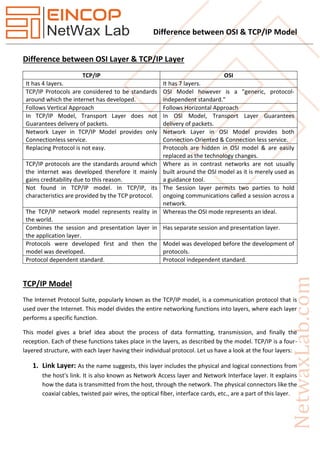
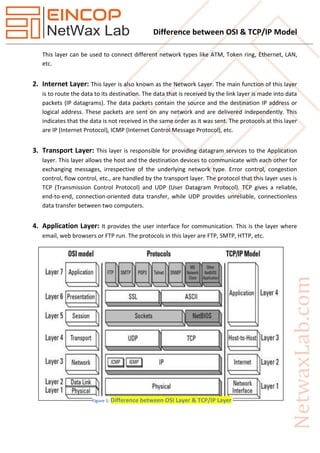
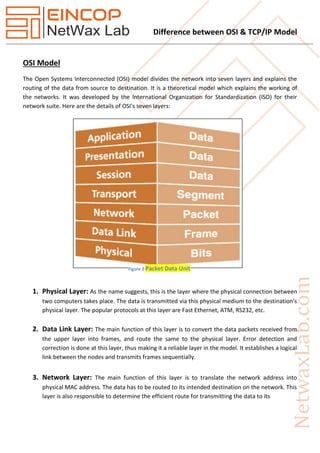
The document highlights the differences between the OSI and TCP/IP models, detailing the number of layers, functions, and operational characteristics of each model. TCP/IP has four layers and is protocol-dependent, primarily used for internet communication, while OSI consists of seven layers and serves as a theoretical framework. Key distinctions include the behavior of the transport and network layers, as well as the practical application of the TCP/IP model compared to the OSI model's guidance role.