This document discusses vectors and their properties. It provides examples of vector addition and multiplication. Some key points:
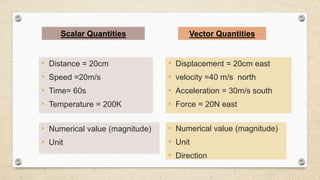
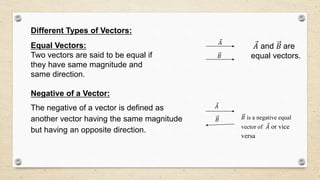
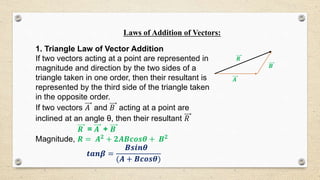
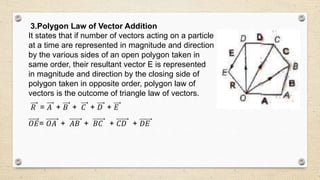
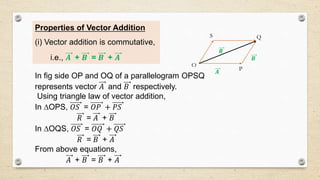
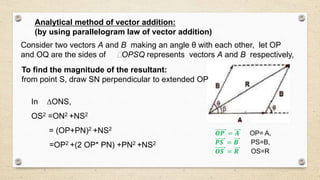
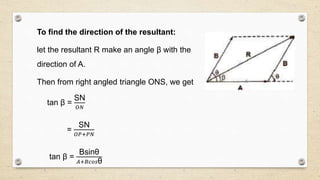
- Vectors have both magnitude and direction, while scalars only have magnitude. Vector addition follows the triangle and parallelogram laws.
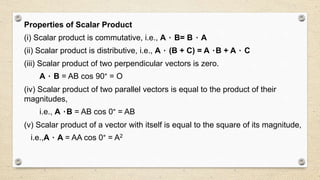
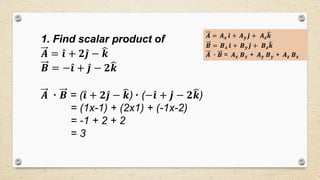
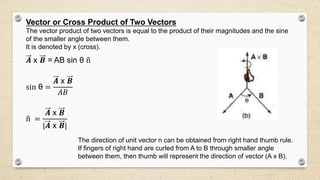
- There are two types of vector multiplication: the dot product, which results in a scalar, and the cross product, which results in another vector.
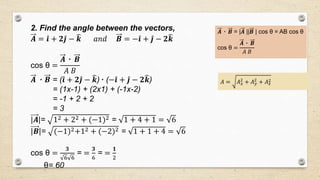
- The dot product of two vectors is equal to their magnitudes multiplied by the cosine of the angle between them. It is used to calculate quantities like work and power.
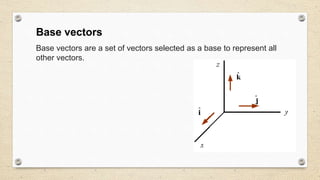
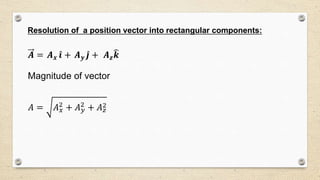
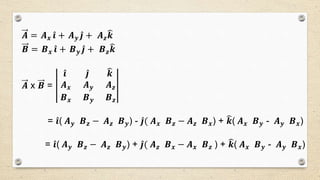
- Vectors can be resolved into rectangular components using a set of base vectors like the i, j, k unit vectors. The magnitude



























![2. Prove that the vectors 𝑨 = 𝟐 𝒊 − 𝟑 𝒋 − 𝒌 𝑎𝑛𝑑 𝑩 = −𝟔 𝒊 + 𝟗 𝒋 + 3 𝒌 are parallel.
𝑨 = 𝟐 𝒊 − 𝟑 𝒋 − 𝒌
𝑩 = −𝟔 𝒊 + 𝟗 𝒋 + 3 𝒌
𝑨 x 𝑩 = 𝟎
𝑨 x 𝑩 =
𝒊 𝒋 𝒌
𝟐 −𝟑 −𝟏
−𝟔 𝟗 3
= 𝒊[(-3x3)−(−1x9)] - 𝒋[(2x3) − (−1x − 6)] + 𝒌[(2x9)-(-3x-6)]
= 𝒊(-9+9) - 𝒋(6 − 6) + 𝒌(18-18)
= 0 𝒊 + 0 𝒋 - 0 𝒌
= 𝟎](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/motioninaplane-201217112709/85/Motion-in-a-plane-44-320.jpg)
![3. Determine the unit vector perpendicular to both 𝑨 = 𝟐 𝒊 + 𝒋 + 𝒌 𝑎𝑛𝑑
𝑩 = 𝒊 − 𝒋 + 2 𝒌 .
𝑨 = 𝟐 𝒊 + 𝒋 + 𝒌
𝑩 = 𝒊 − 𝒋 + 2 𝒌
n =
𝑨 x 𝑩
|𝑨 x 𝑩|
𝑨 x 𝑩 =
𝒊 𝒋 𝒌
𝟐 𝟏 𝟏
𝟏 −𝟏 2
= 𝒊[(1x2)−(1x − 1)] - 𝒋[(2x2) − (1x1)] + 𝒌[(2x-1)-(1x-1)]
= 𝒊(2+1) - 𝒋(4 − 1) + 𝒌(-2-1)
= 3 𝒊 - 3 𝒋 - 3 𝒌](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/motioninaplane-201217112709/85/Motion-in-a-plane-45-320.jpg)