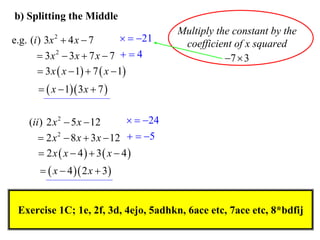
The document discusses different methods for factorising expressions:
1) Looking for a common factor and dividing it out of all terms
2) Using the difference of two squares formula (a2 - b2 = (a - b)(a + b))
3) Factorising quadratic trinomials into two binomial factors by identifying the values that multiply to give the constant term and sum to give the coefficient of the linear term.