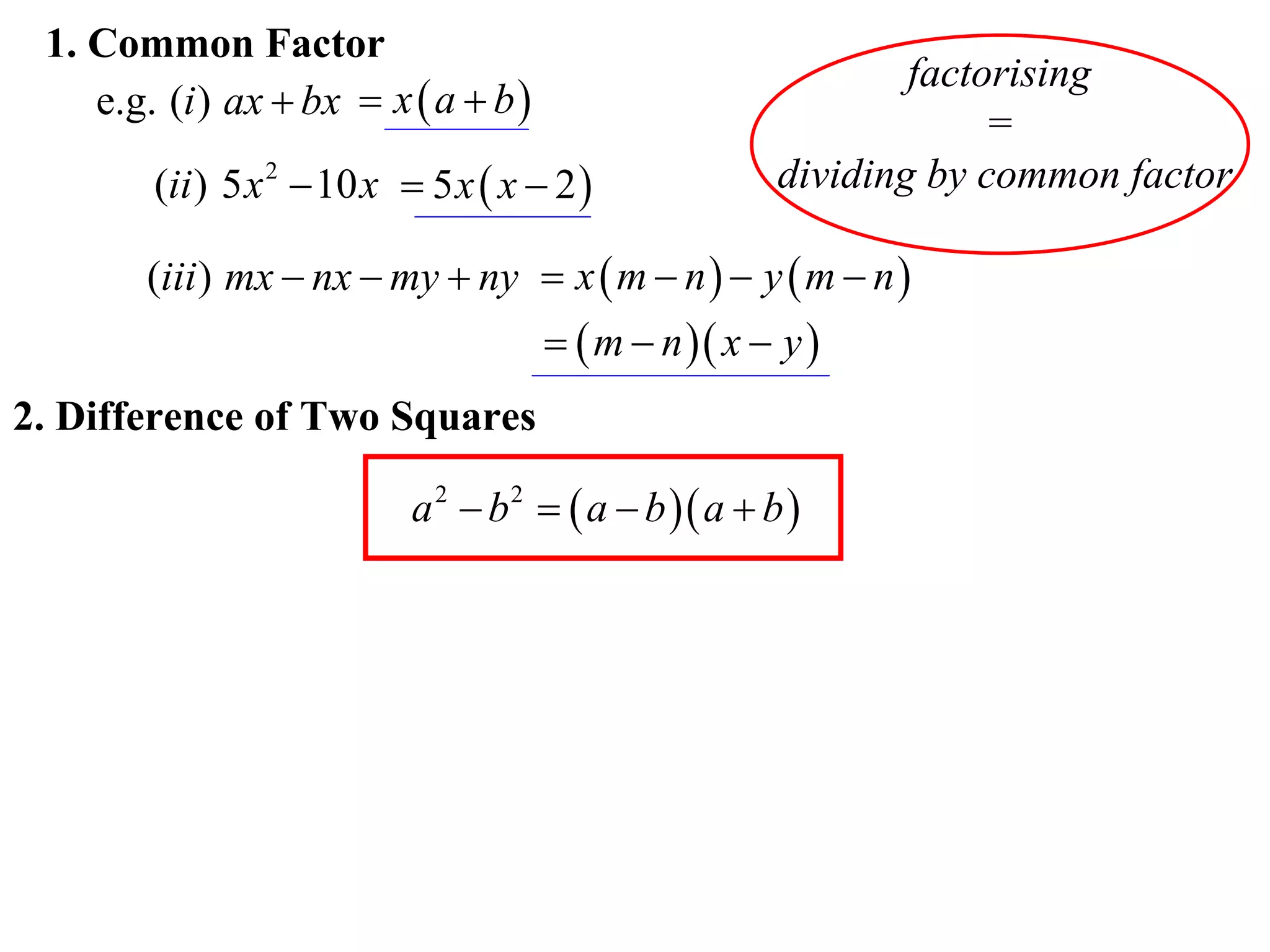
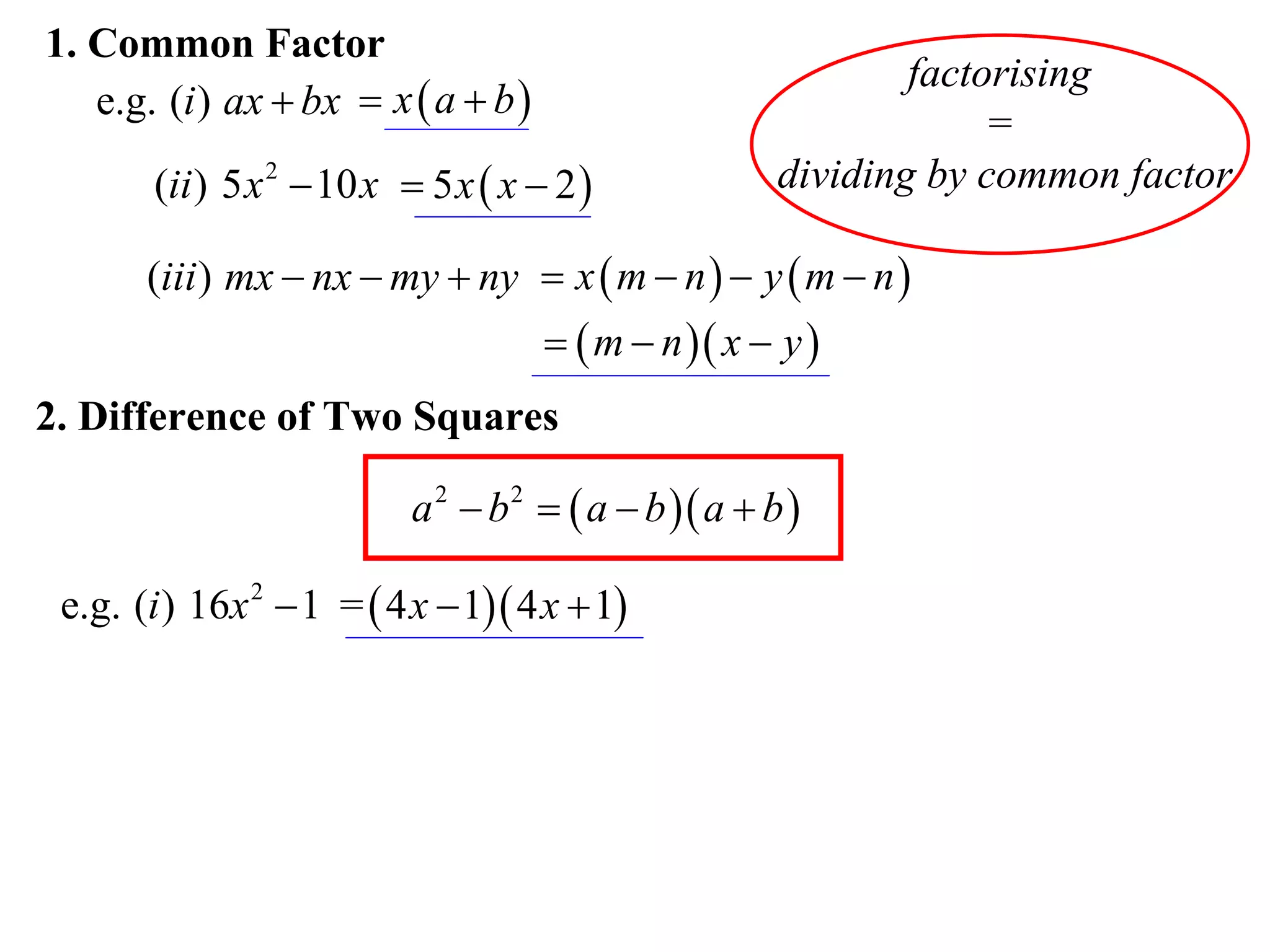
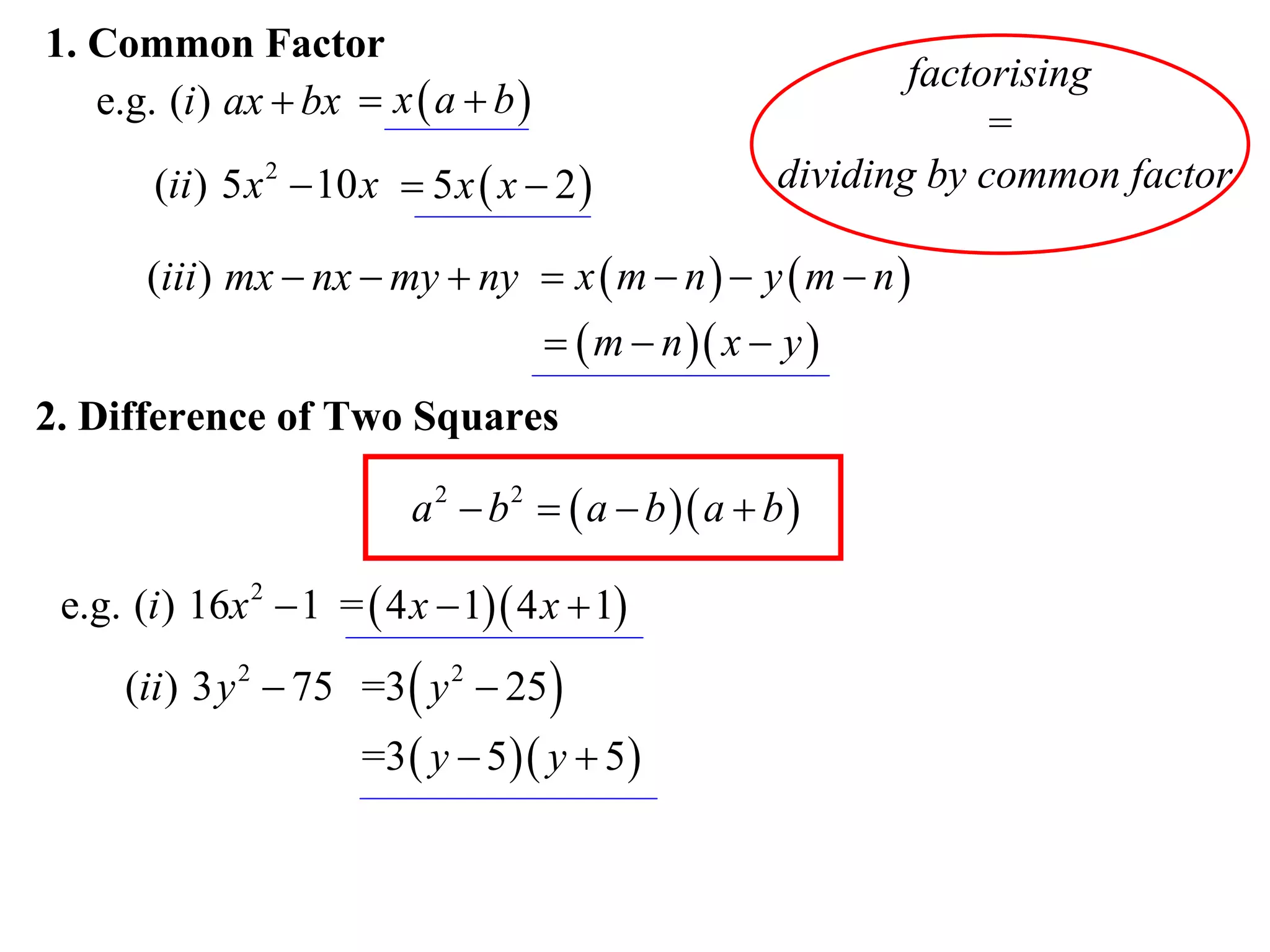
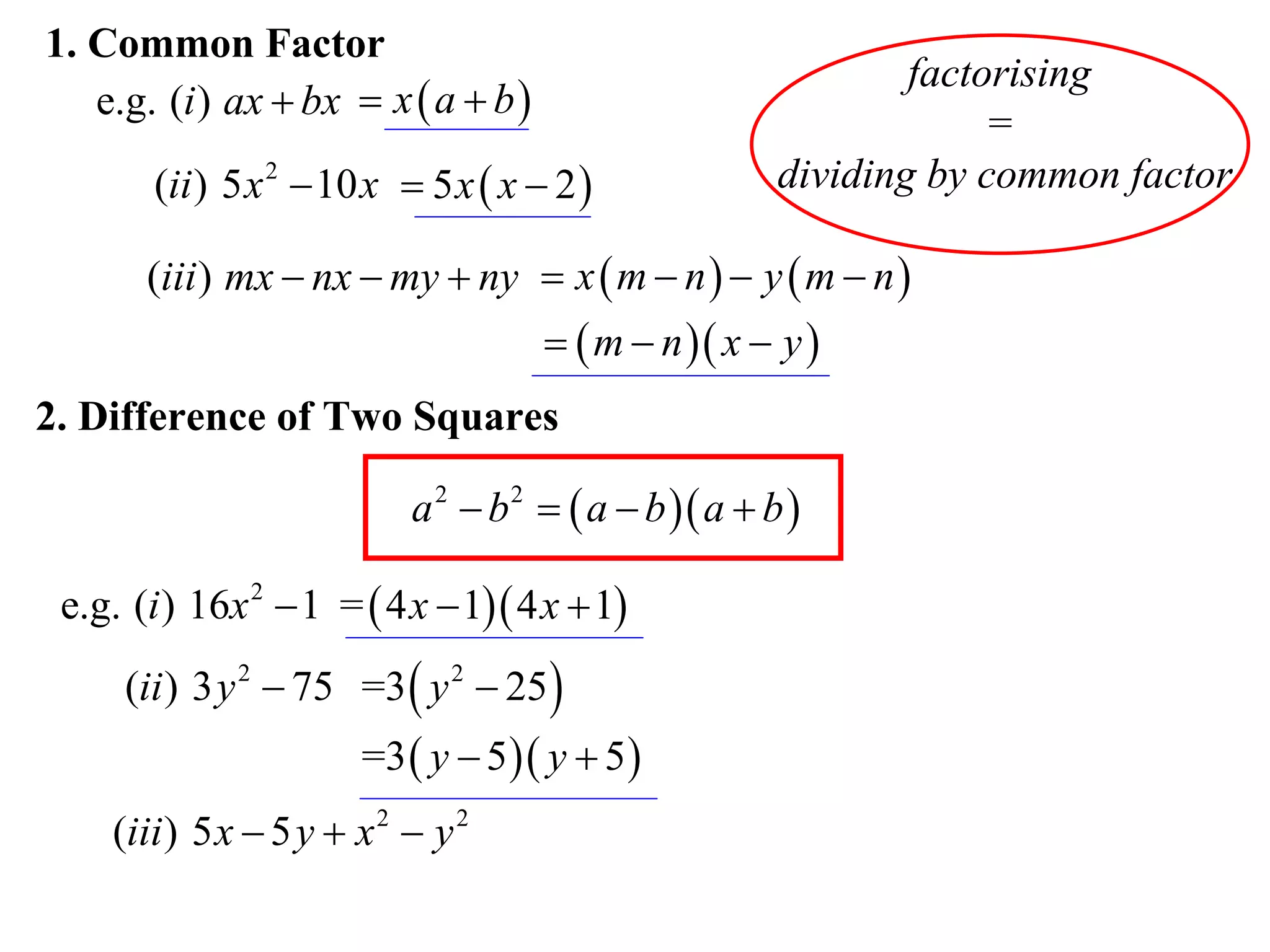
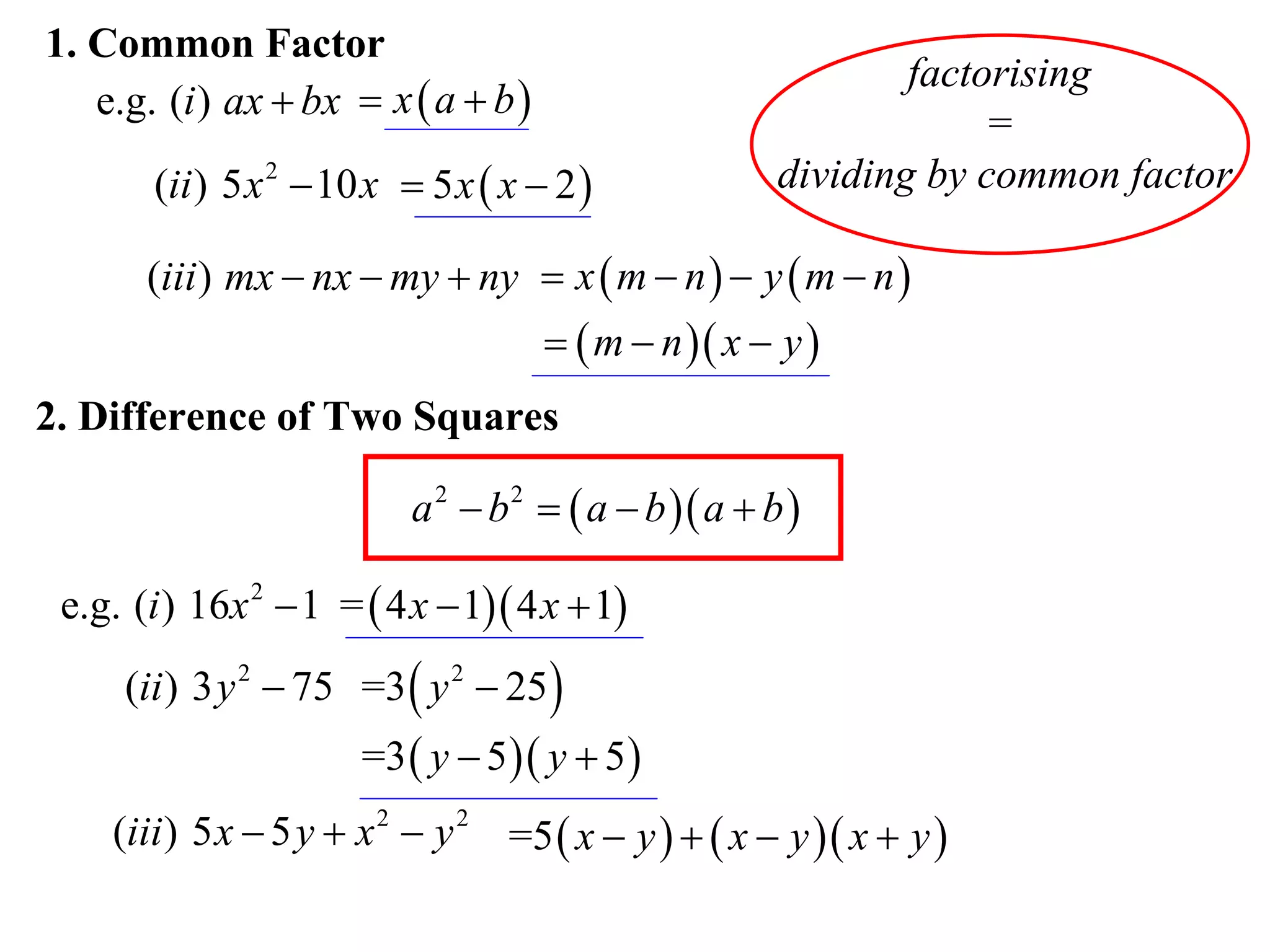
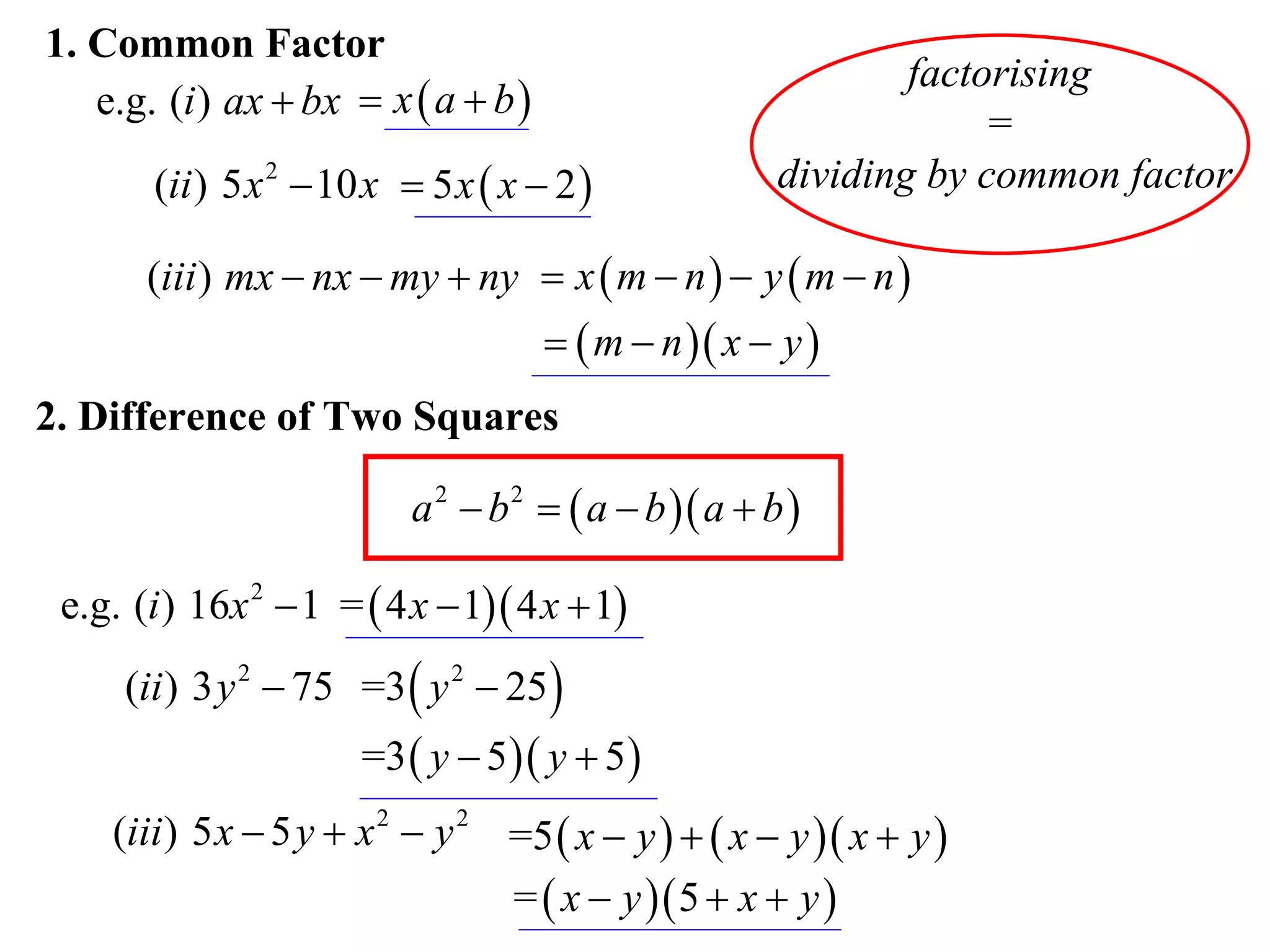
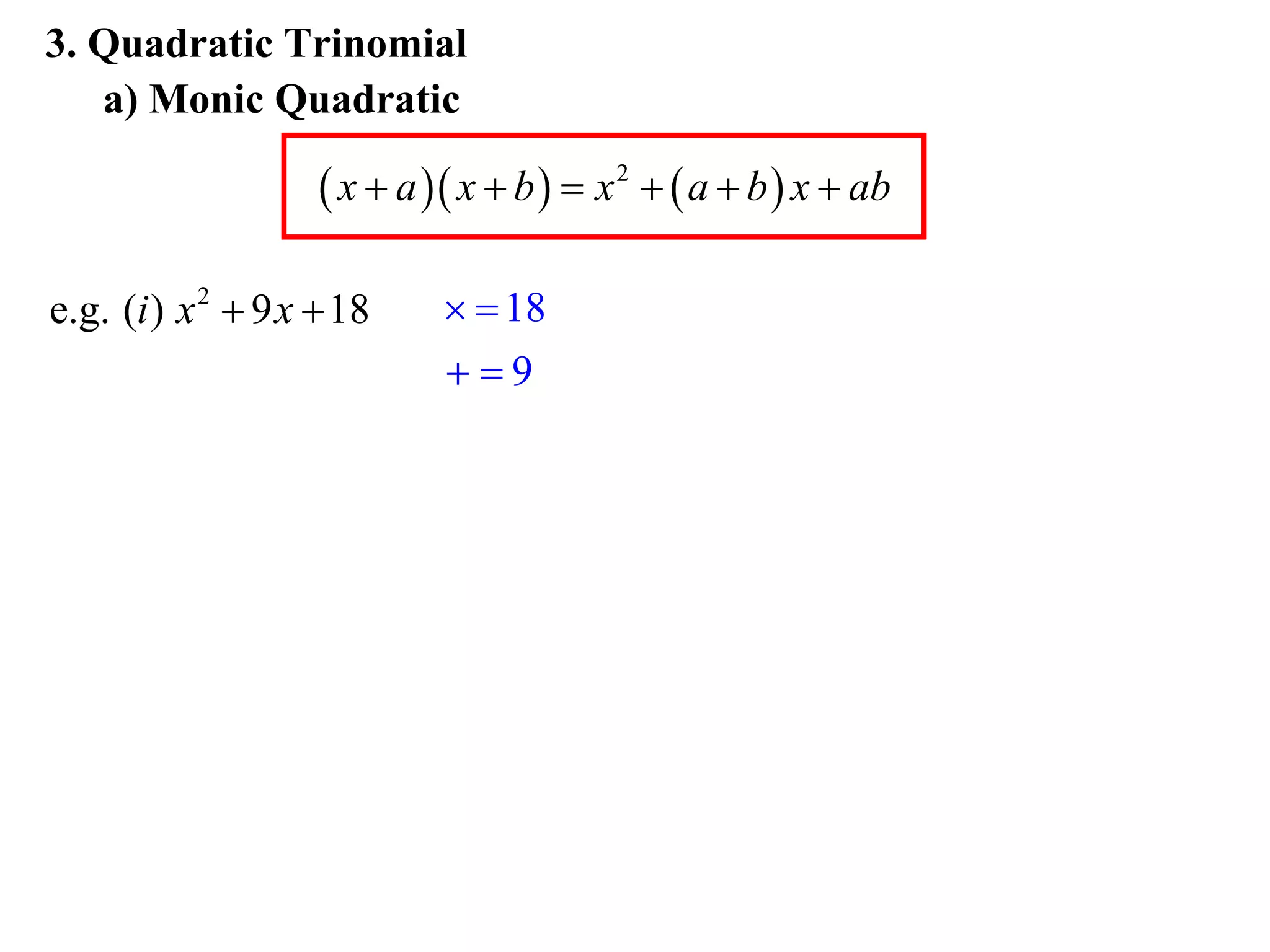
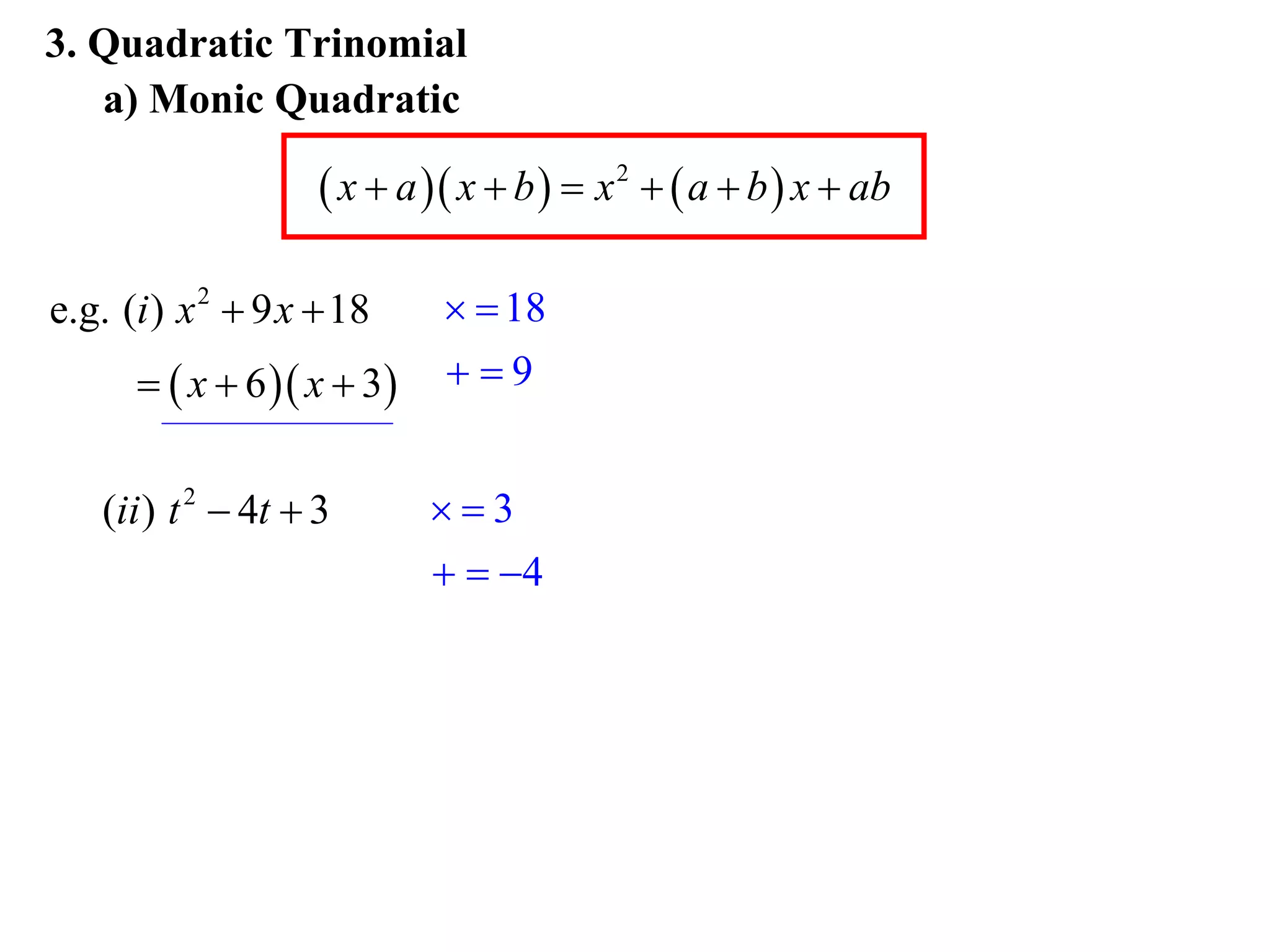
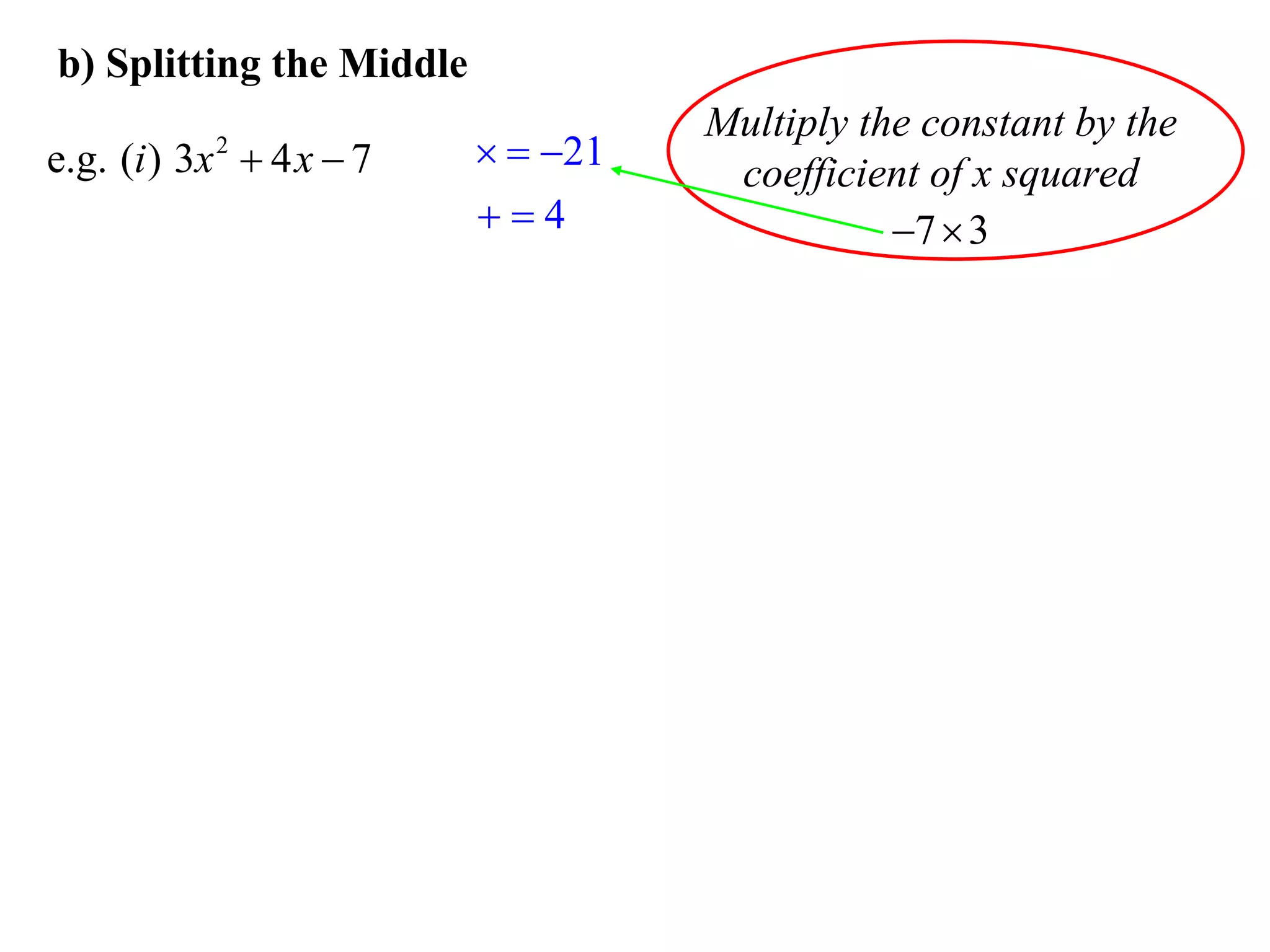
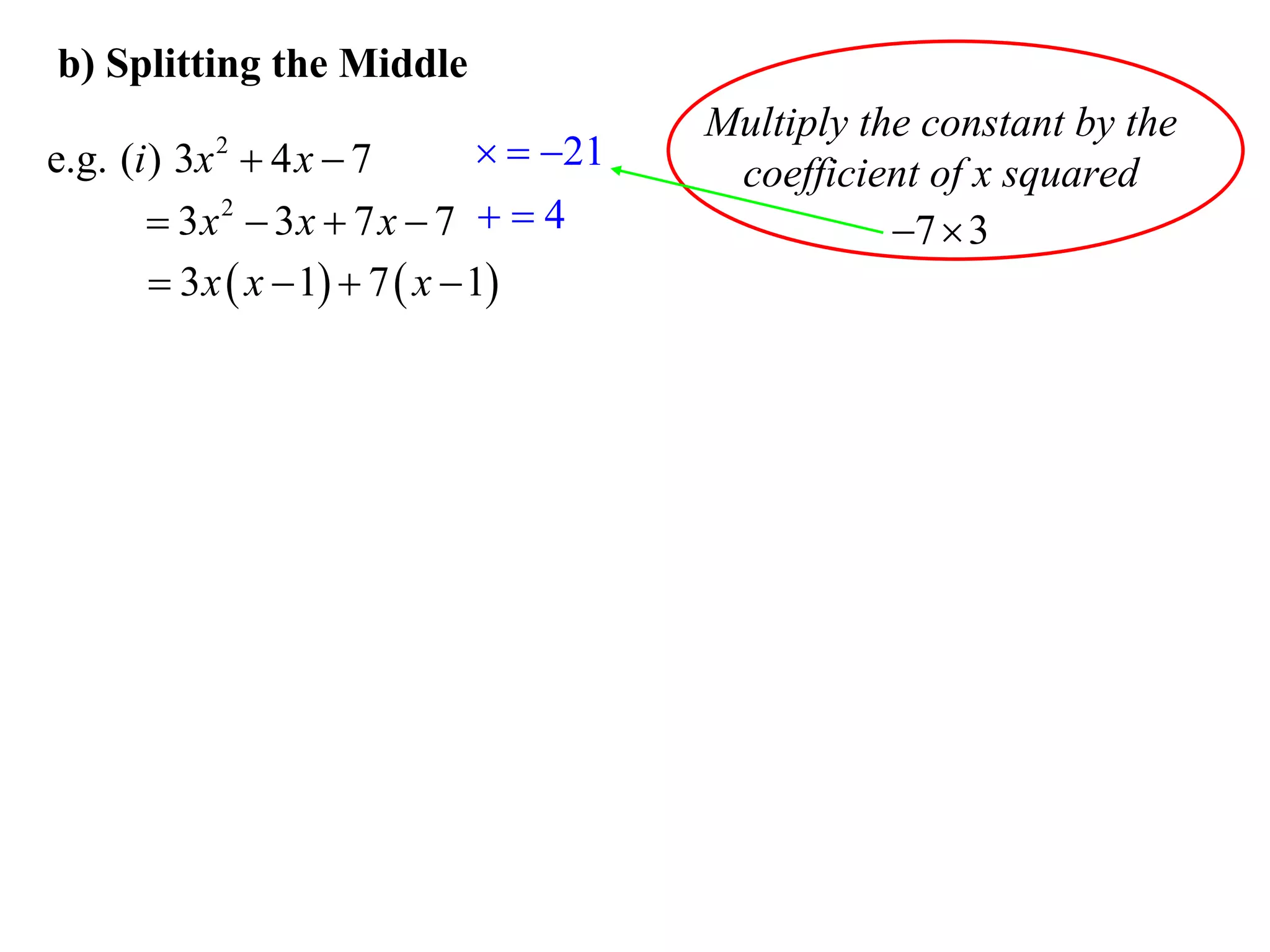
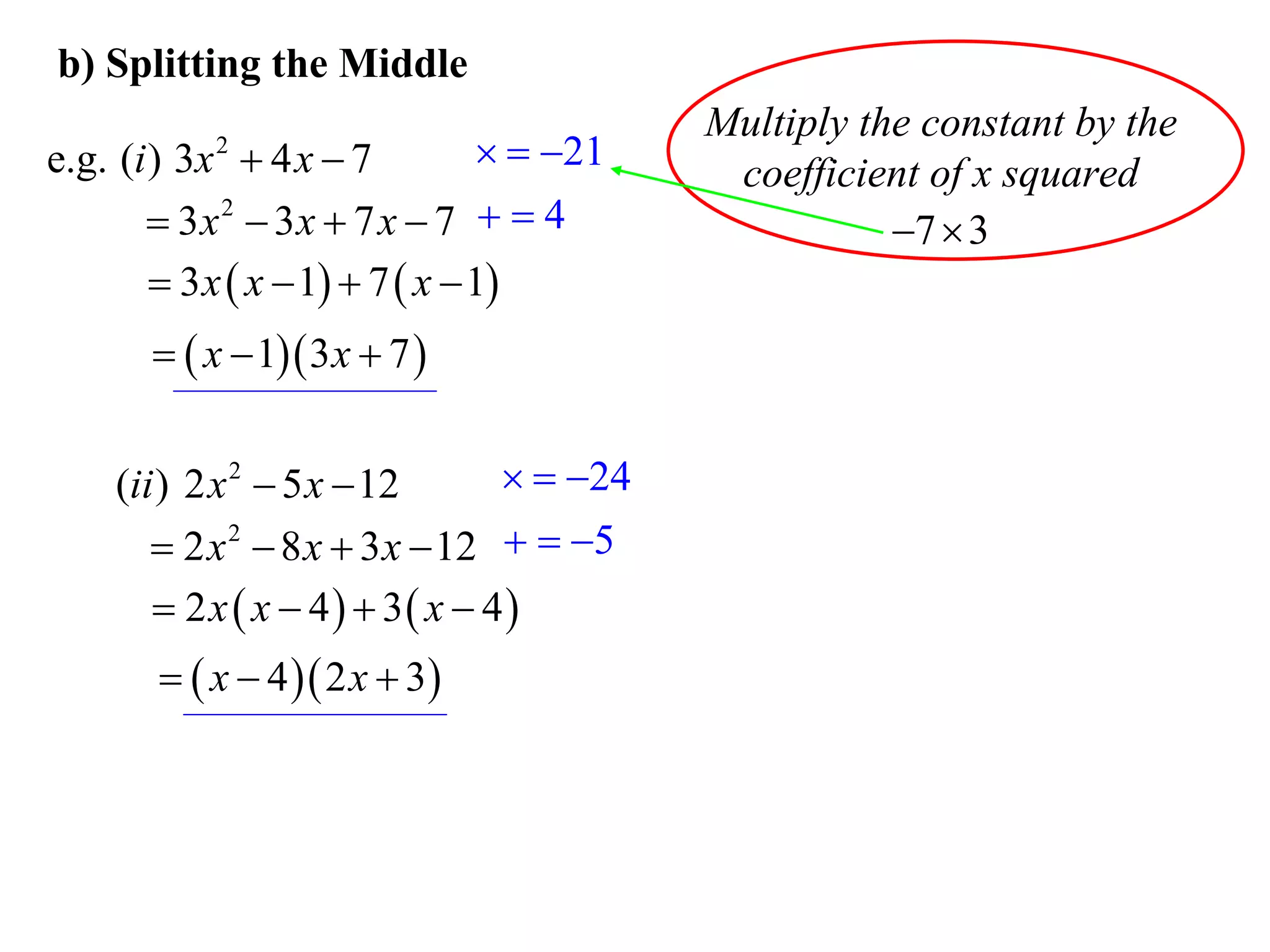
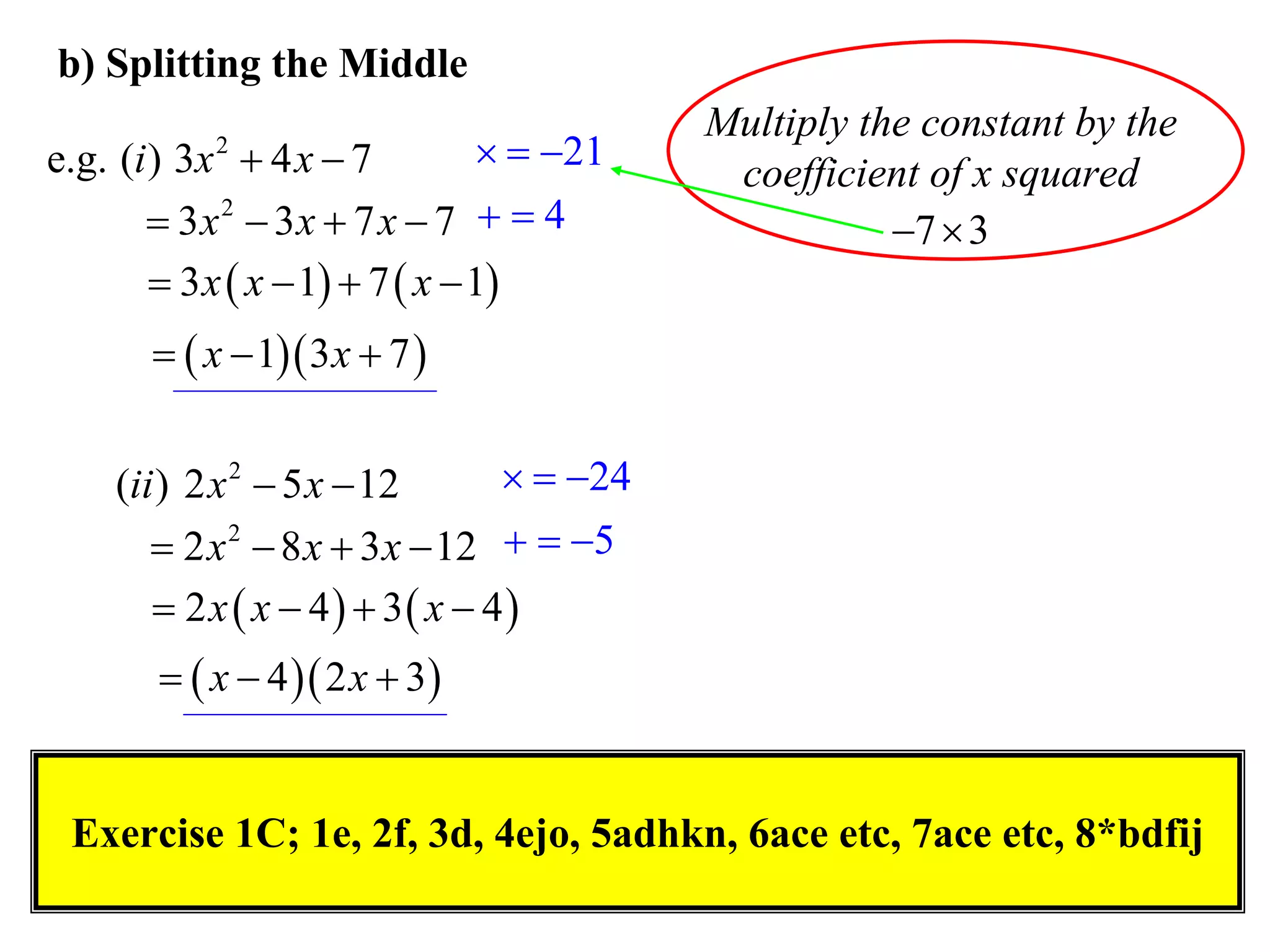
The document provides steps for factorising expressions:
1) Look for common factors and divide them out
2) Factorise the difference of two squares using the form (a-b)(a+b)
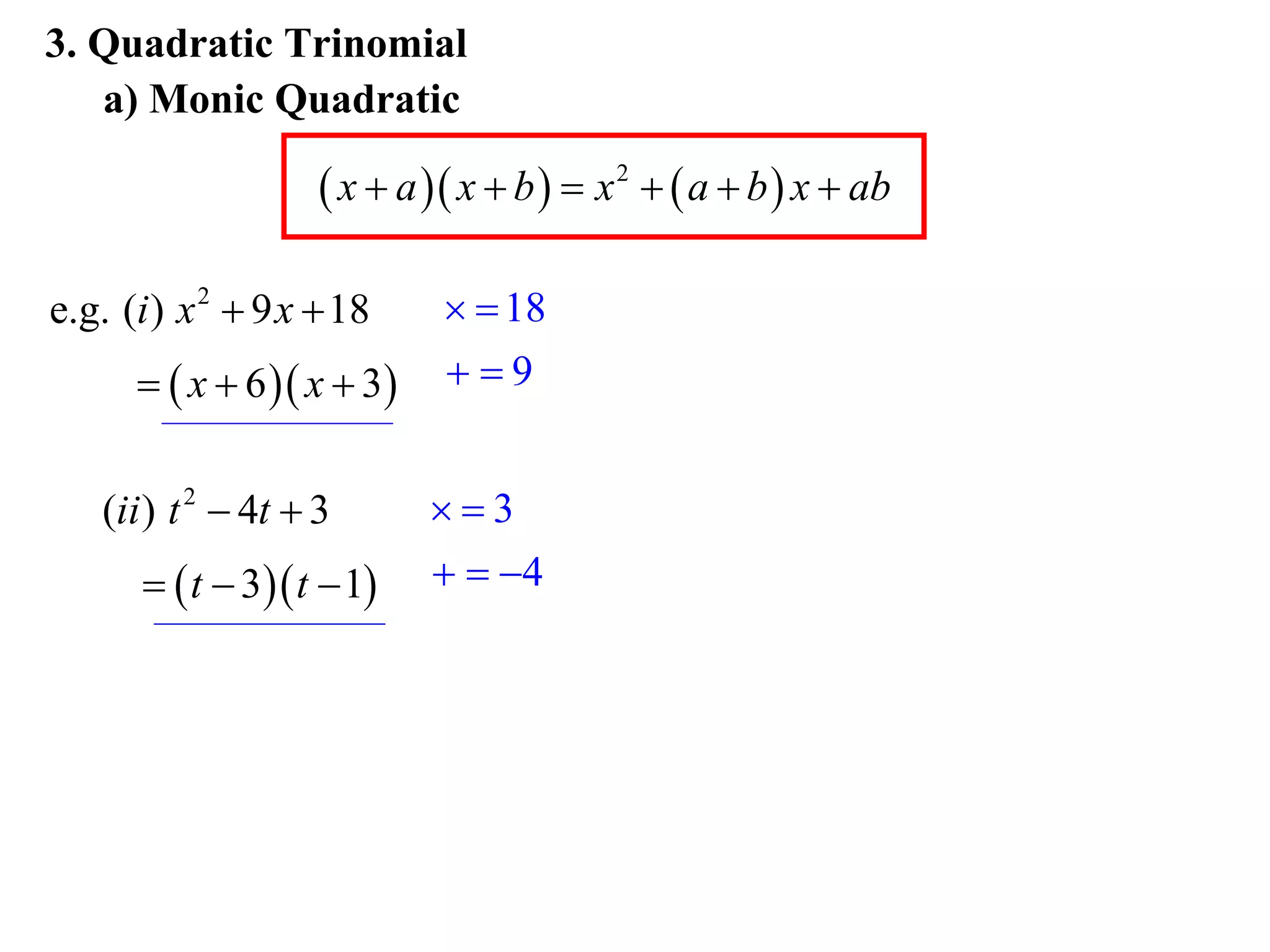
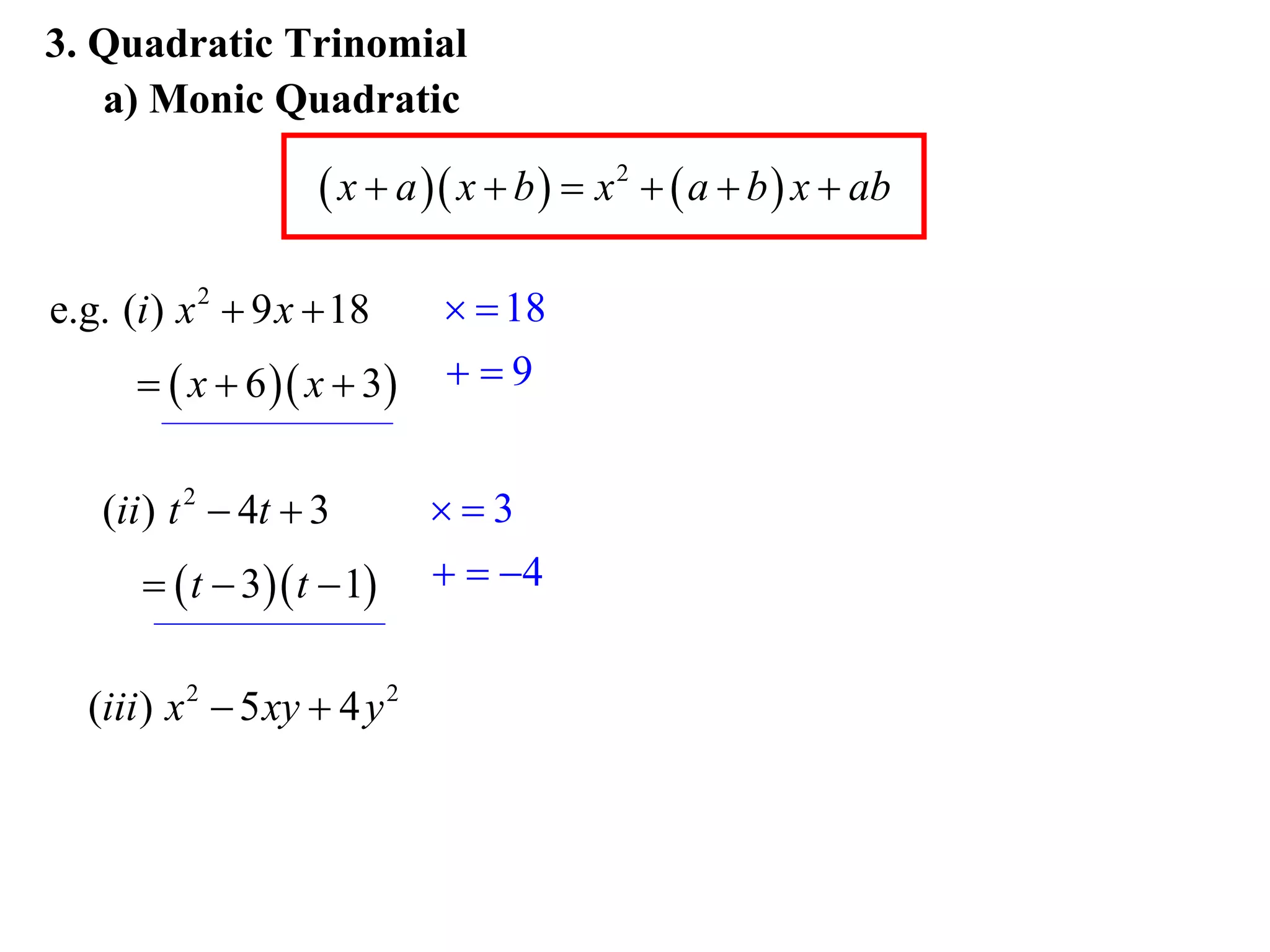
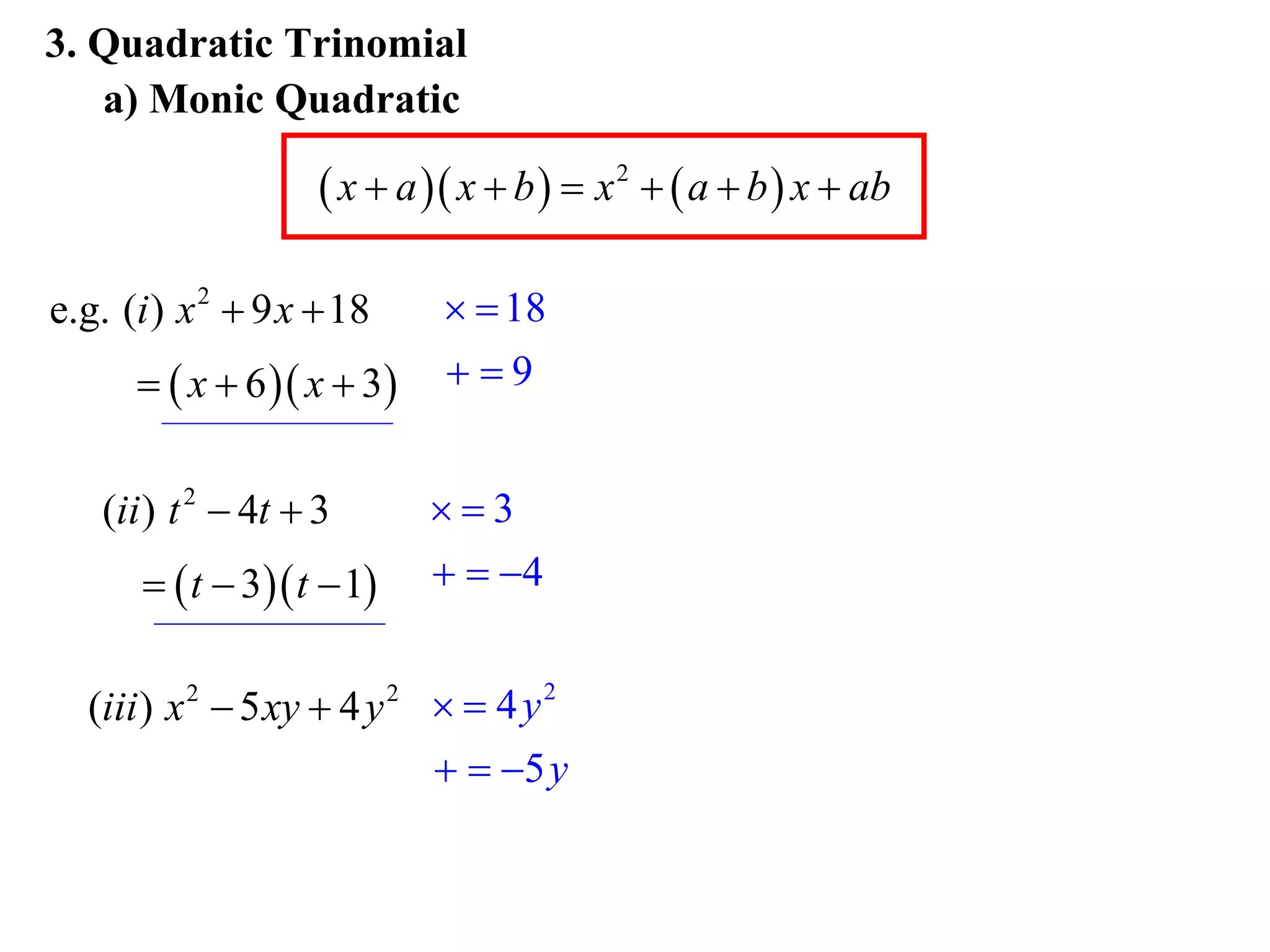
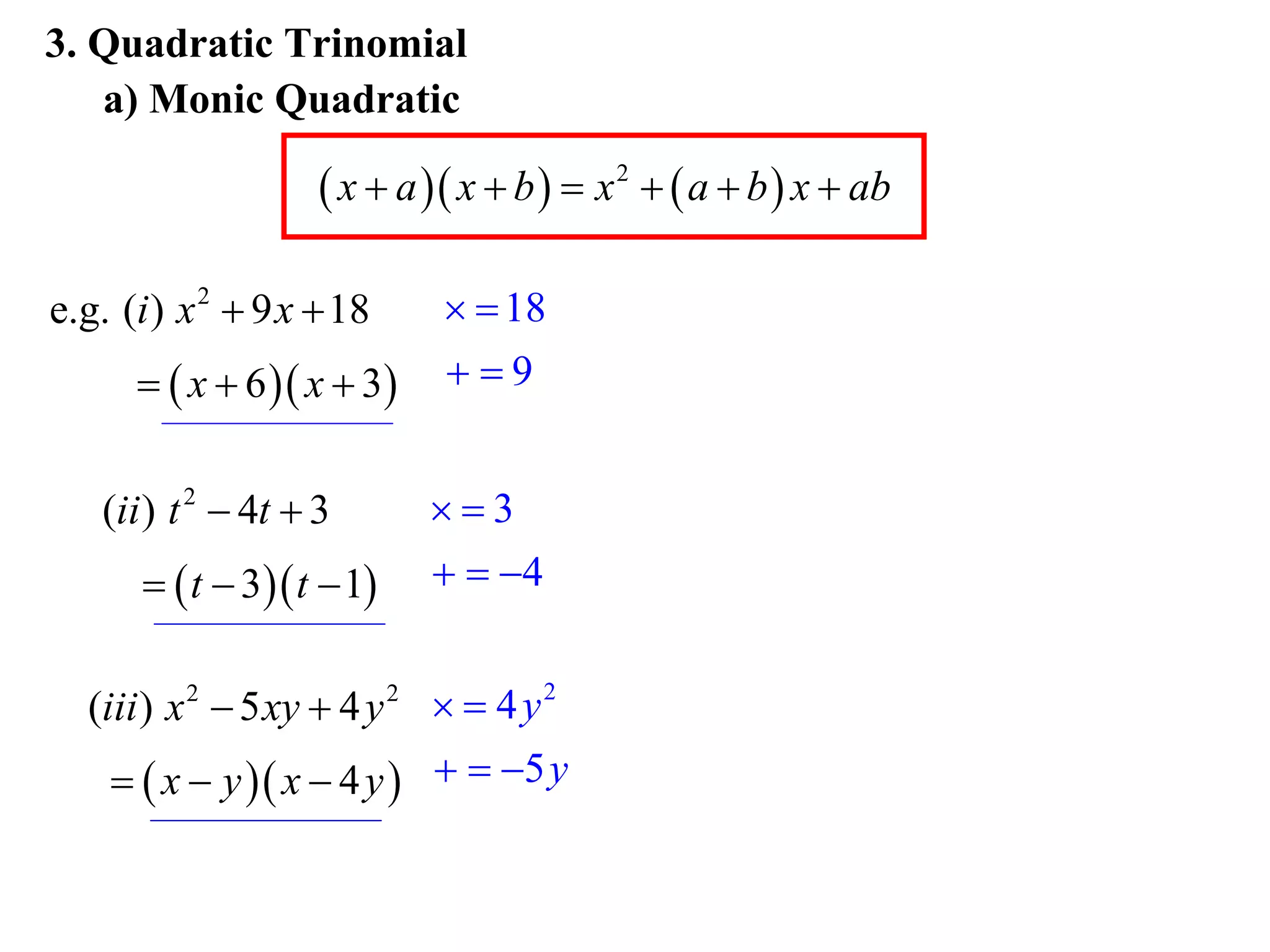
3) Factorise quadratic trinomials into the product of two binomials using the forms x2 + (a+b)x + ab or (x+a)(x+b)
Examples are provided for each type of factorisation.