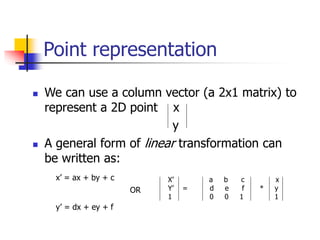
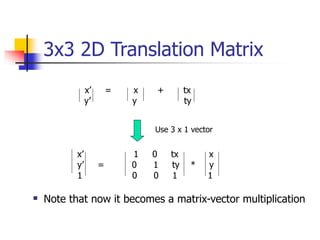
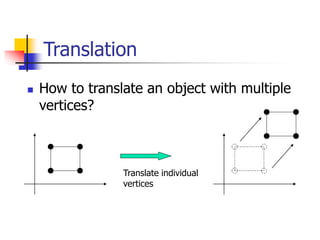
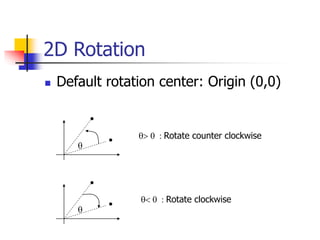
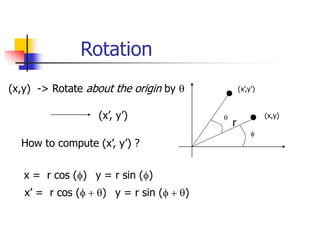
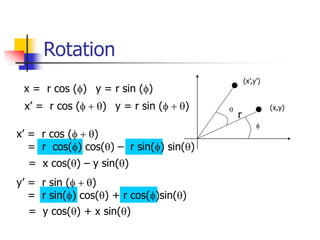
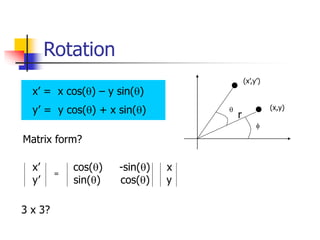
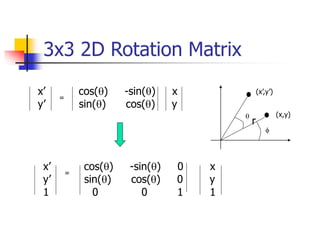
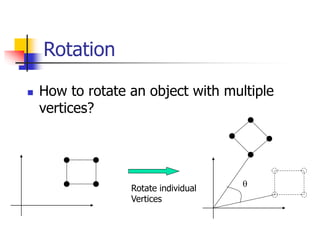
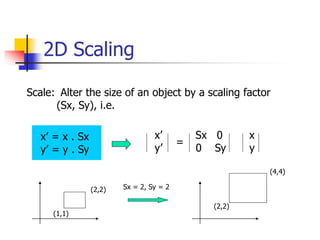
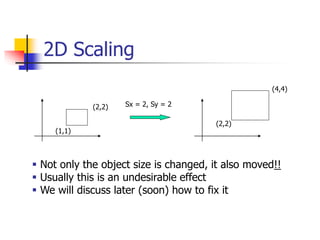
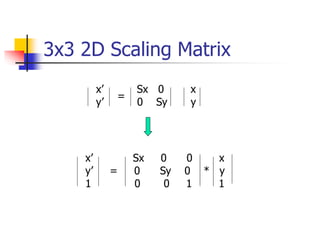
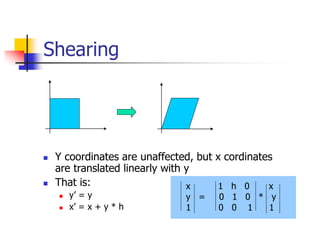
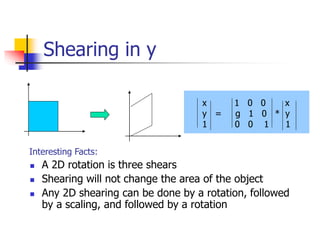
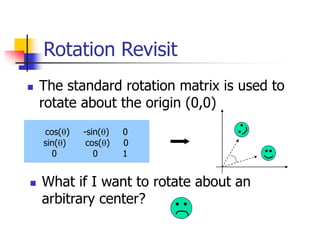
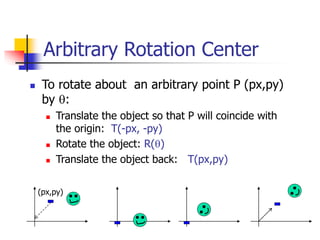
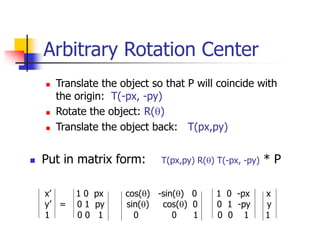
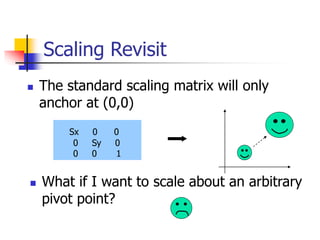
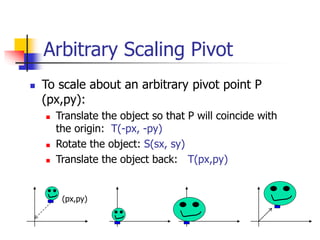
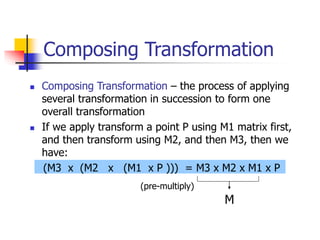
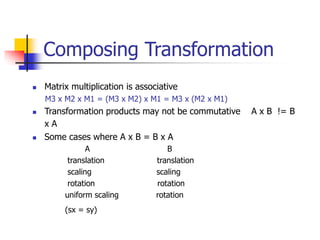
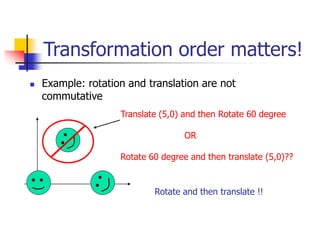
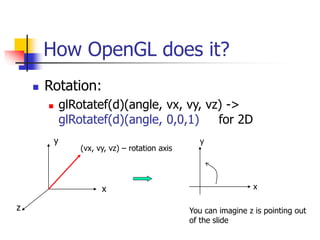
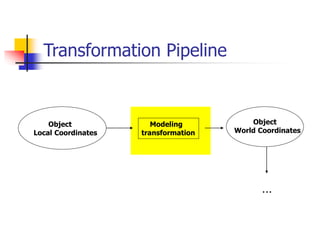
This document discusses various 2D transformations including translation, rotation, scaling, shearing, and their implementations using transformation matrices. Translation moves an object along a straight line and can be represented by a 3x3 matrix. Rotation rotates an object around a center point, with the standard rotation matrix rotating around the origin. Scaling changes the size of an object, which can cause undesirable movement. Shearing skews an object along an axis. The document also covers composing multiple transformations using matrix multiplication and how OpenGL applies transformations through a global model-view matrix.