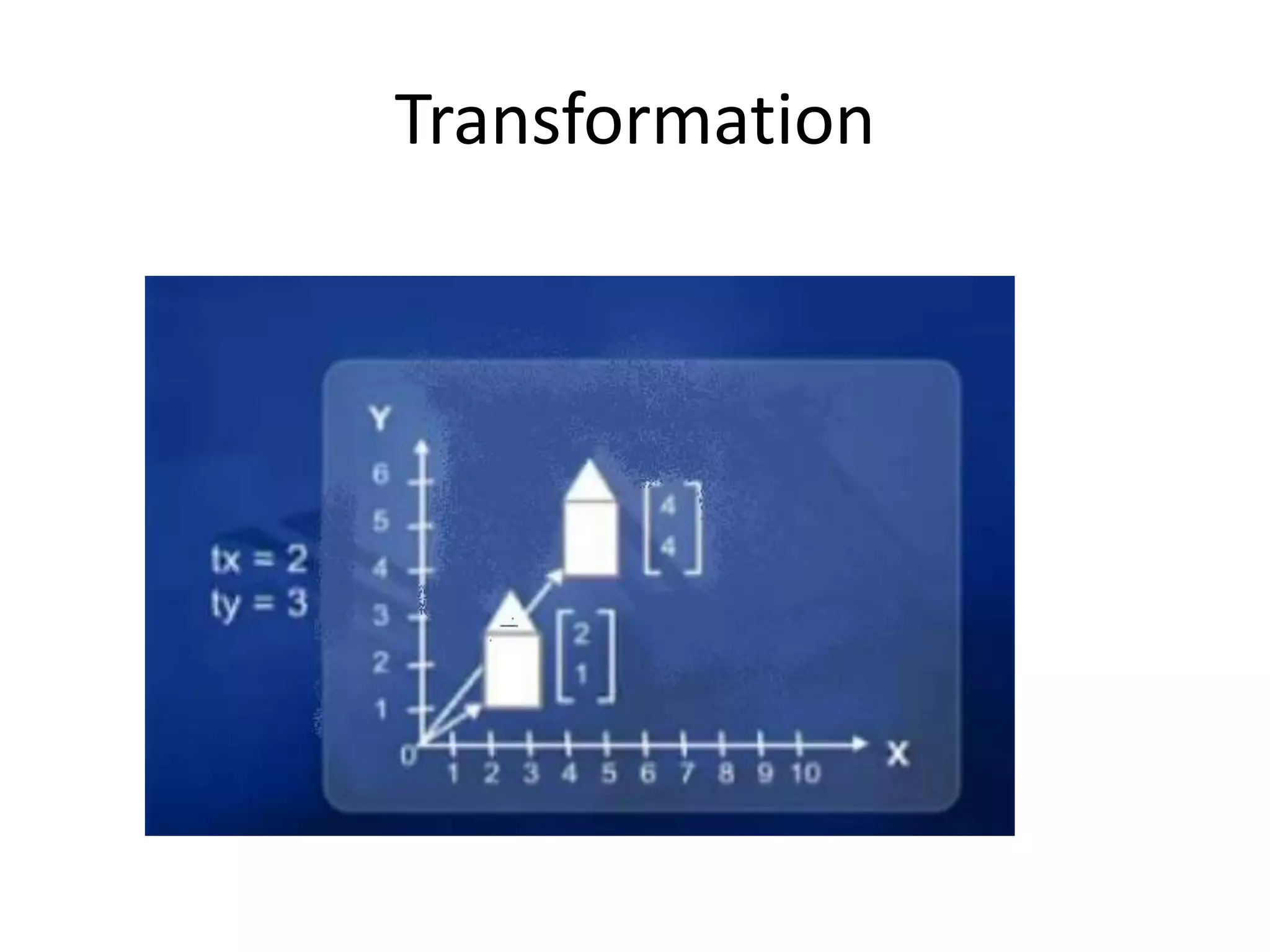
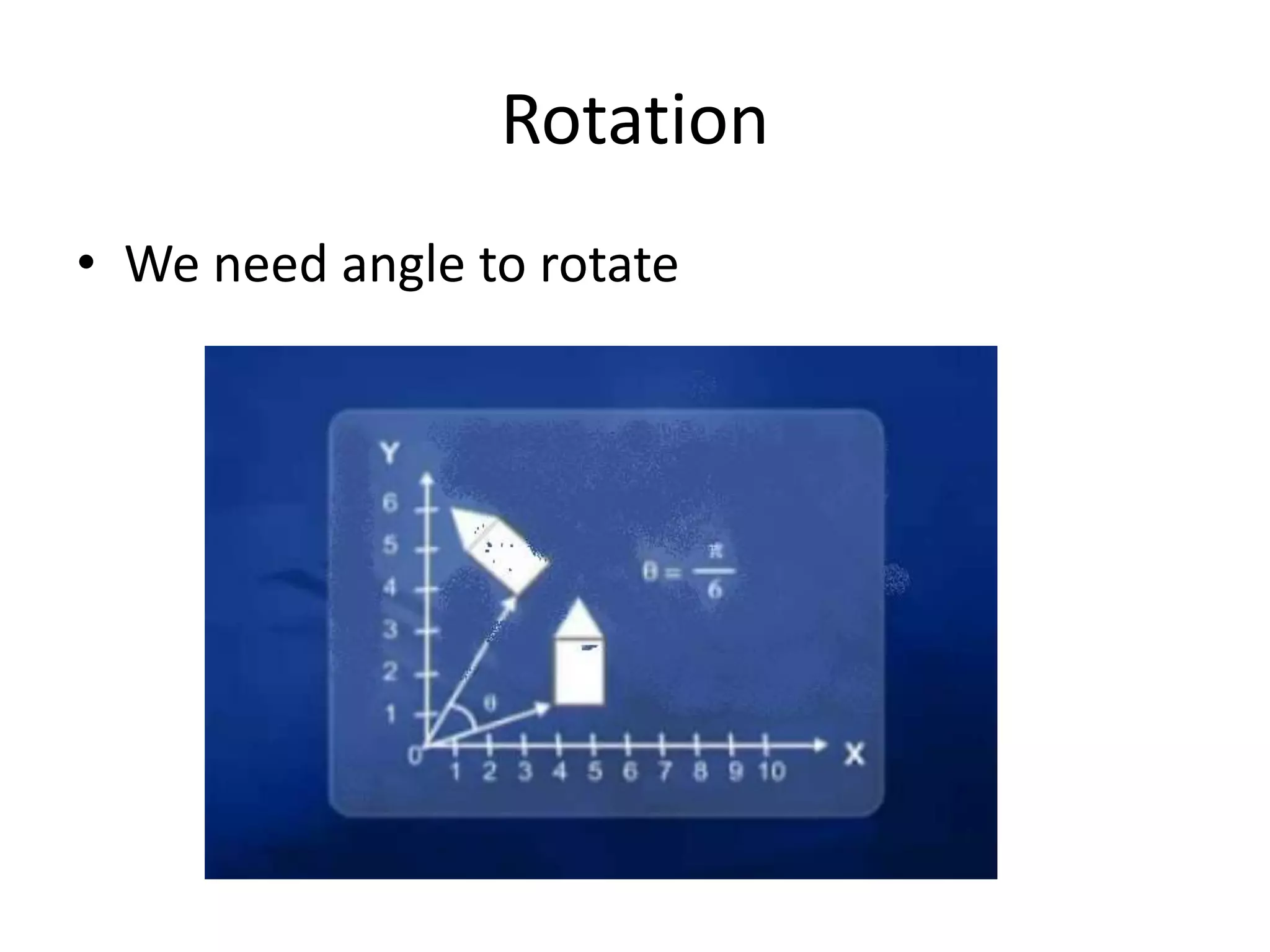
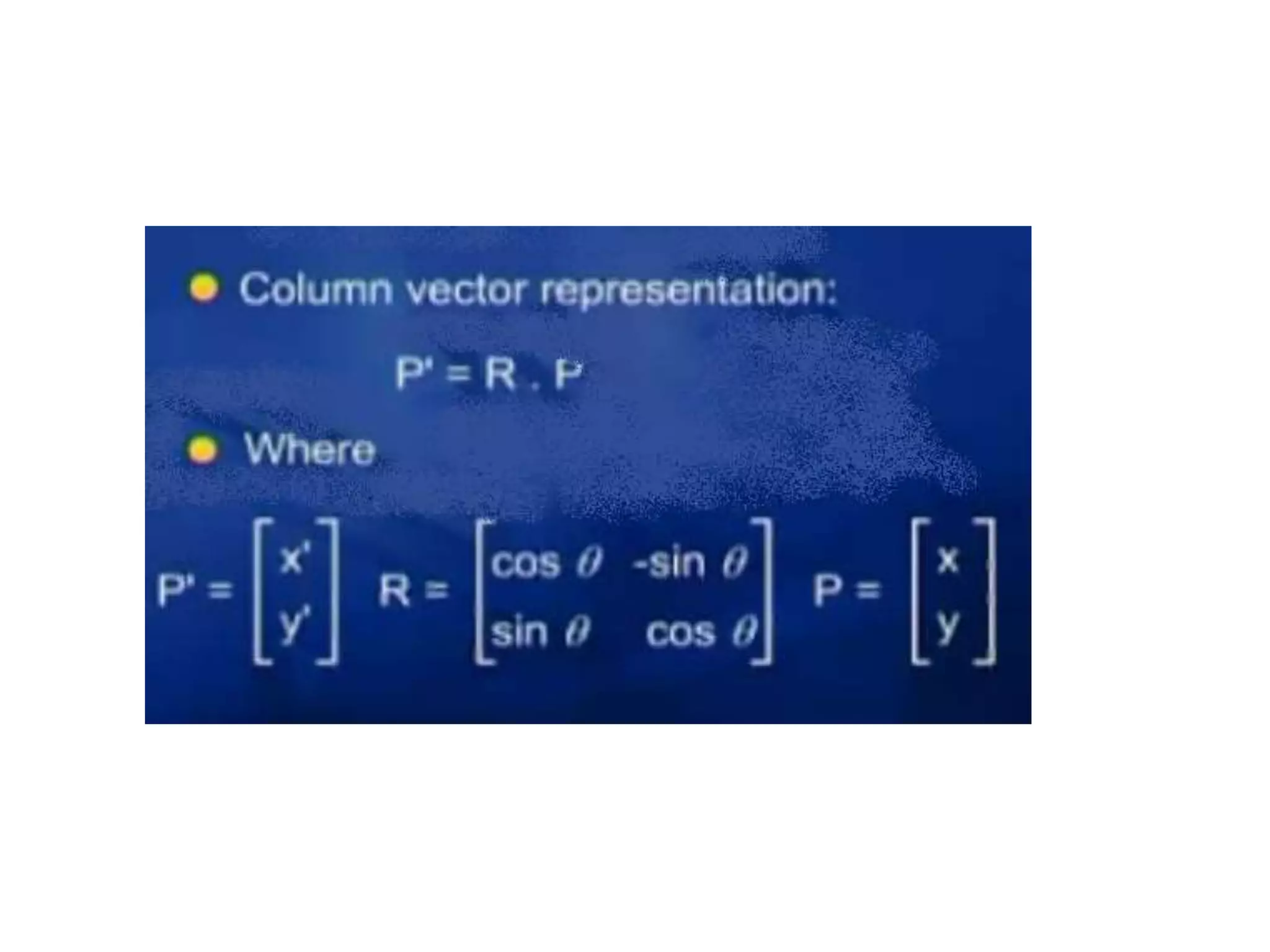
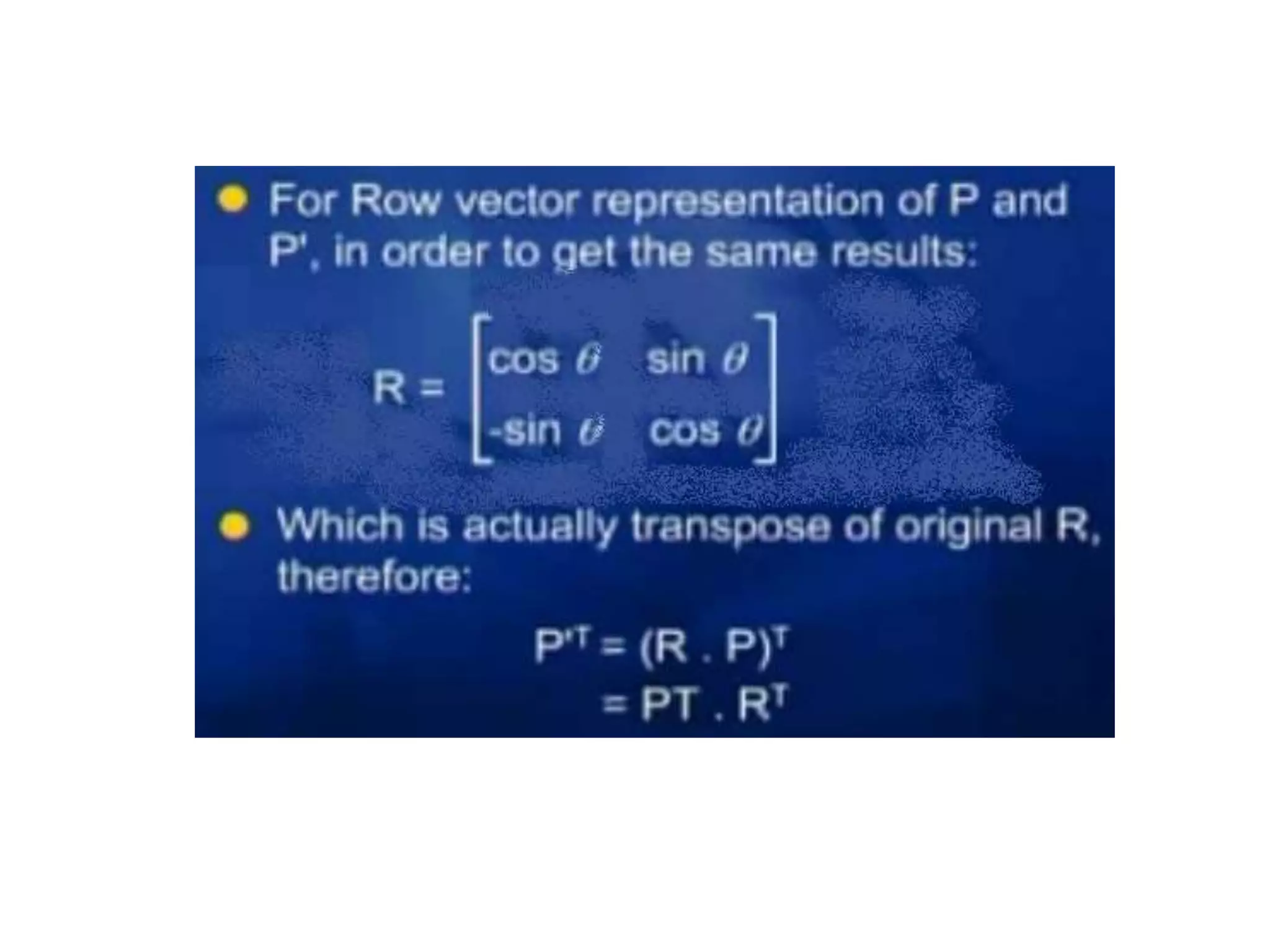
This document discusses 2D transformations including vector addition, dot products, cross products, translation, rotation, and scaling. Vector addition involves adding the x and y components of two vectors. The dot product of two vectors produces a scalar value based on the cosine of the angle between the vectors and can be used to determine if they are perpendicular. The cross product of two vectors produces a new vector perpendicular to both input vectors, determined by the right hand rule. Translation moves every point of an object by the same displacement amounts. Rotation rotates every point of an object by the same angle. Scaling enlarges or shrinks an object by a uniform scaling factor.