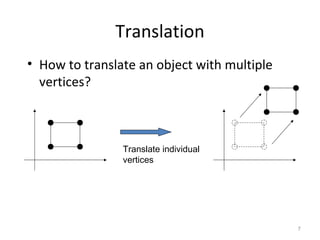
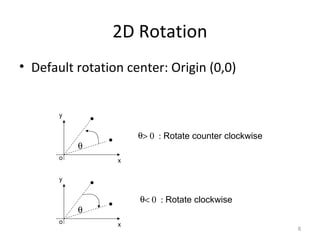
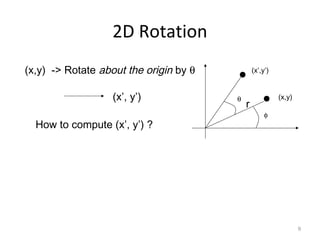
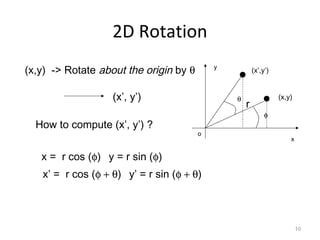
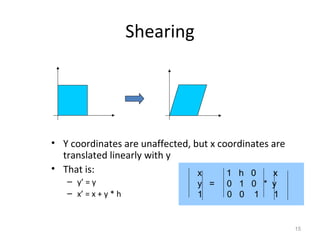
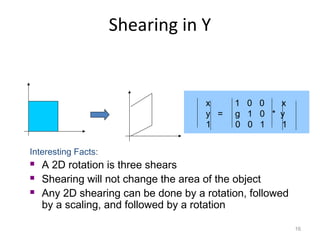
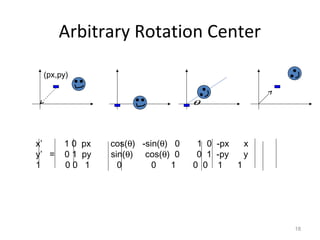
1. 2D transformations include translation, rotation, scaling, and shearing. They can change an object's position, size, orientation, and shape.
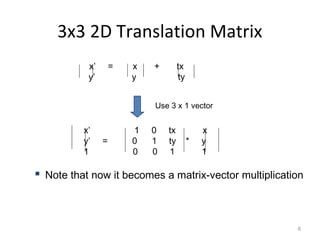
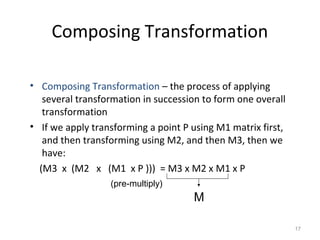
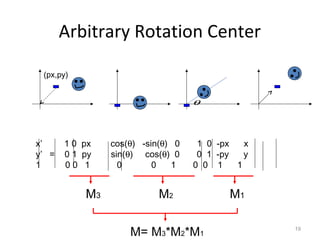
2. Transformations are represented by matrices and applied through matrix multiplication. A sequence of transformations can be combined into a single matrix by multiplying the matrices.
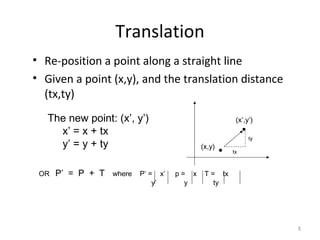
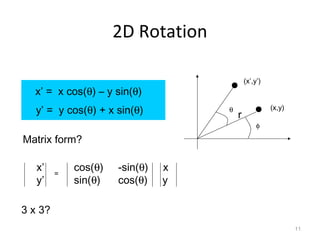
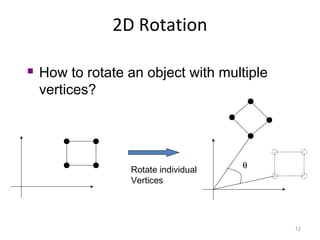
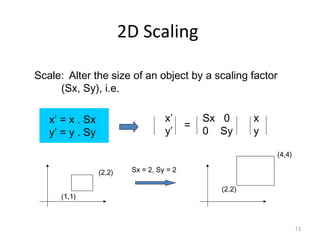
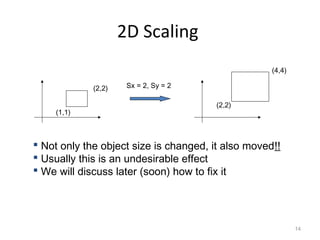
3. Common 2D transformations include translating an object by adding offsets to x and y, rotating objects around an origin by adjusting x and y coordinates, and scaling by multiplying x and y by factors.