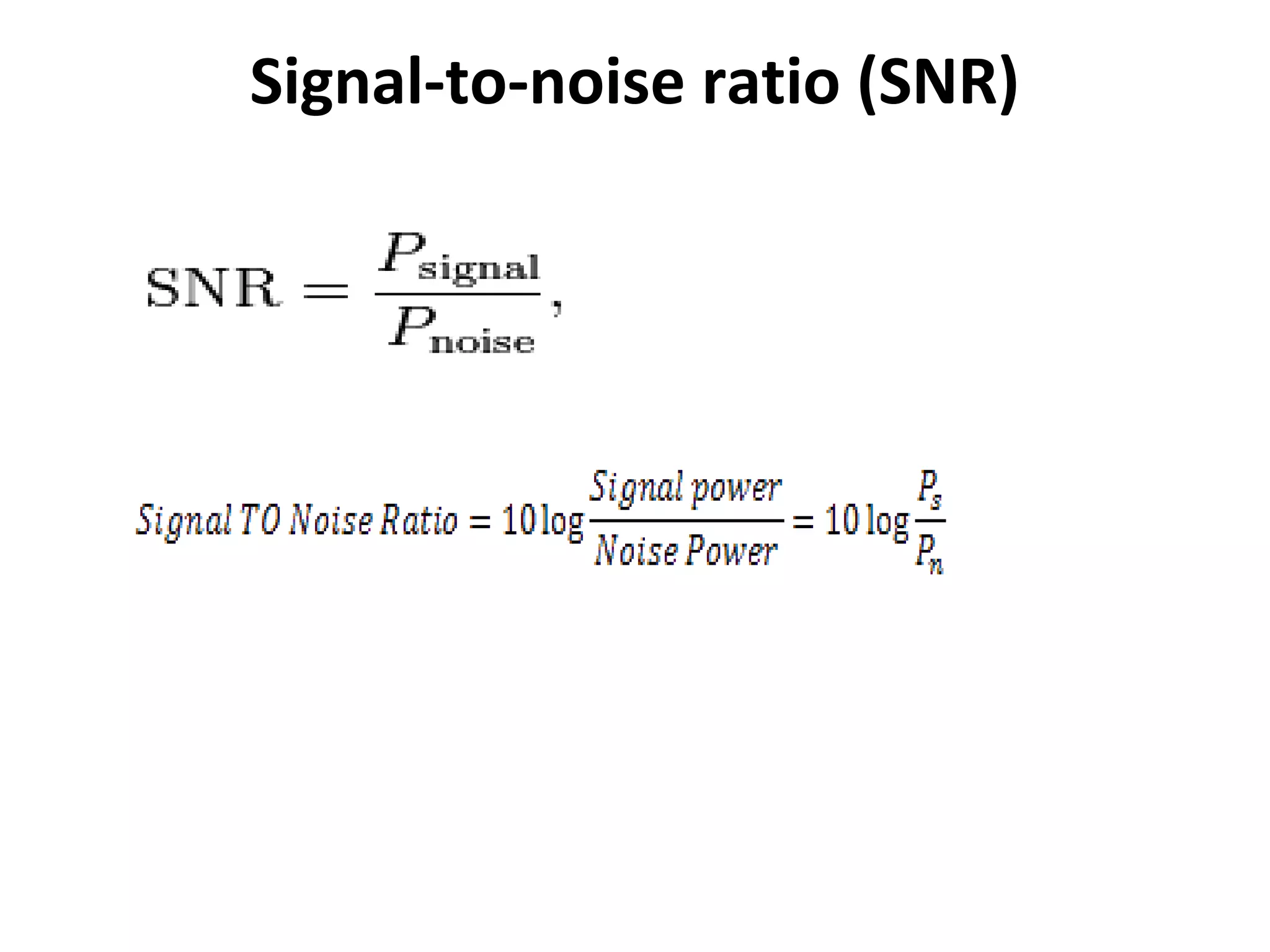
This document discusses various types of transmission impairments including attenuation, distortion, and noise. Attenuation is the reduction of signal strength during transmission, while distortion alters the original signal shape. There are different types of distortion such as amplitude, delay, and frequency distortion. Noise refers to random electrical signals that interfere with reception, and can come from internal or external sources. Signal-to-noise ratio and noise figure are discussed as ways to measure noise levels relative to signals.