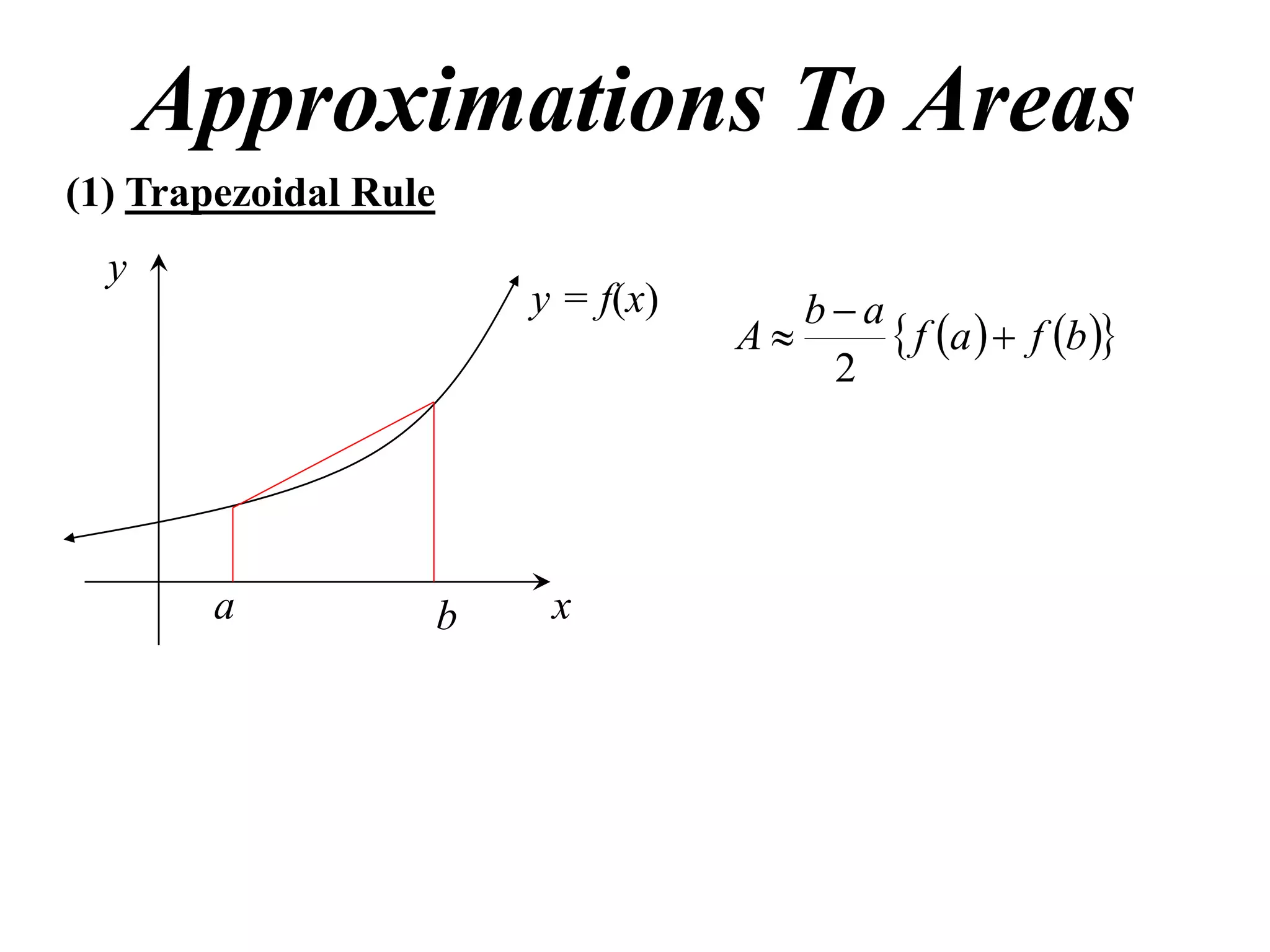
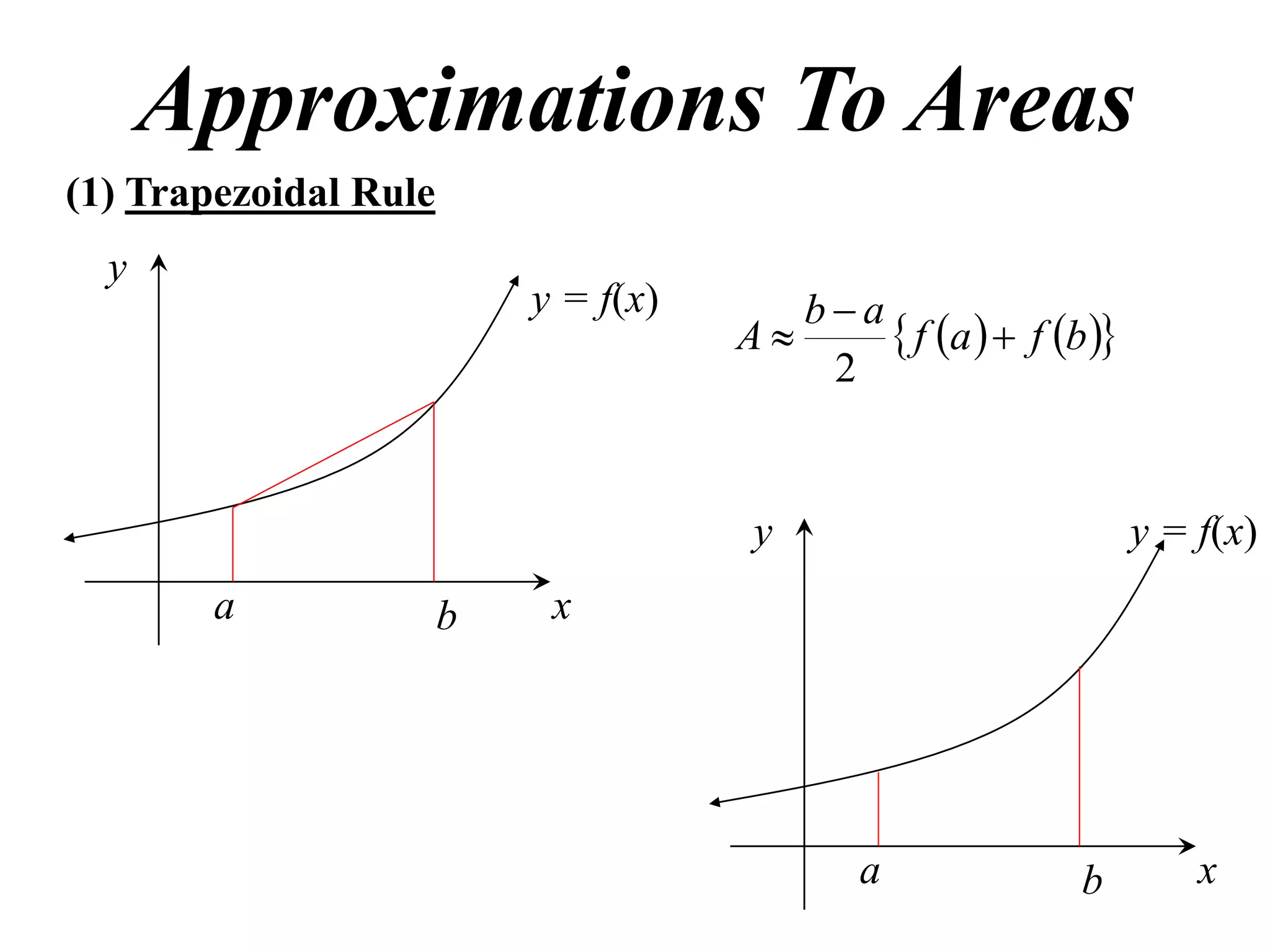
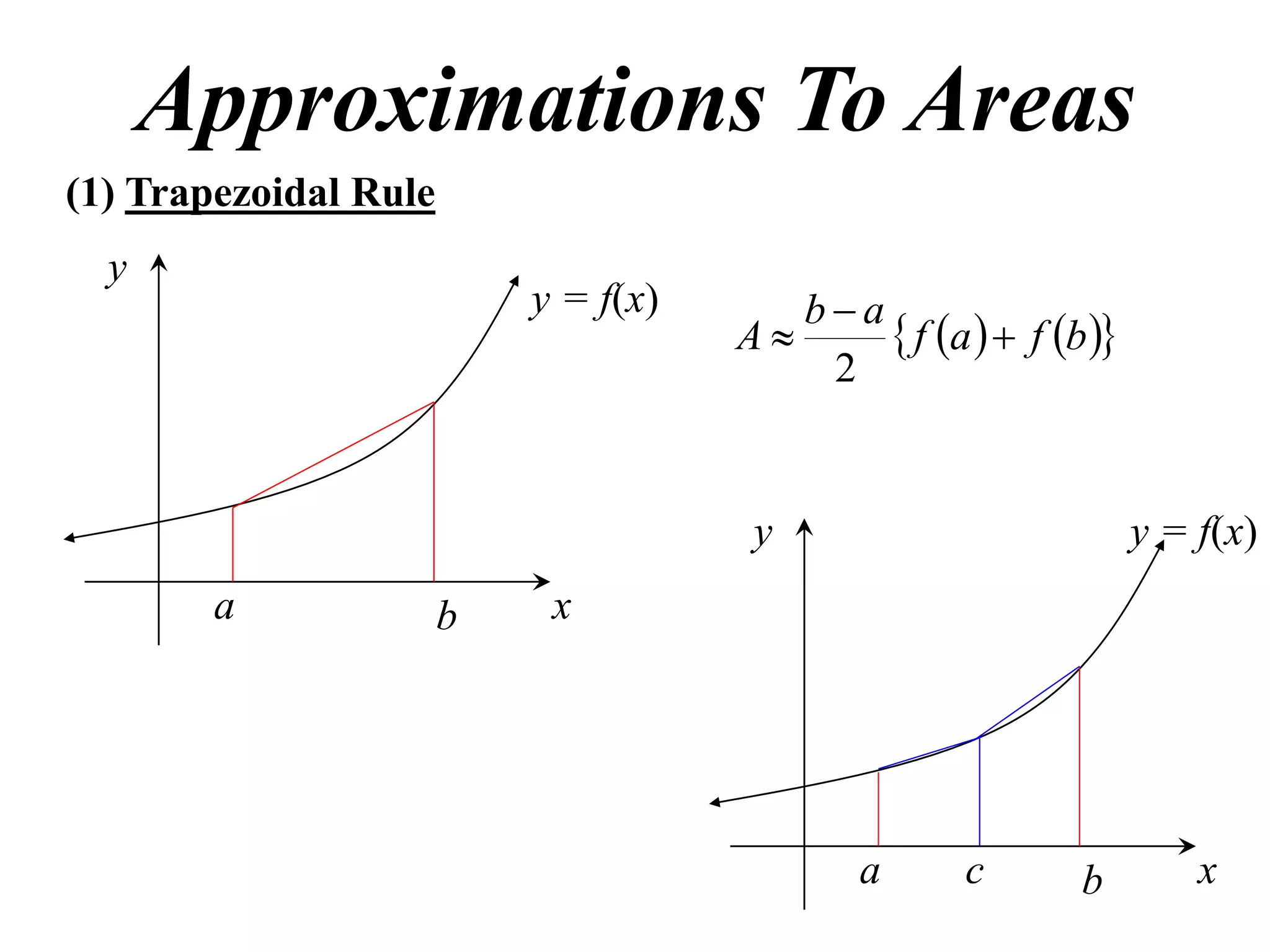
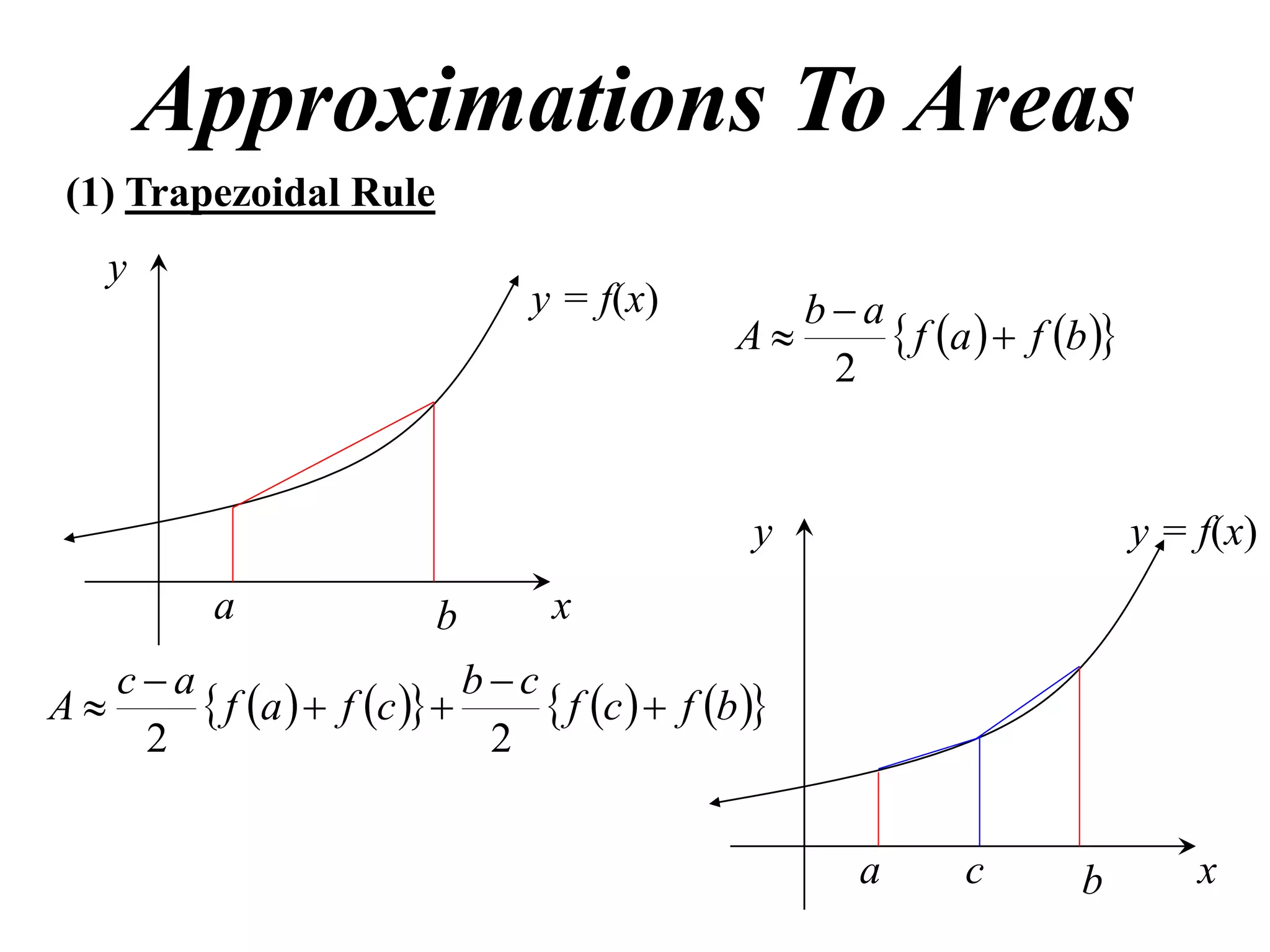
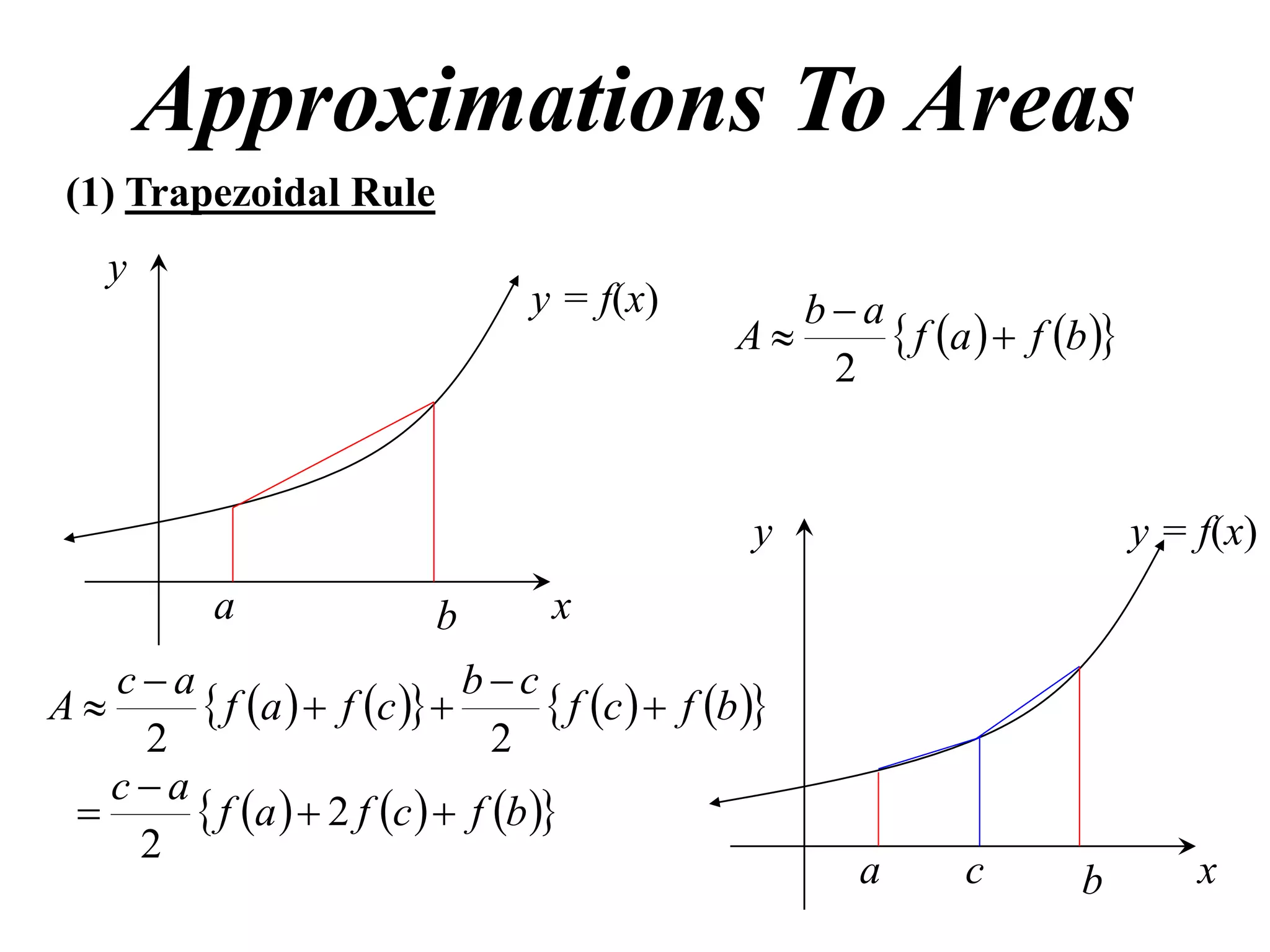
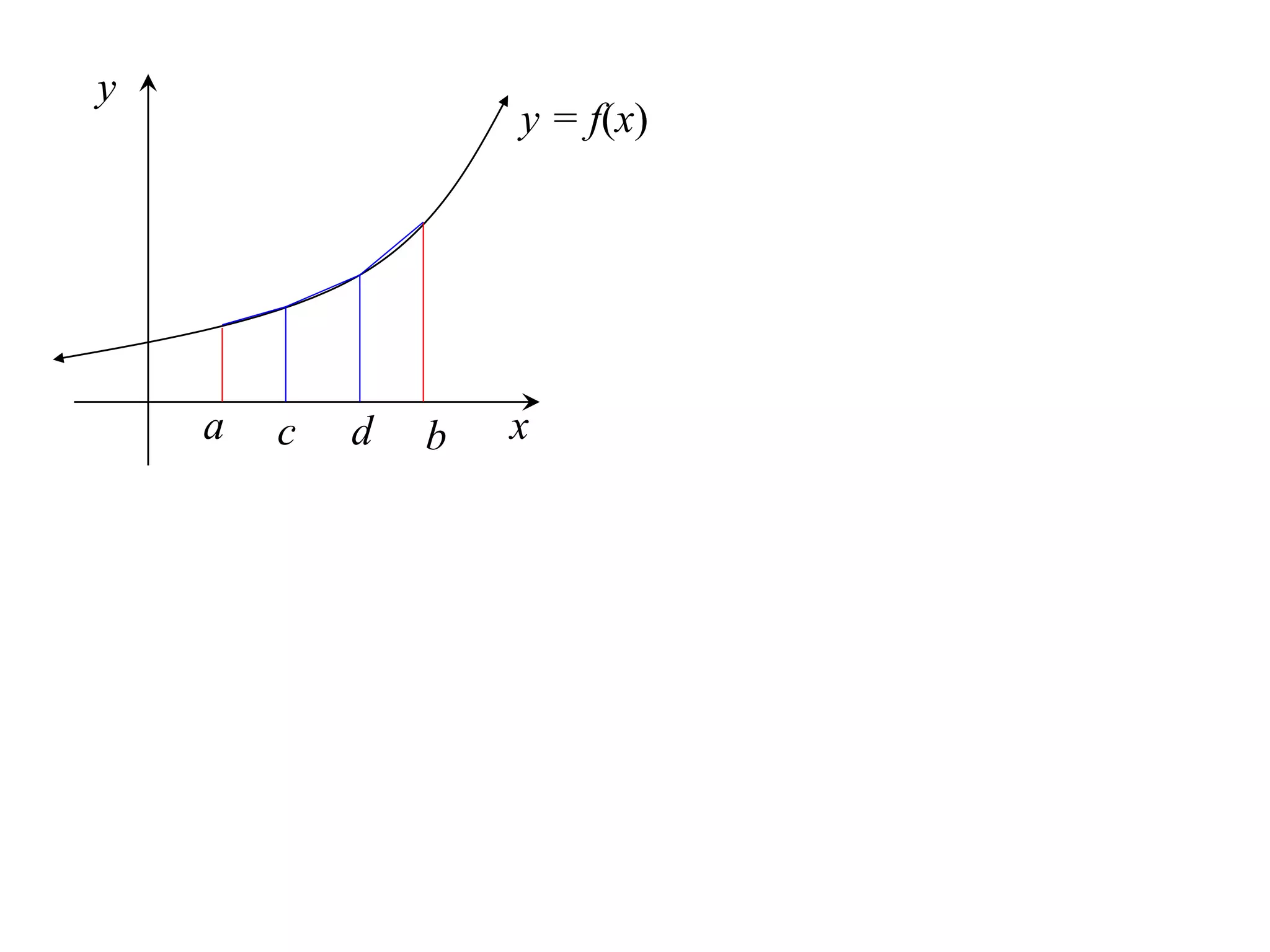
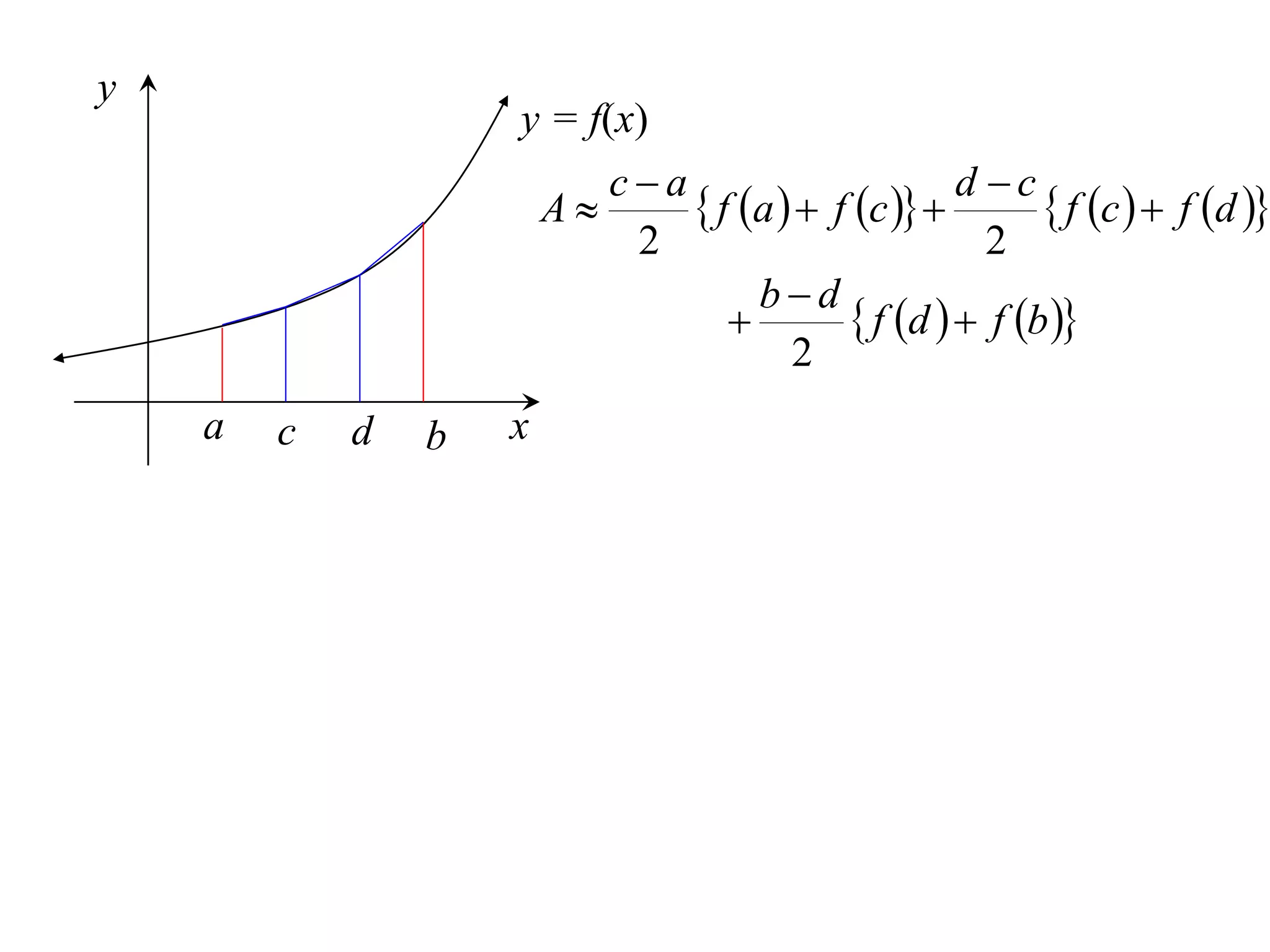
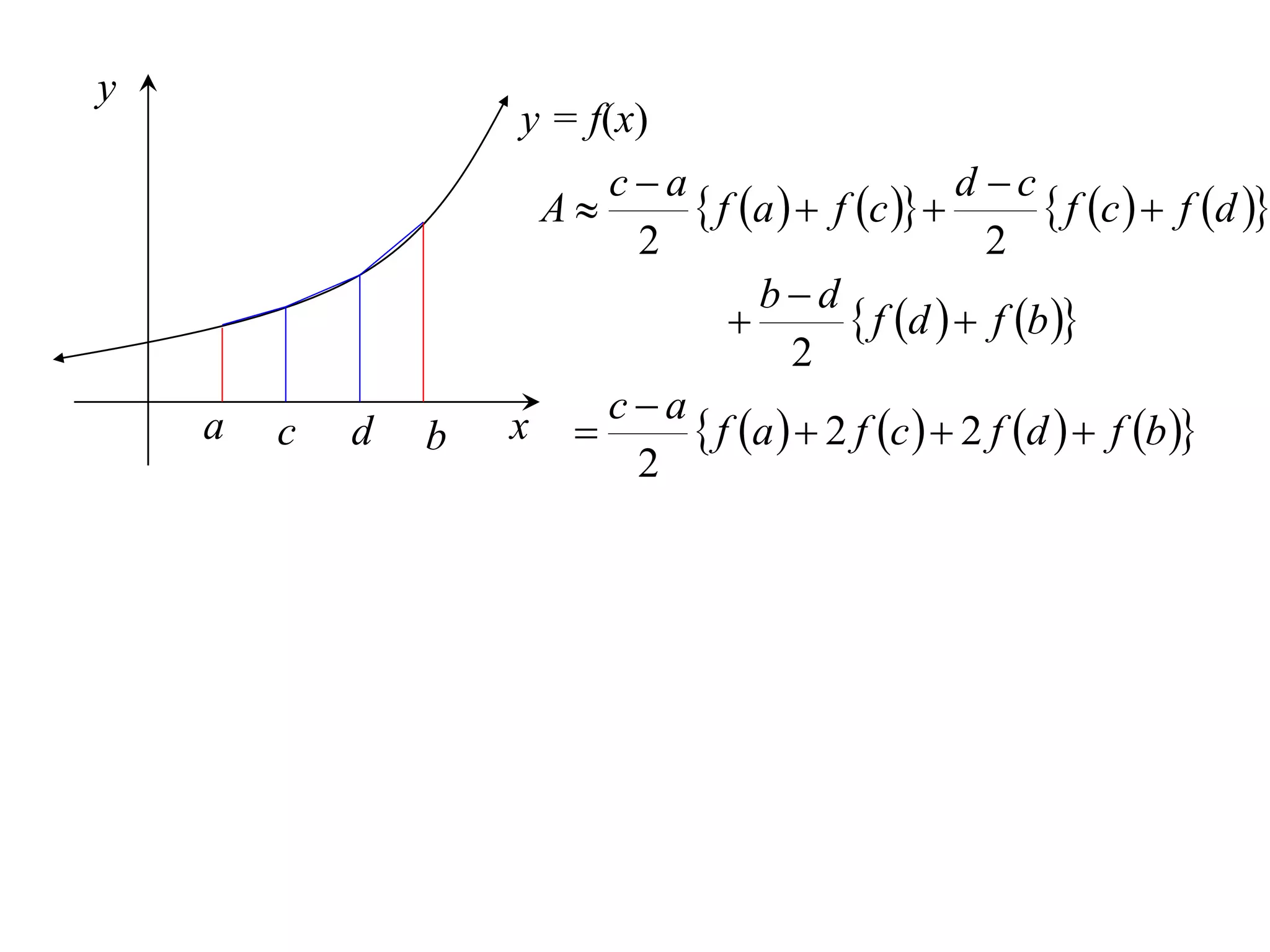
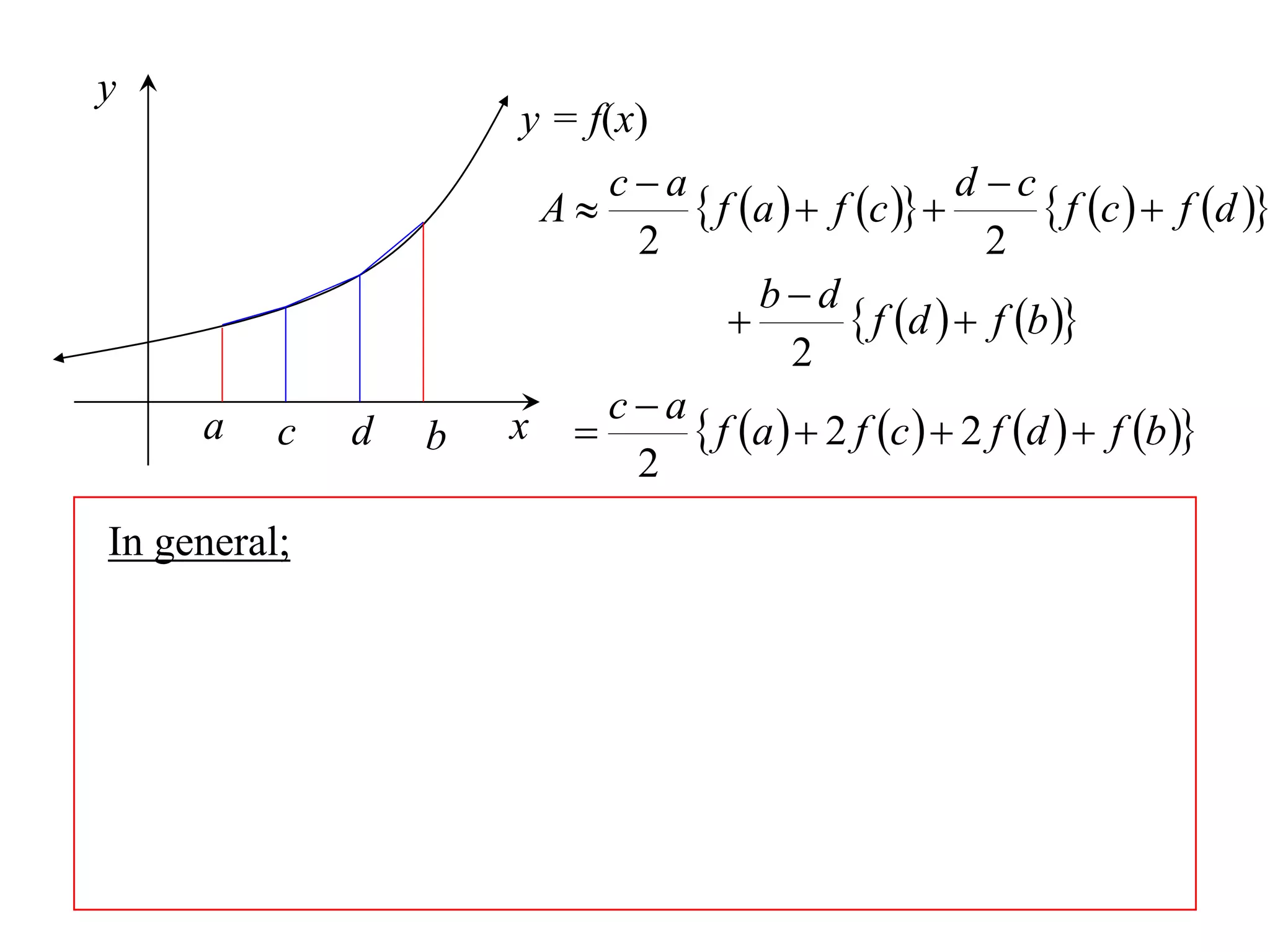
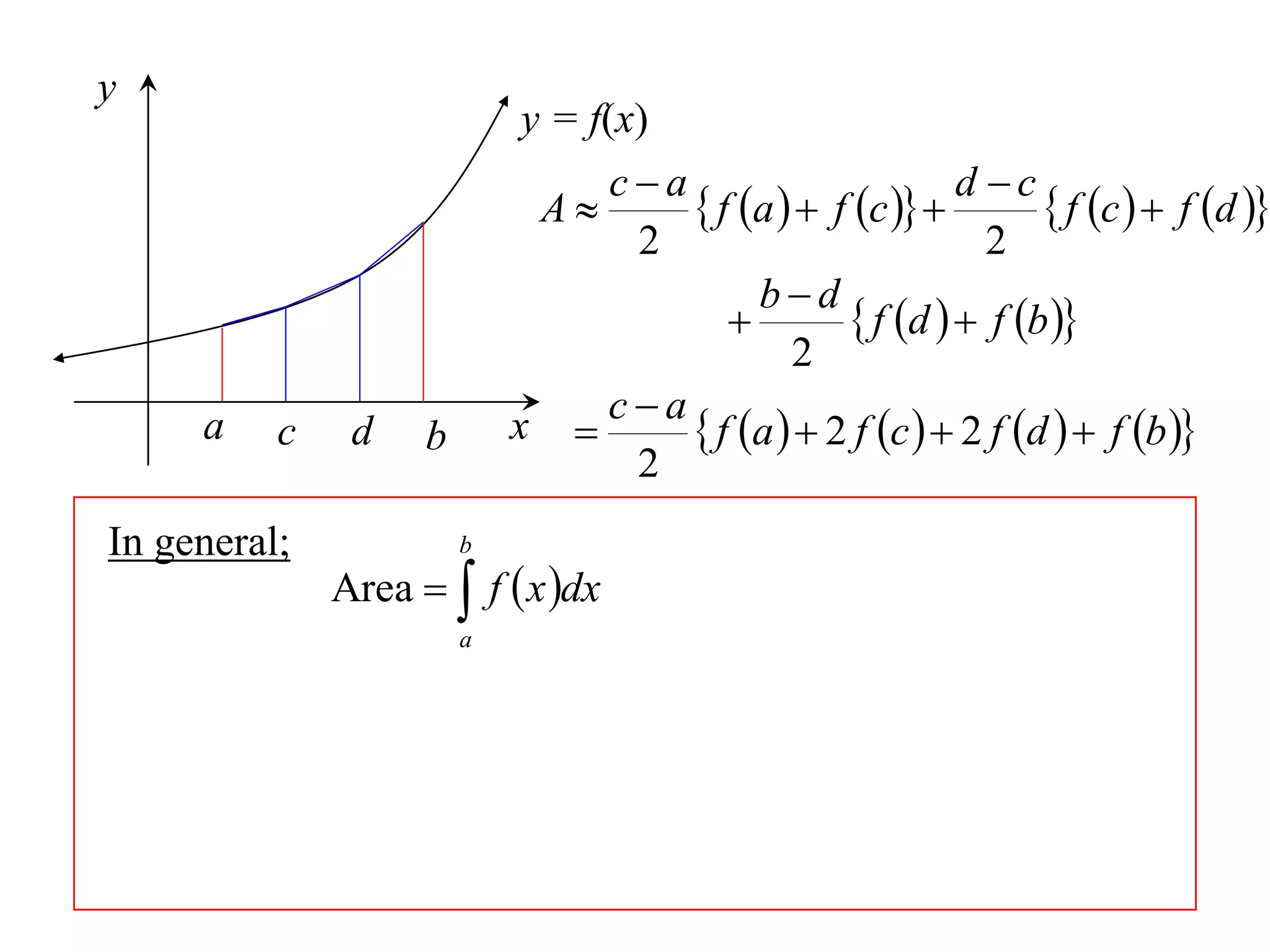
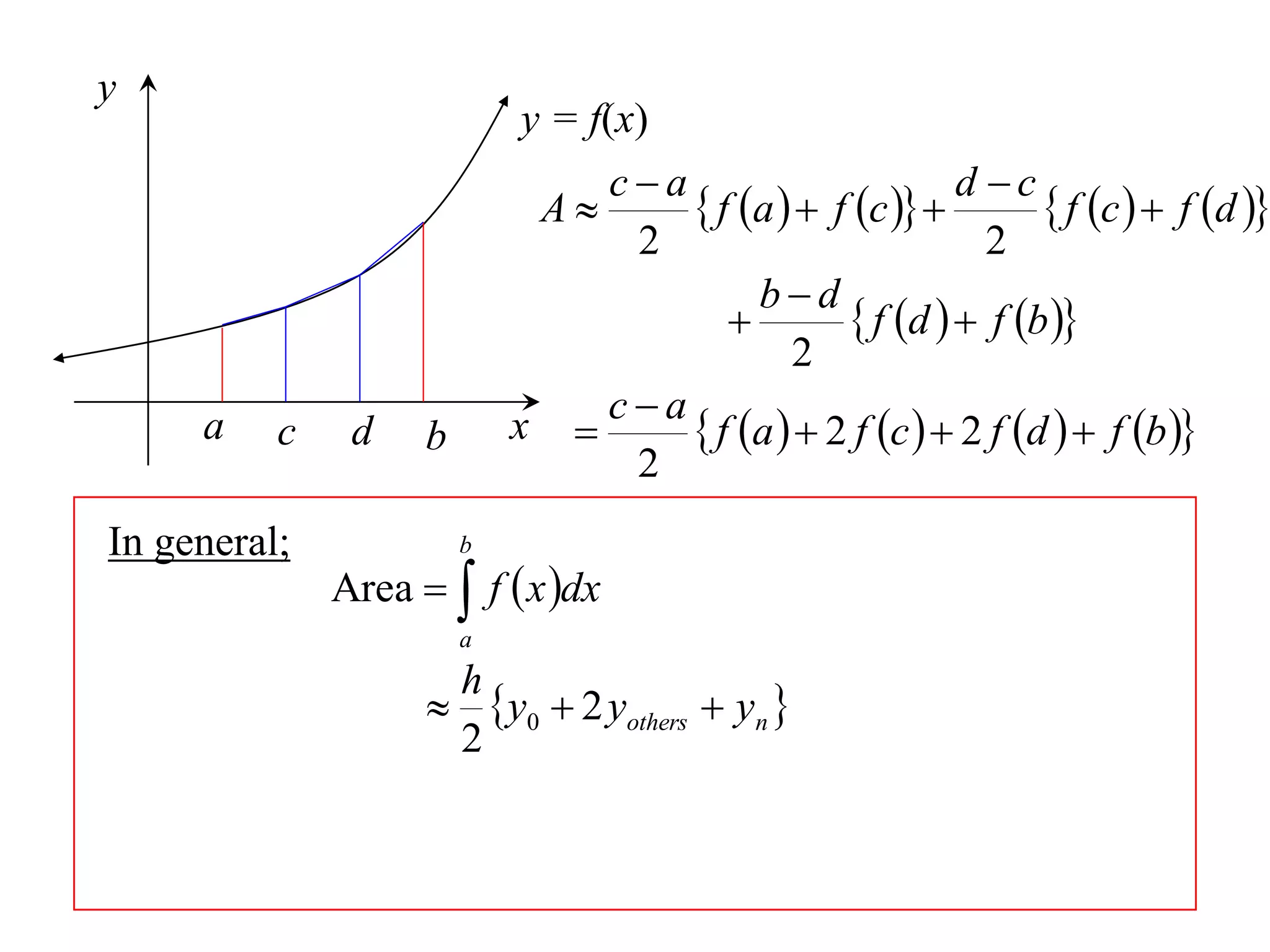
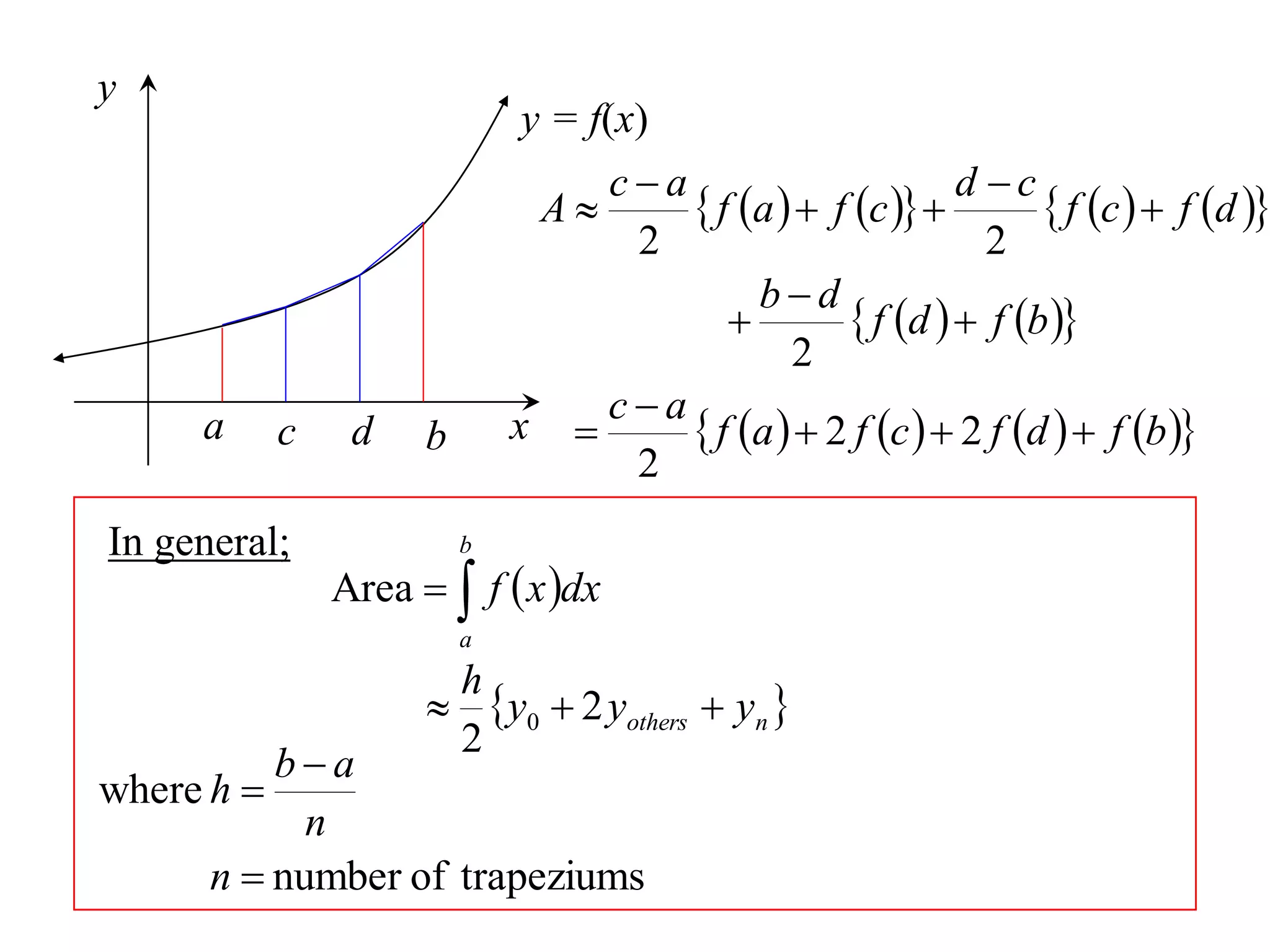
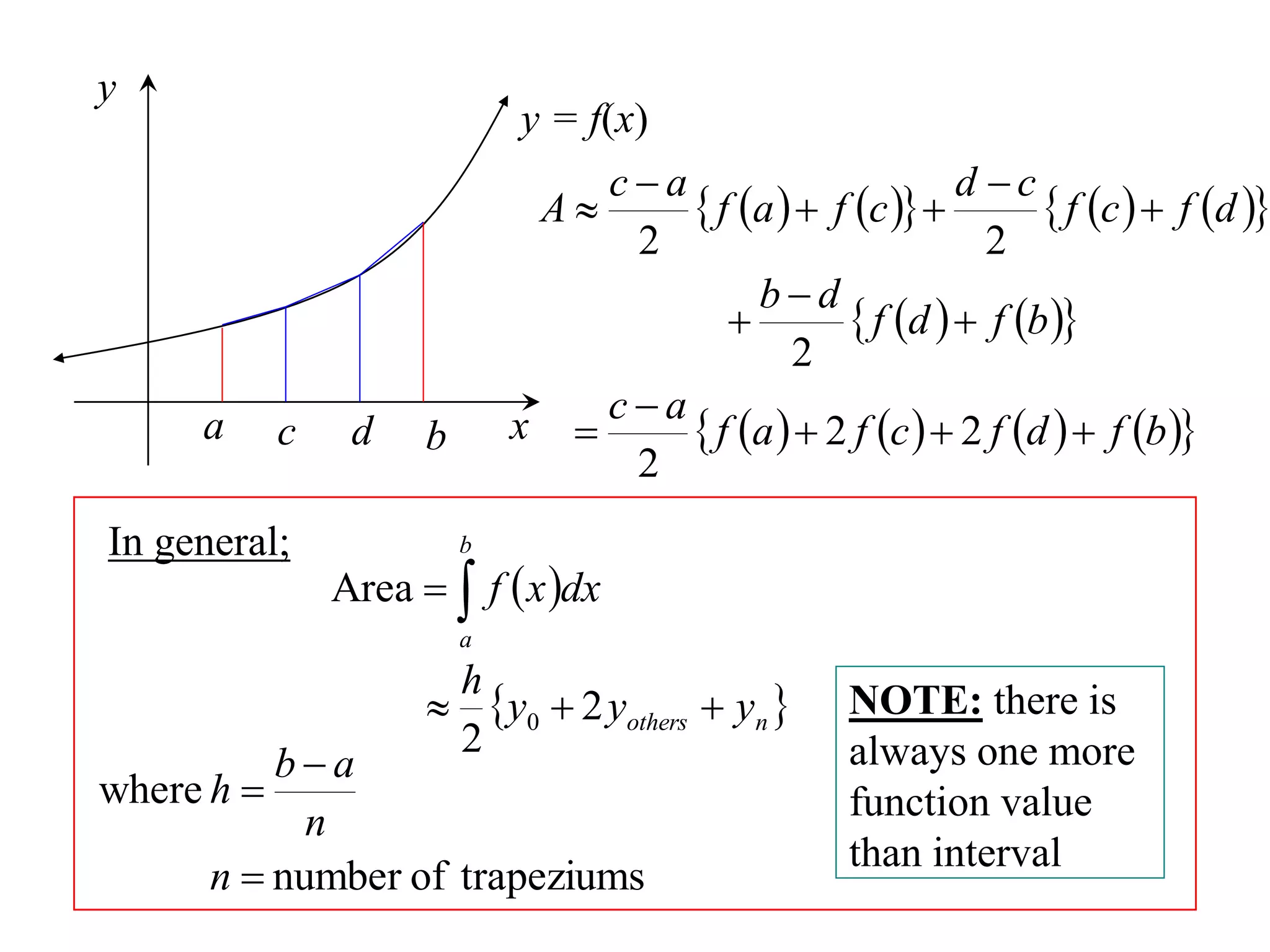
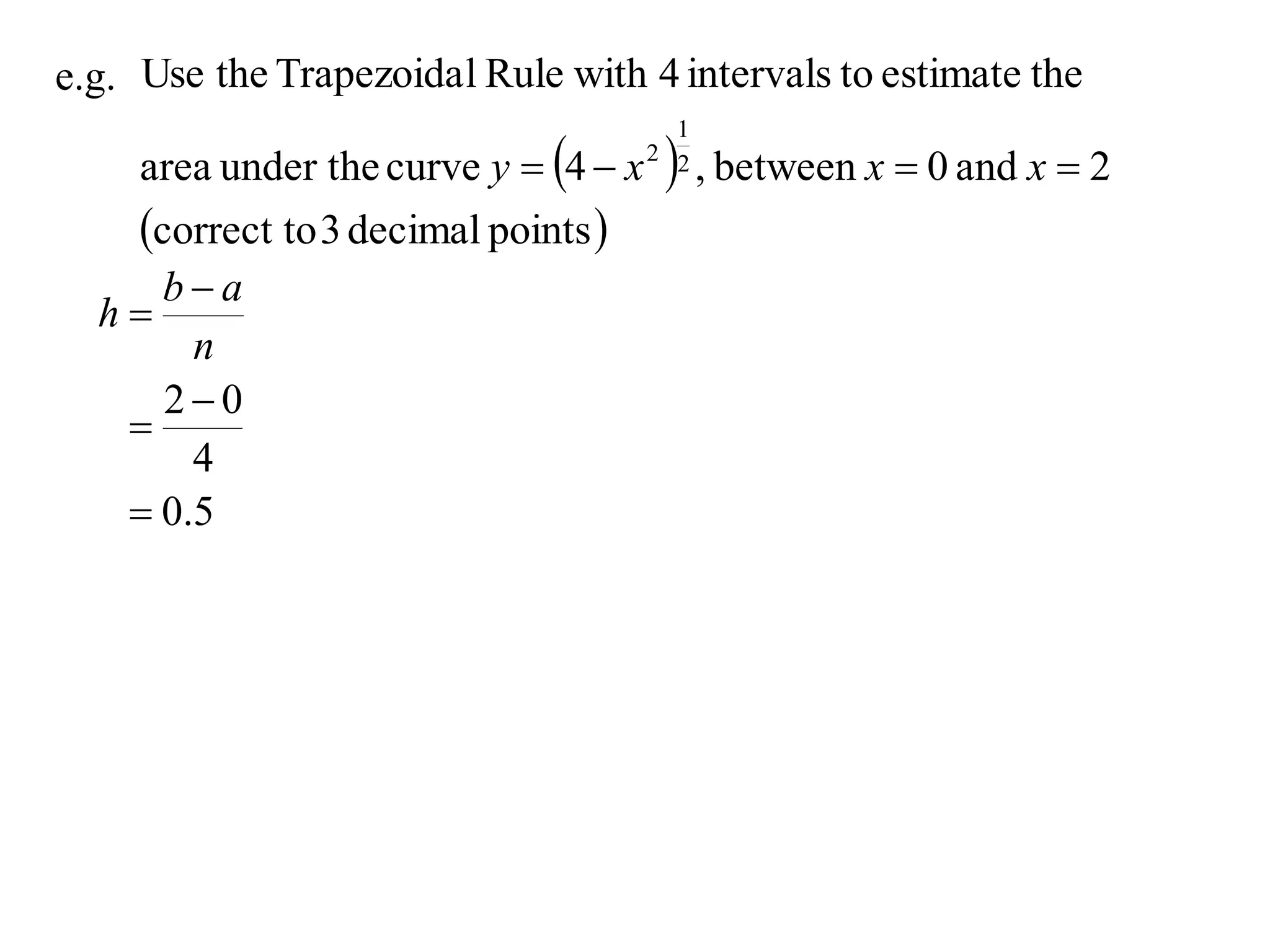
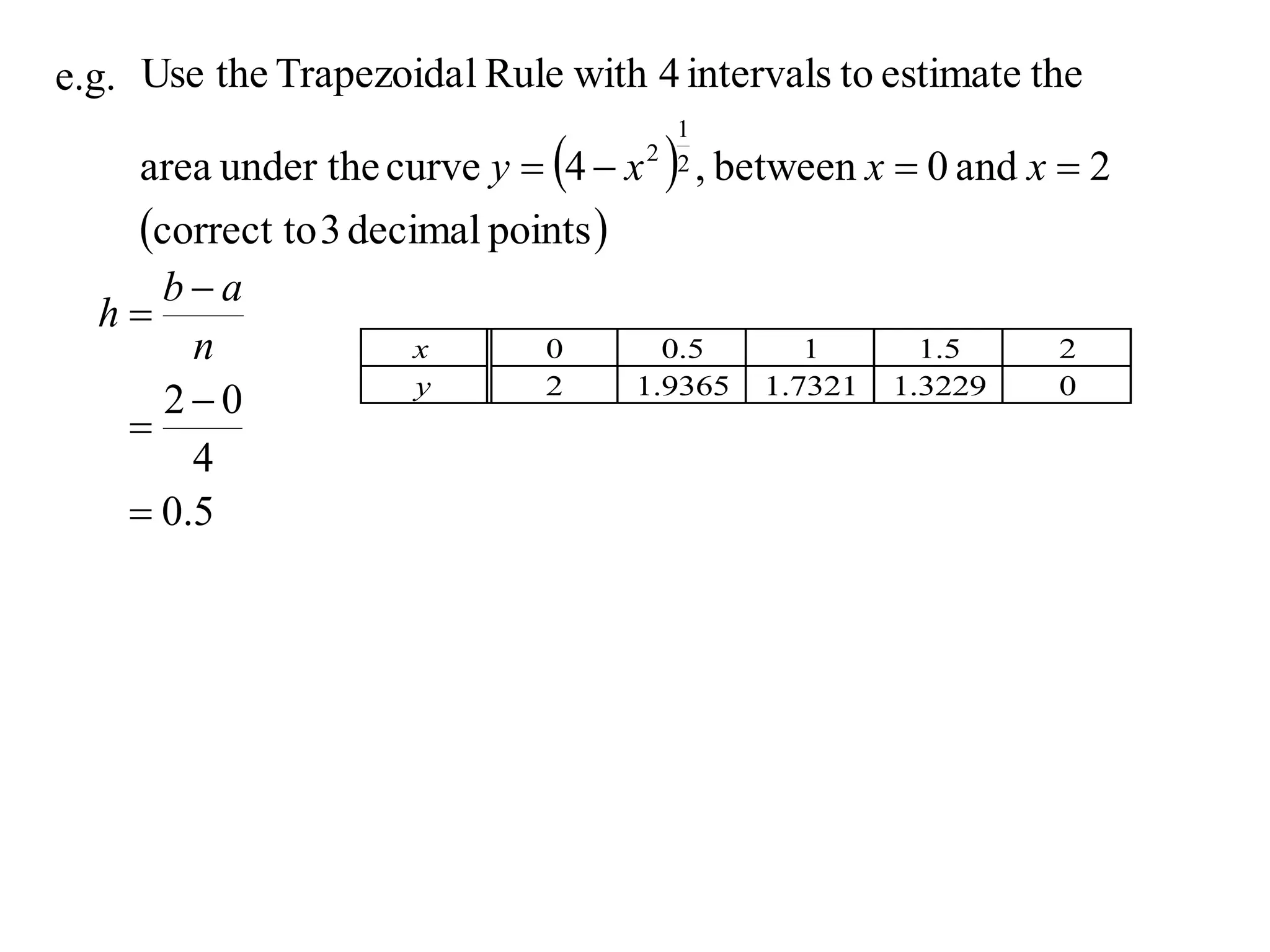
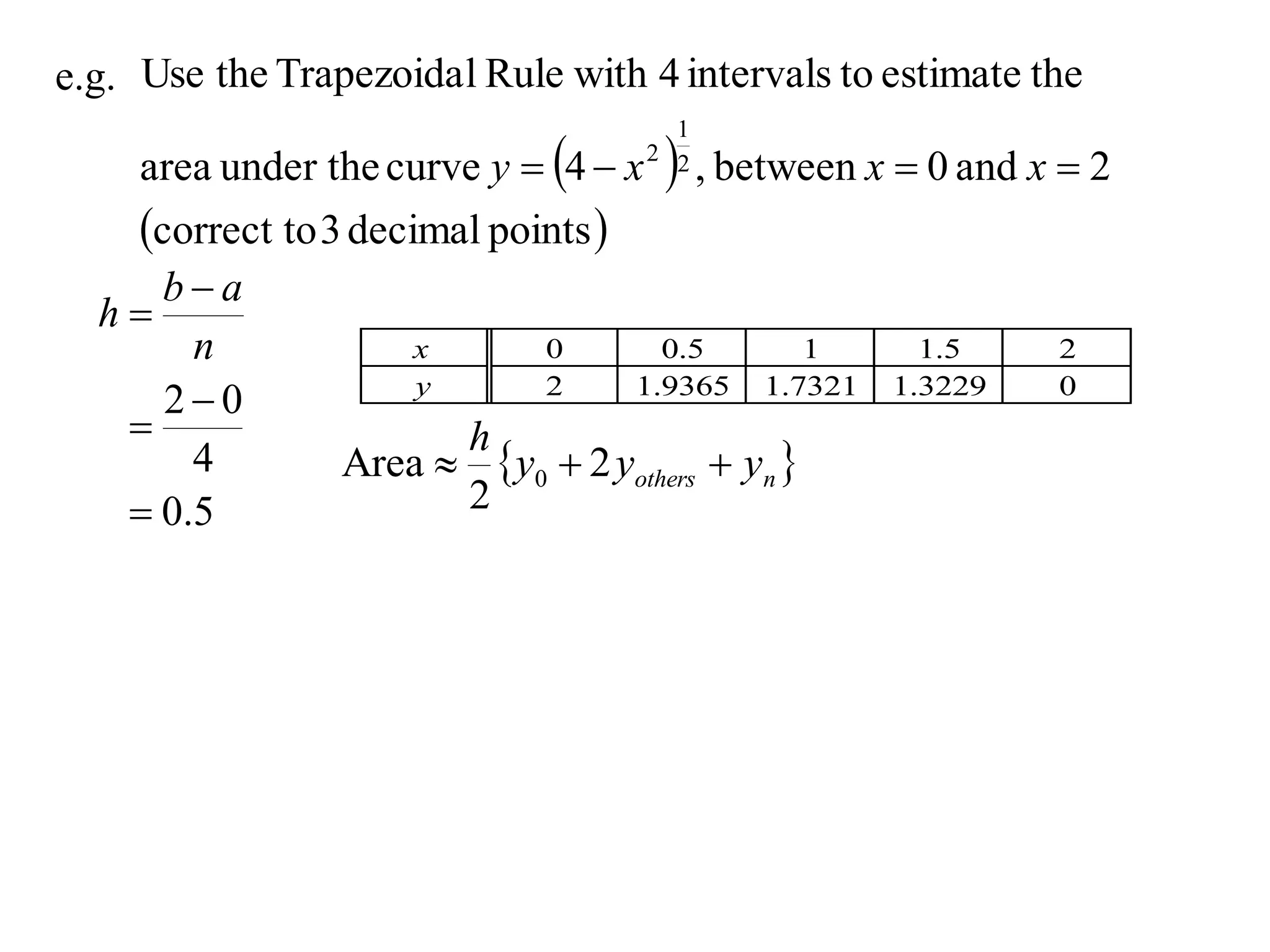
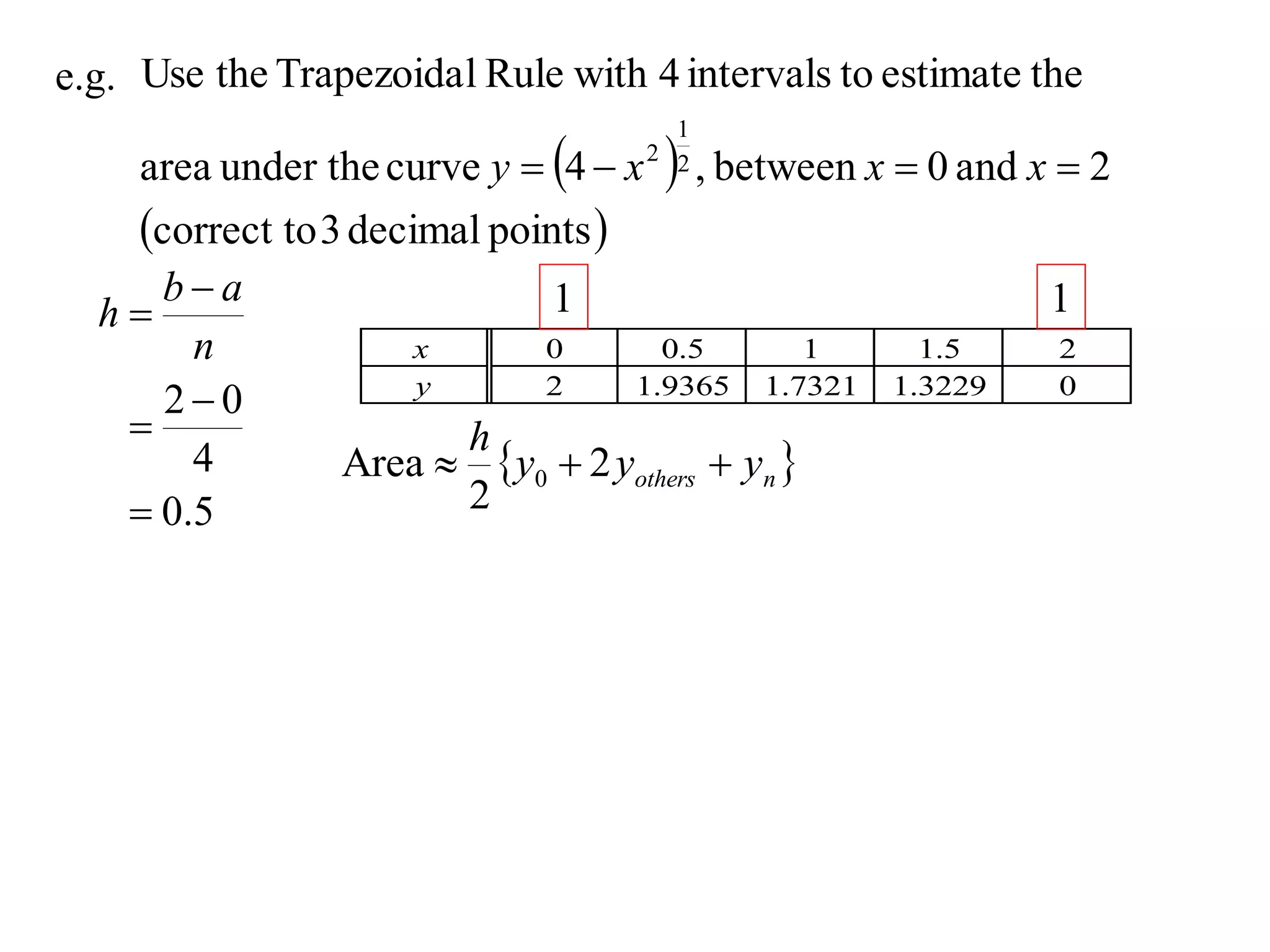
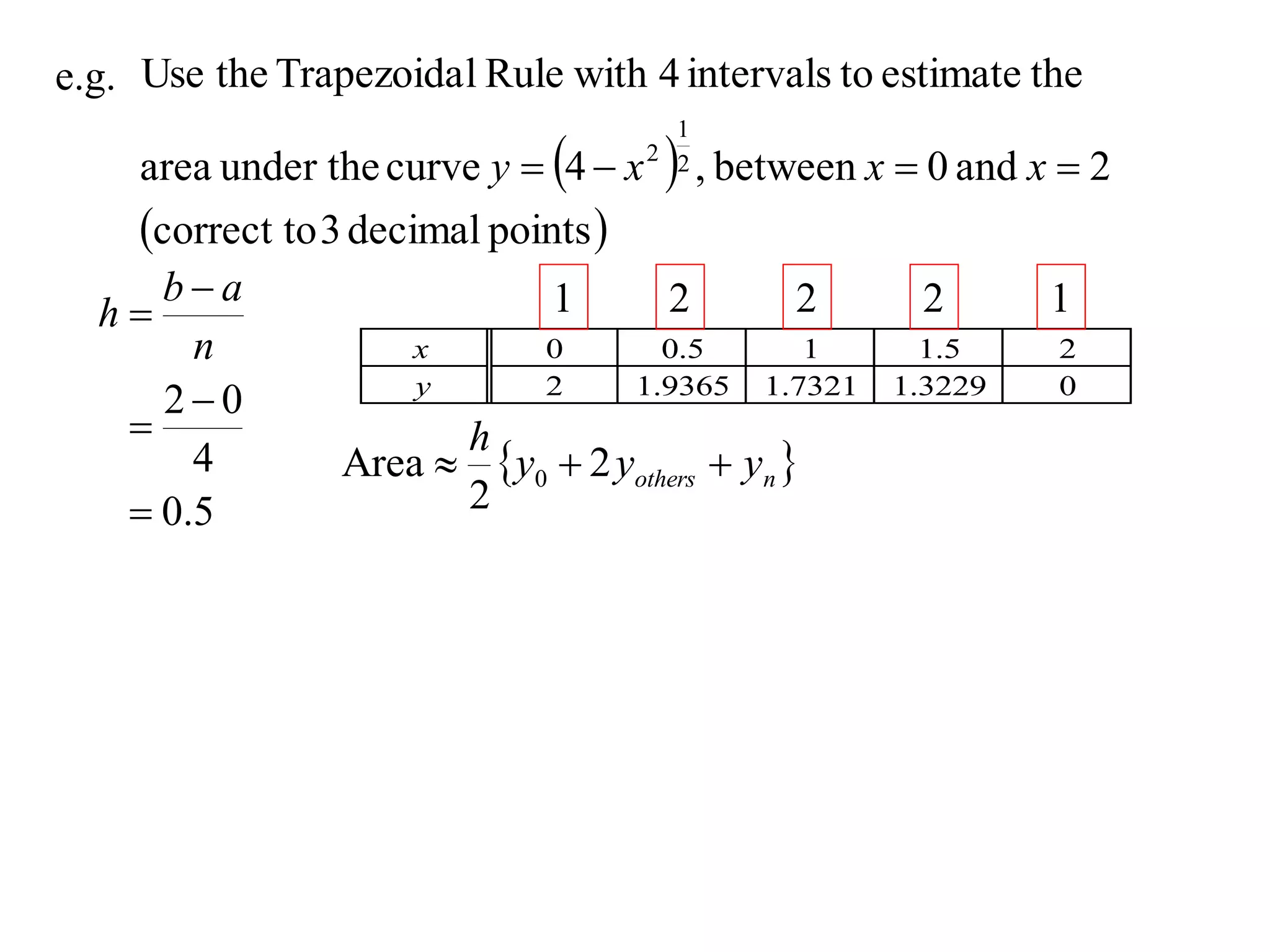
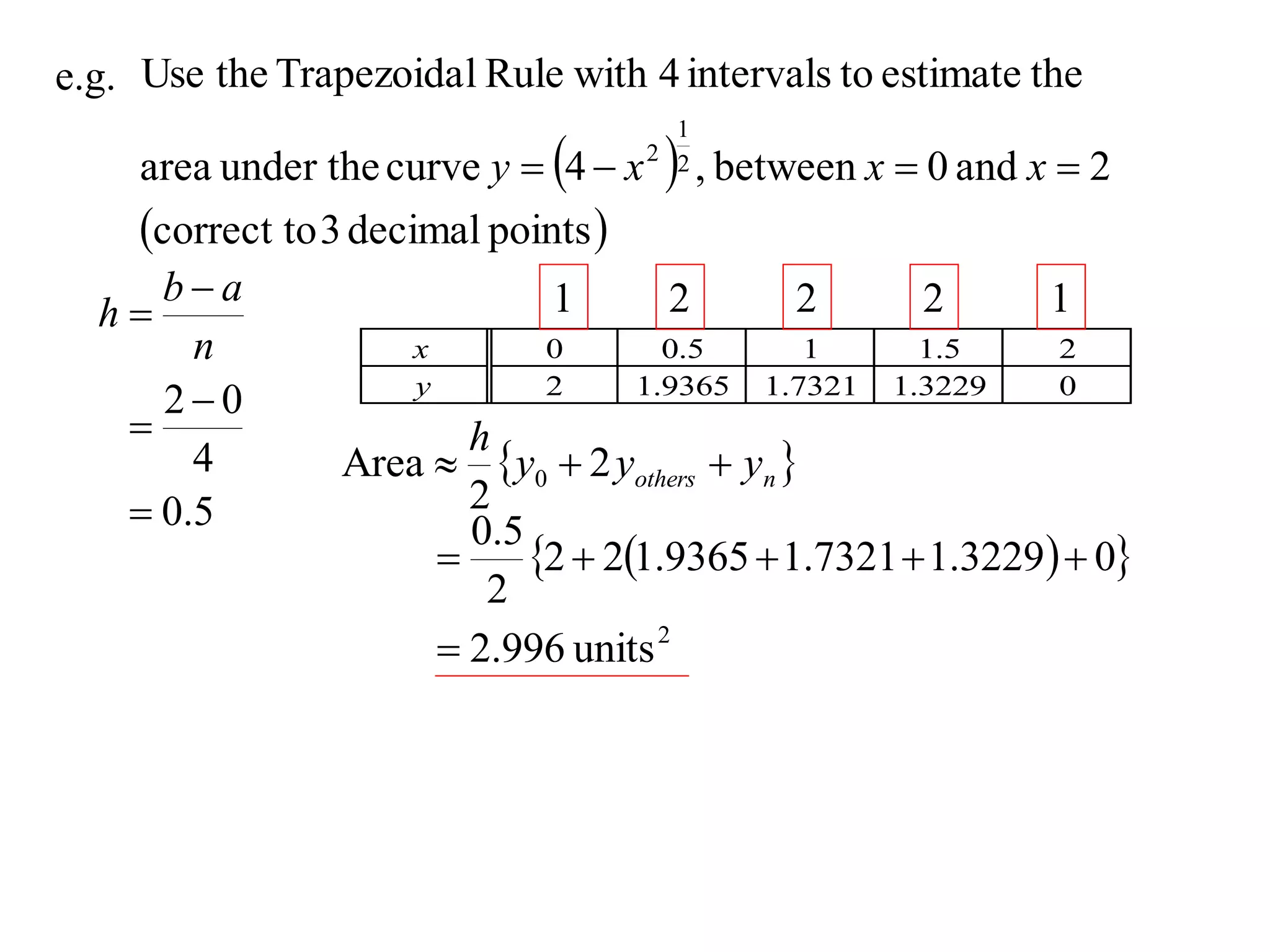
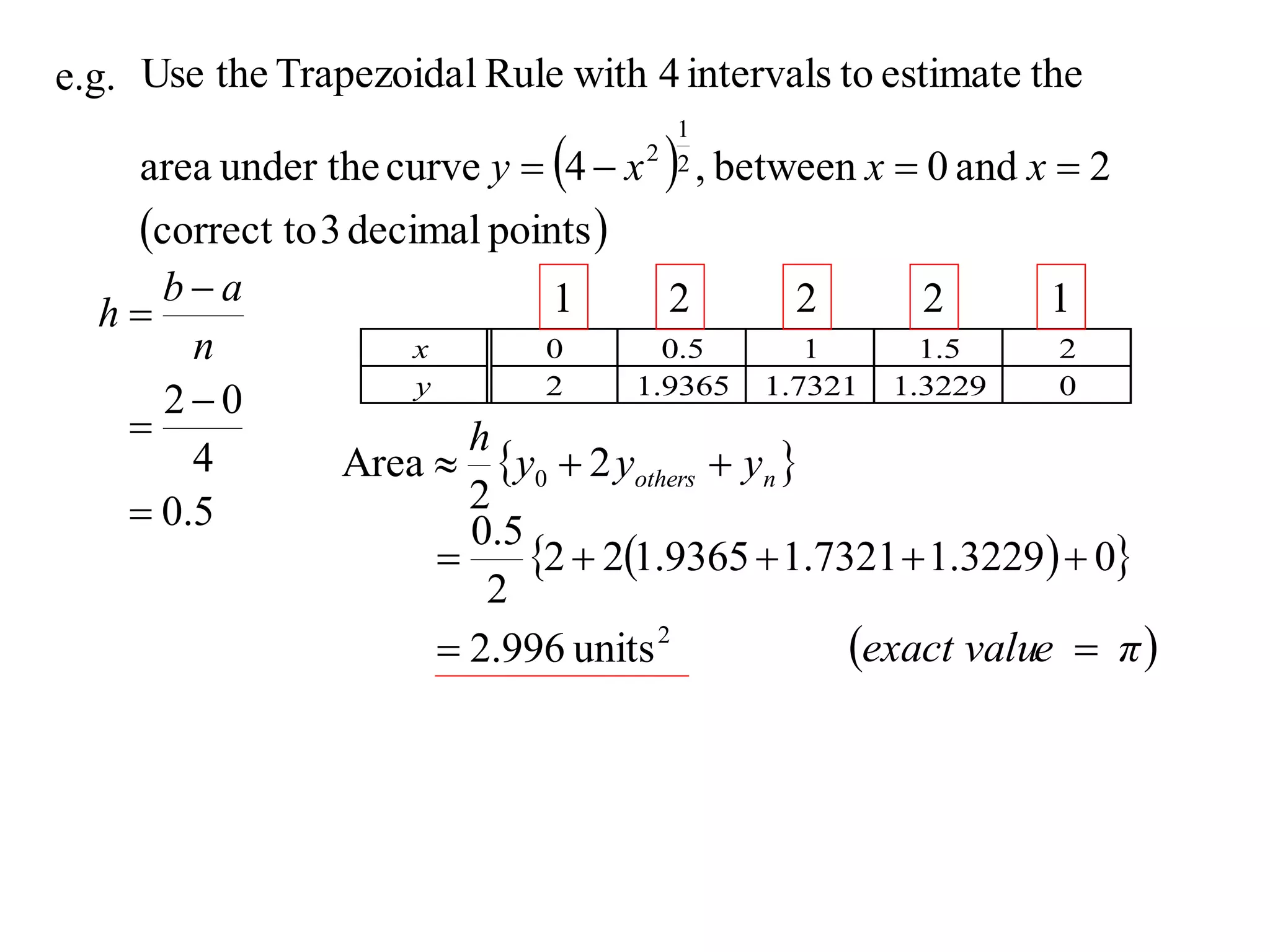
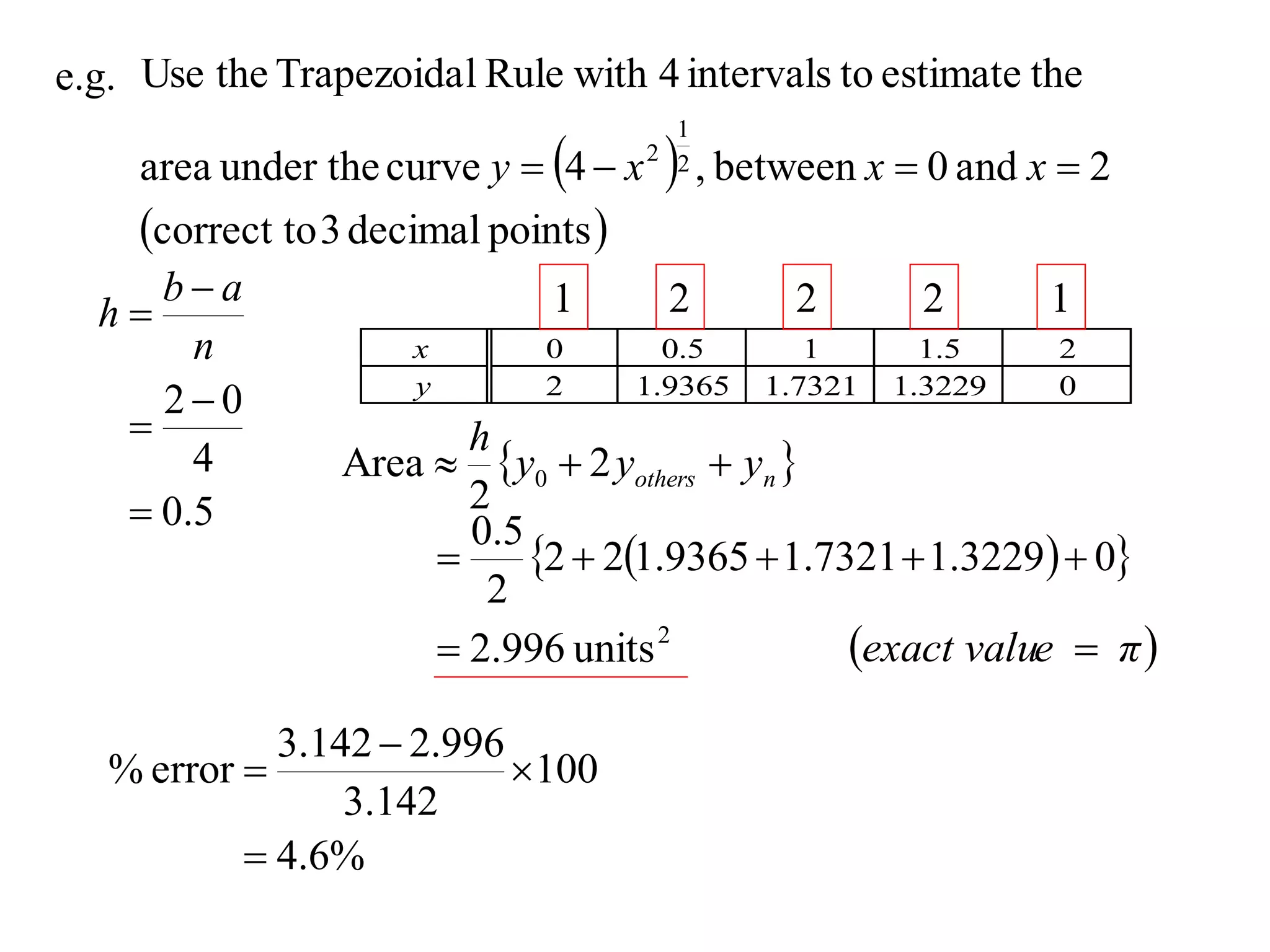
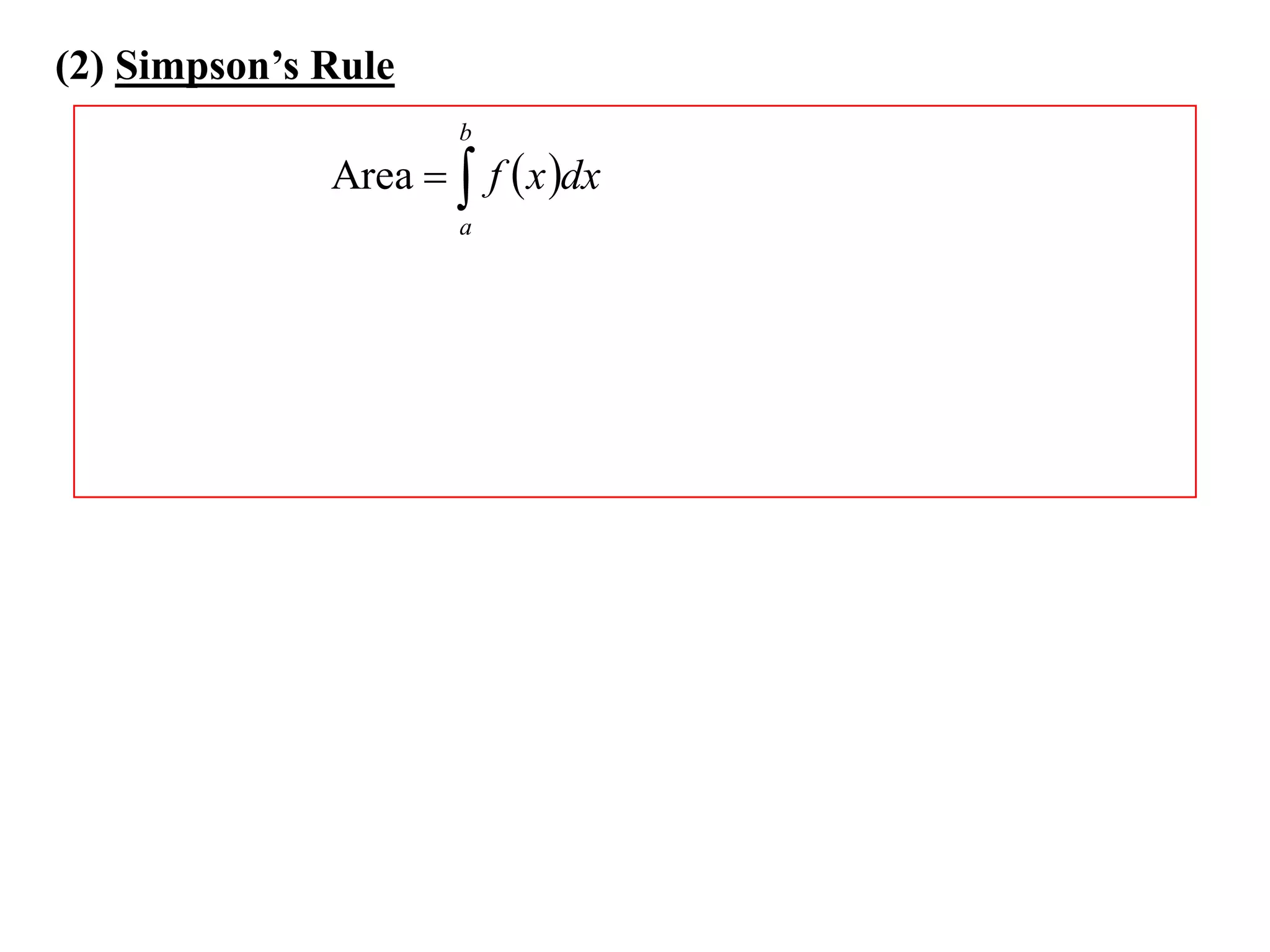
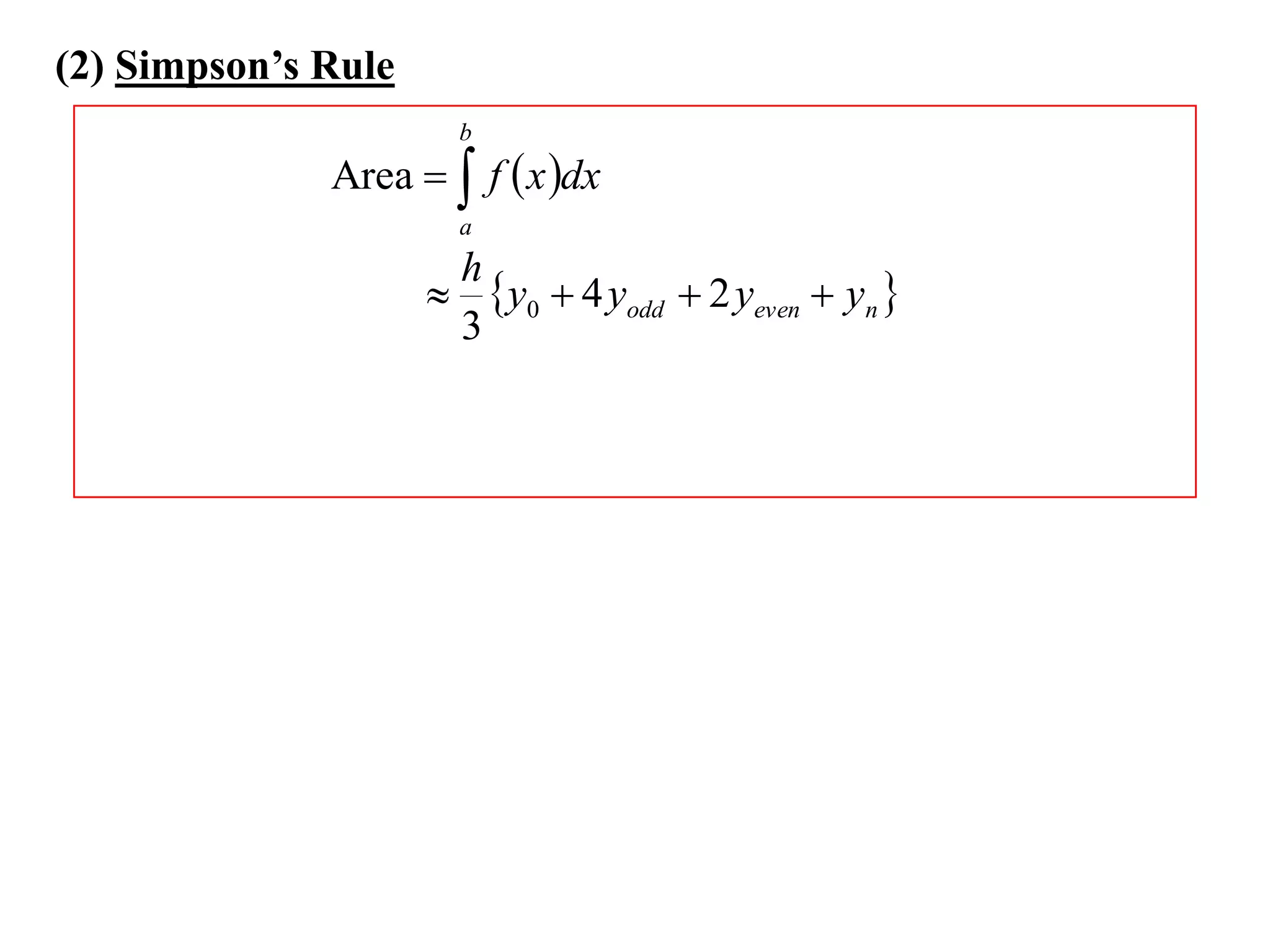
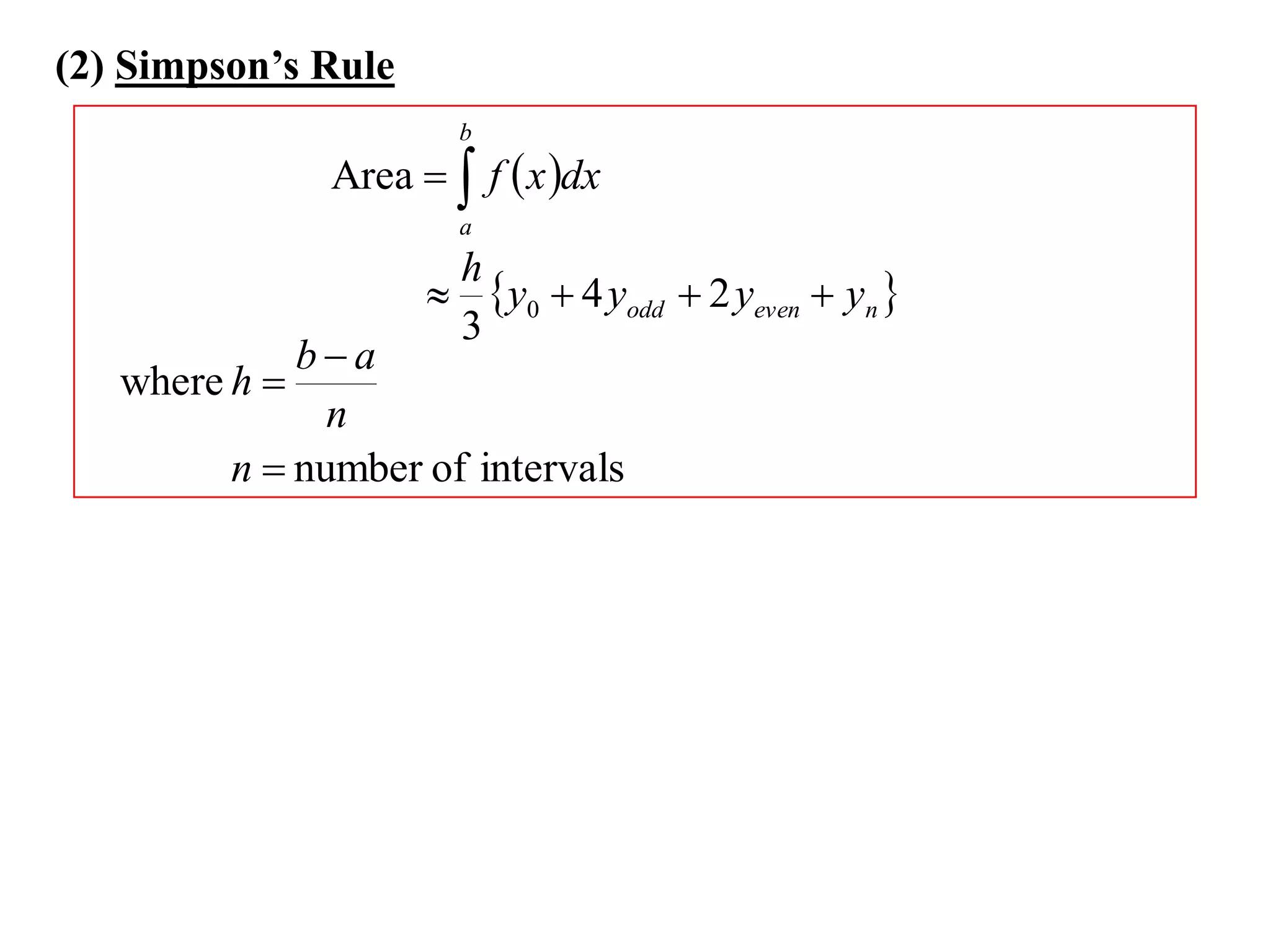
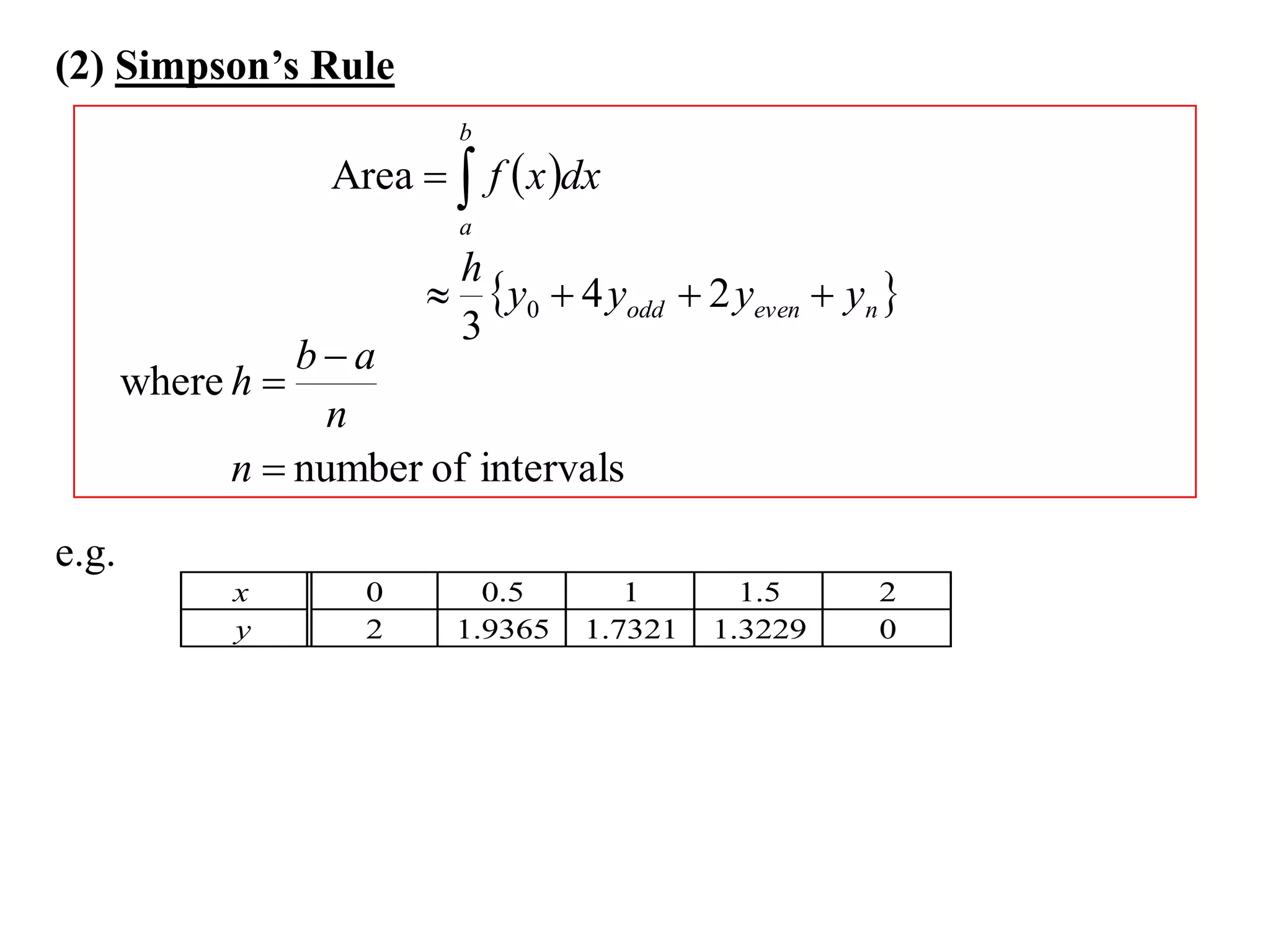
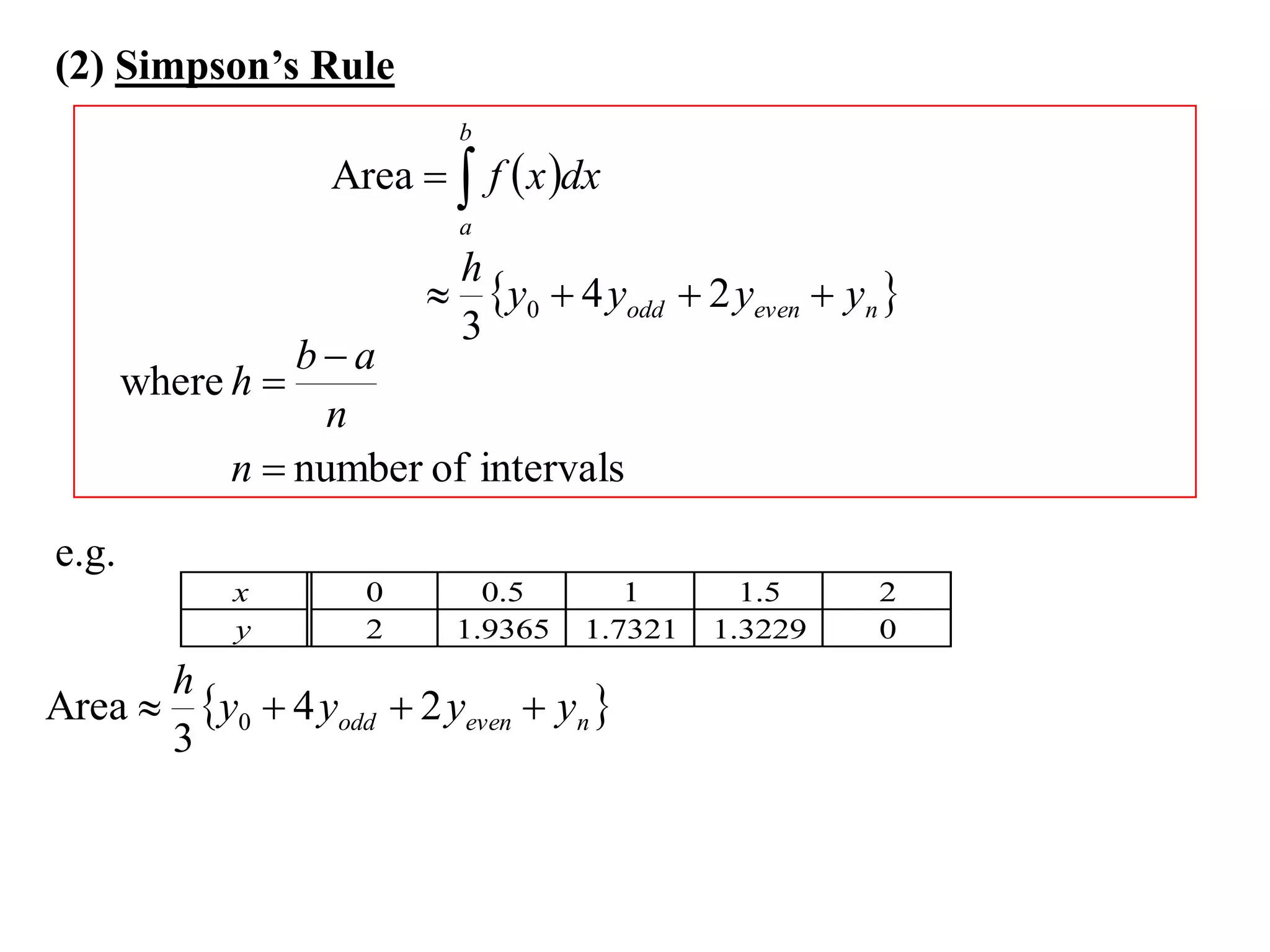
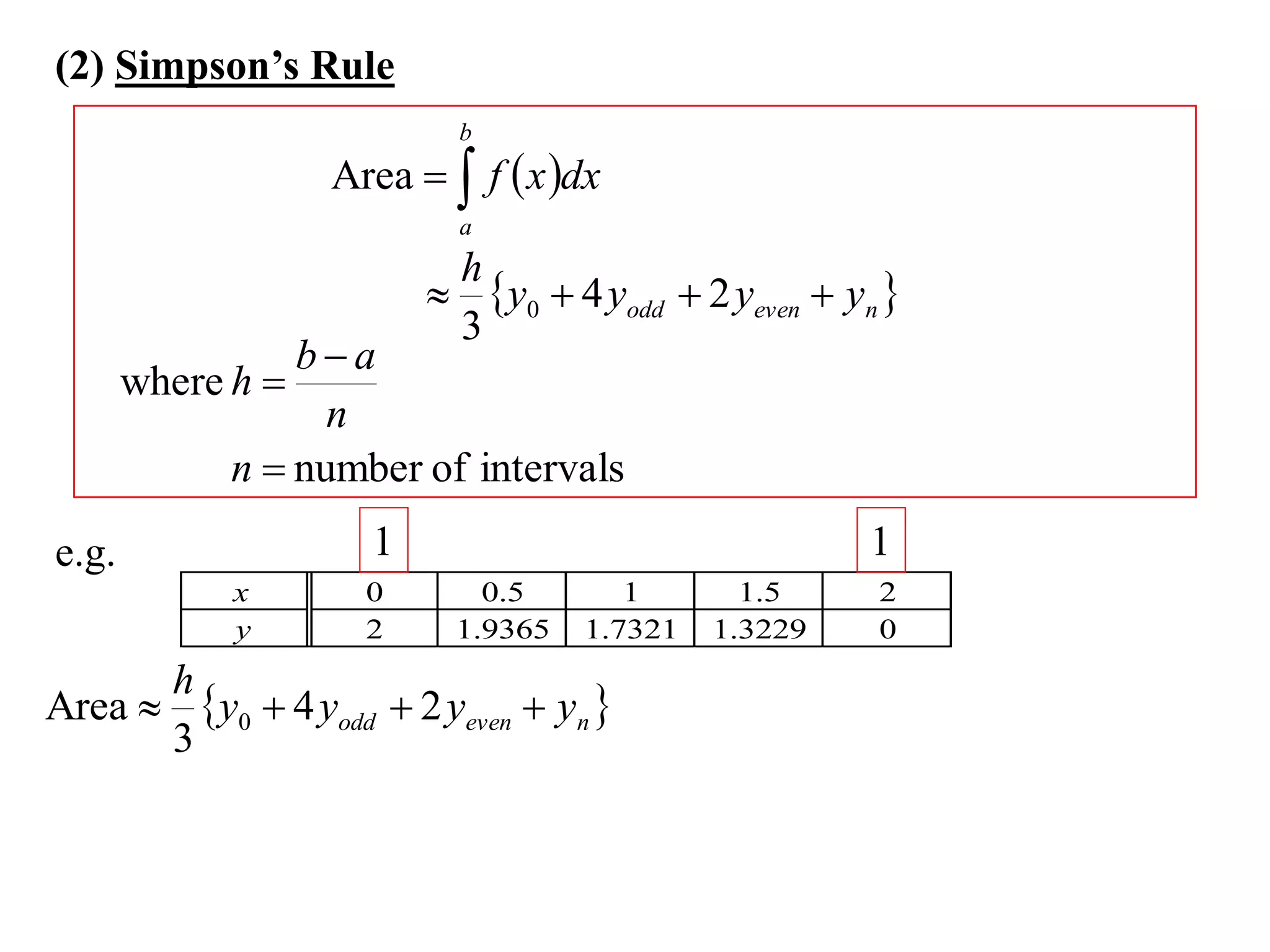
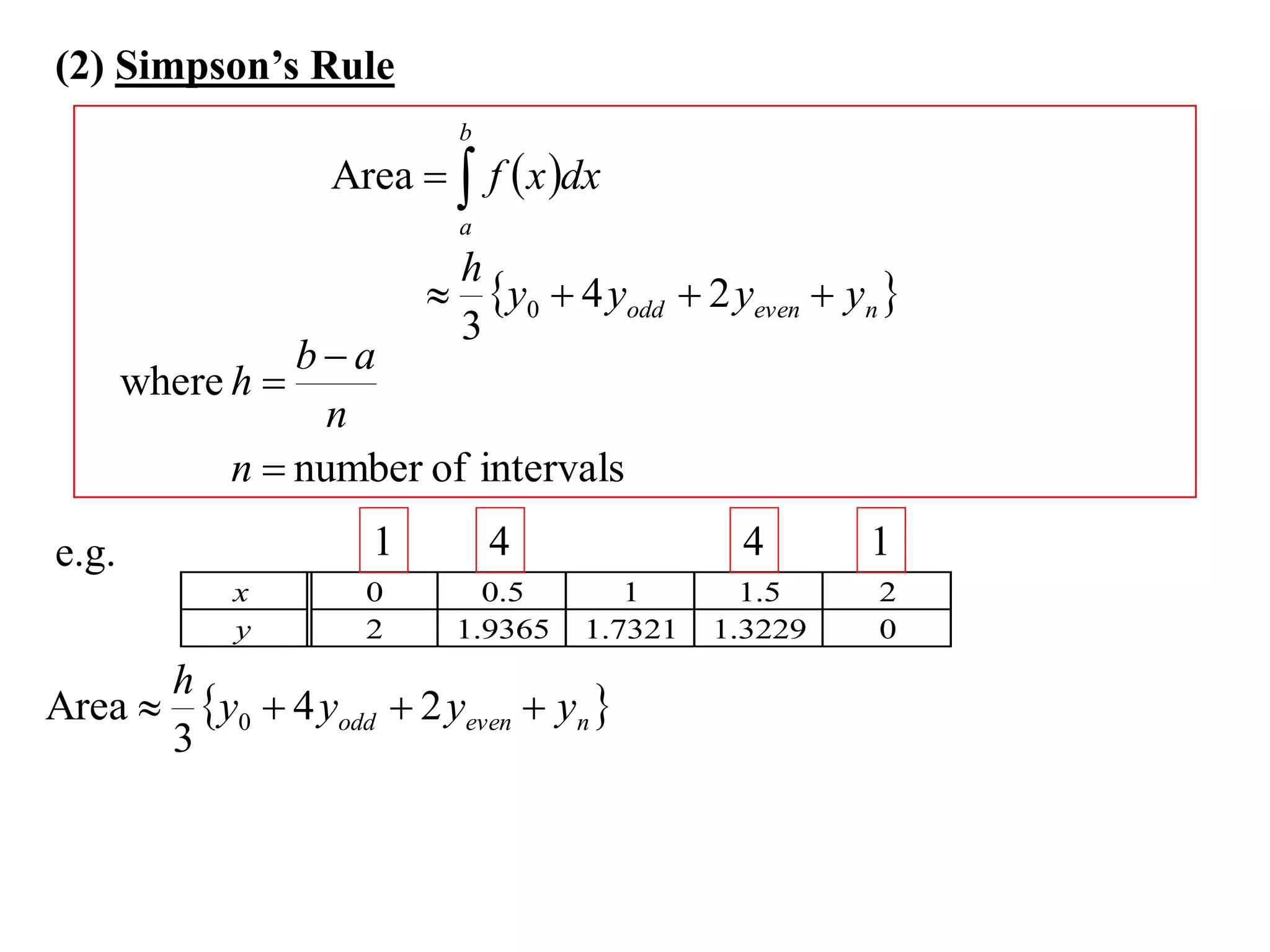
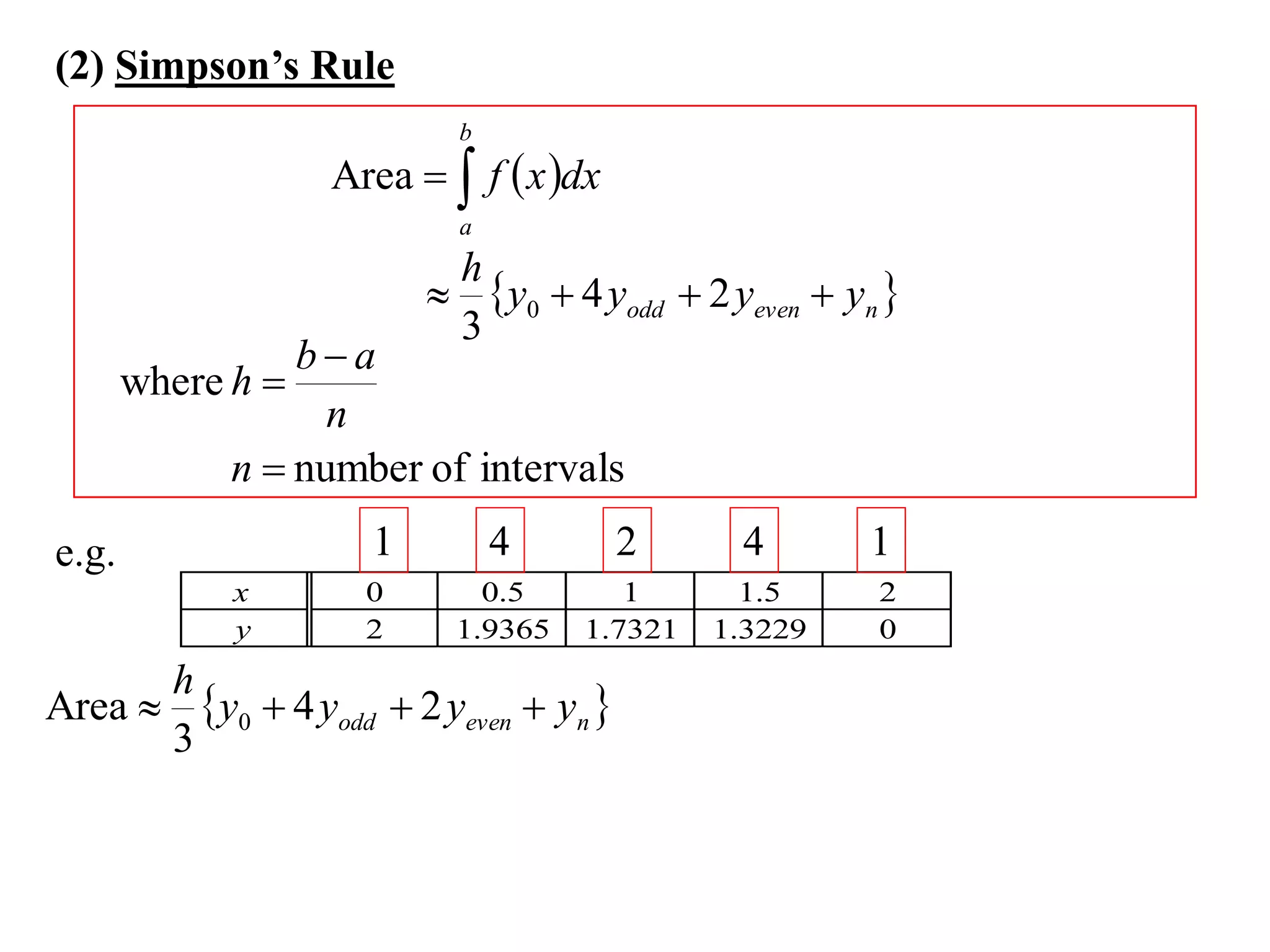
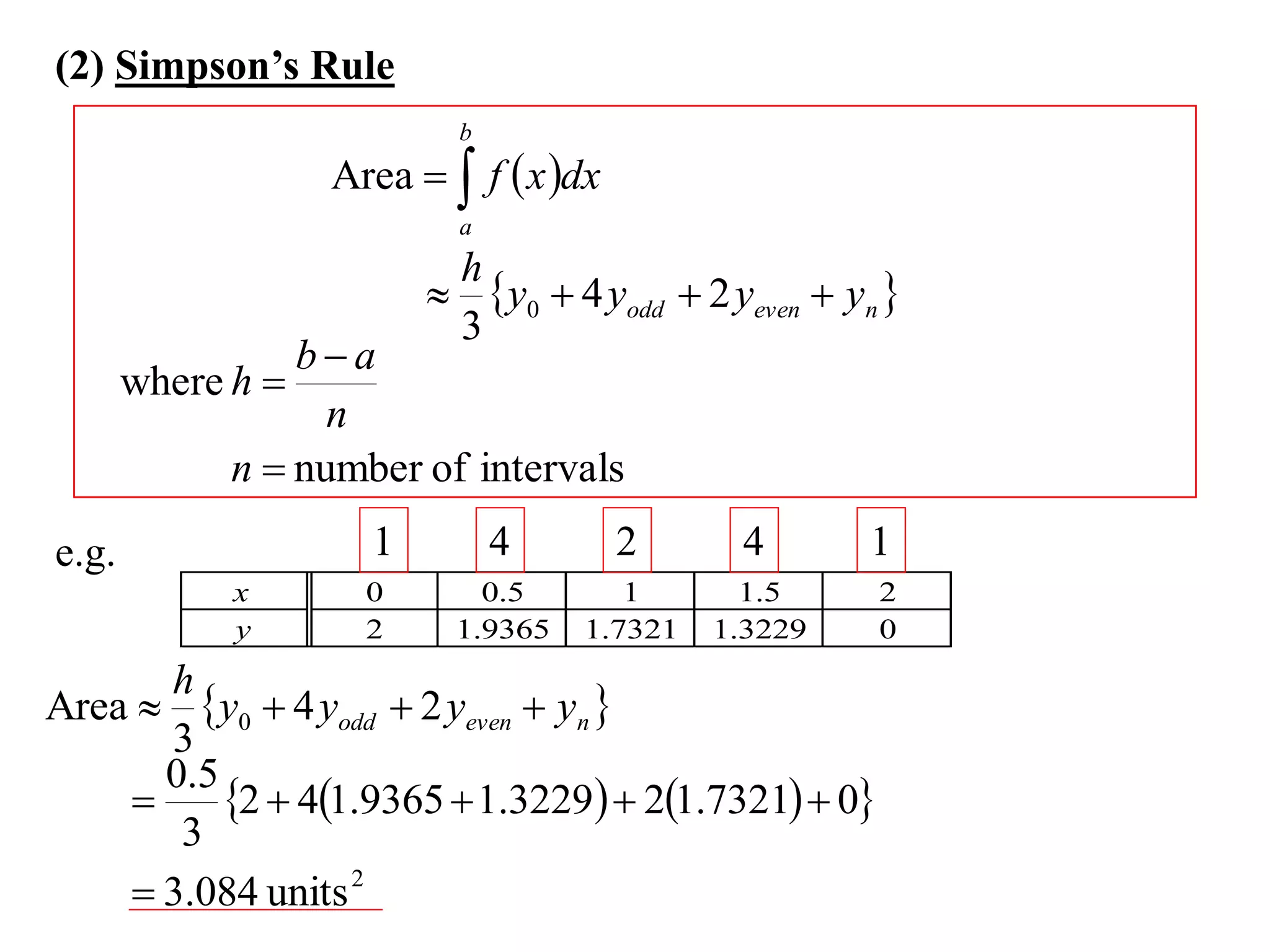
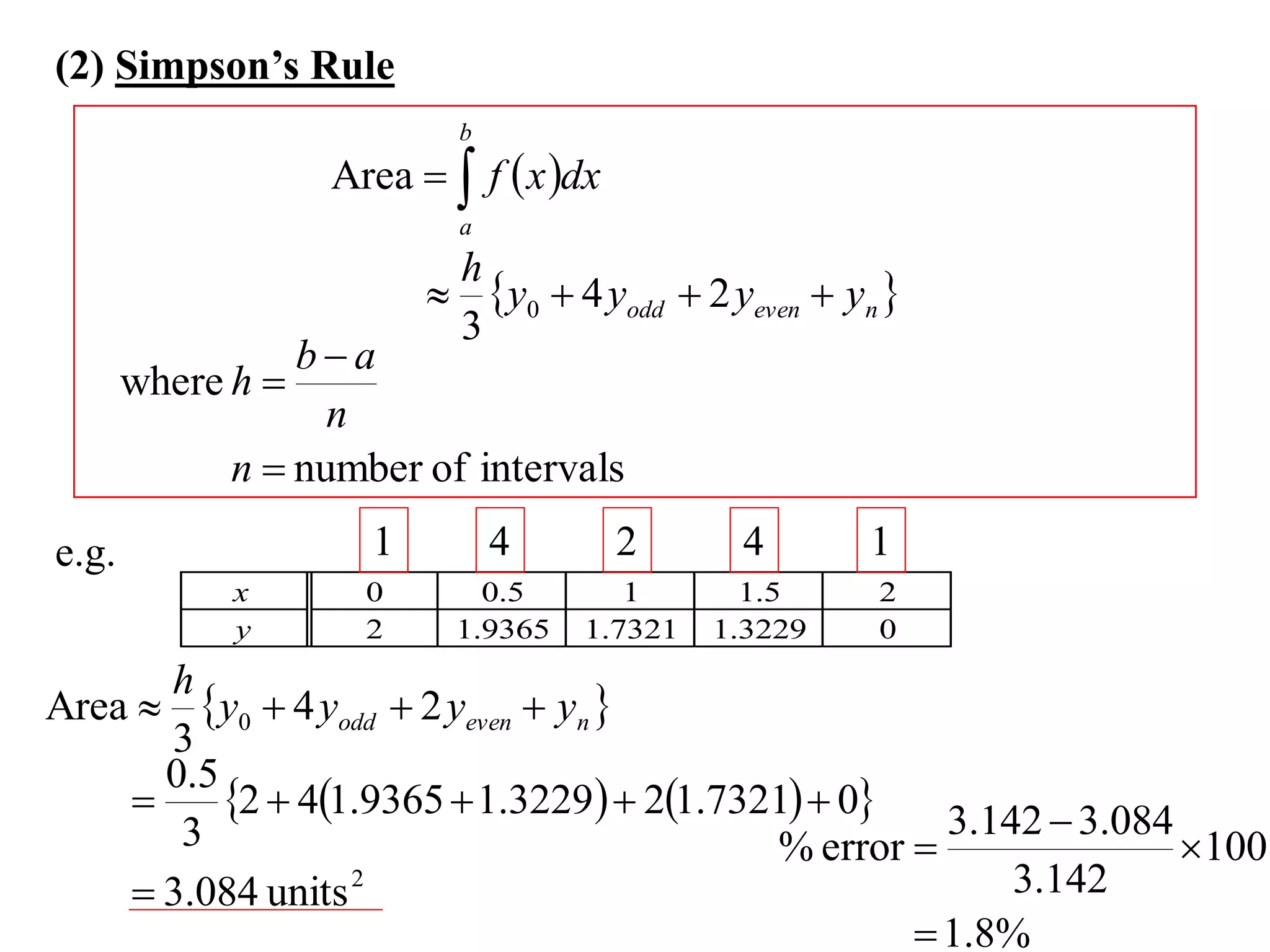
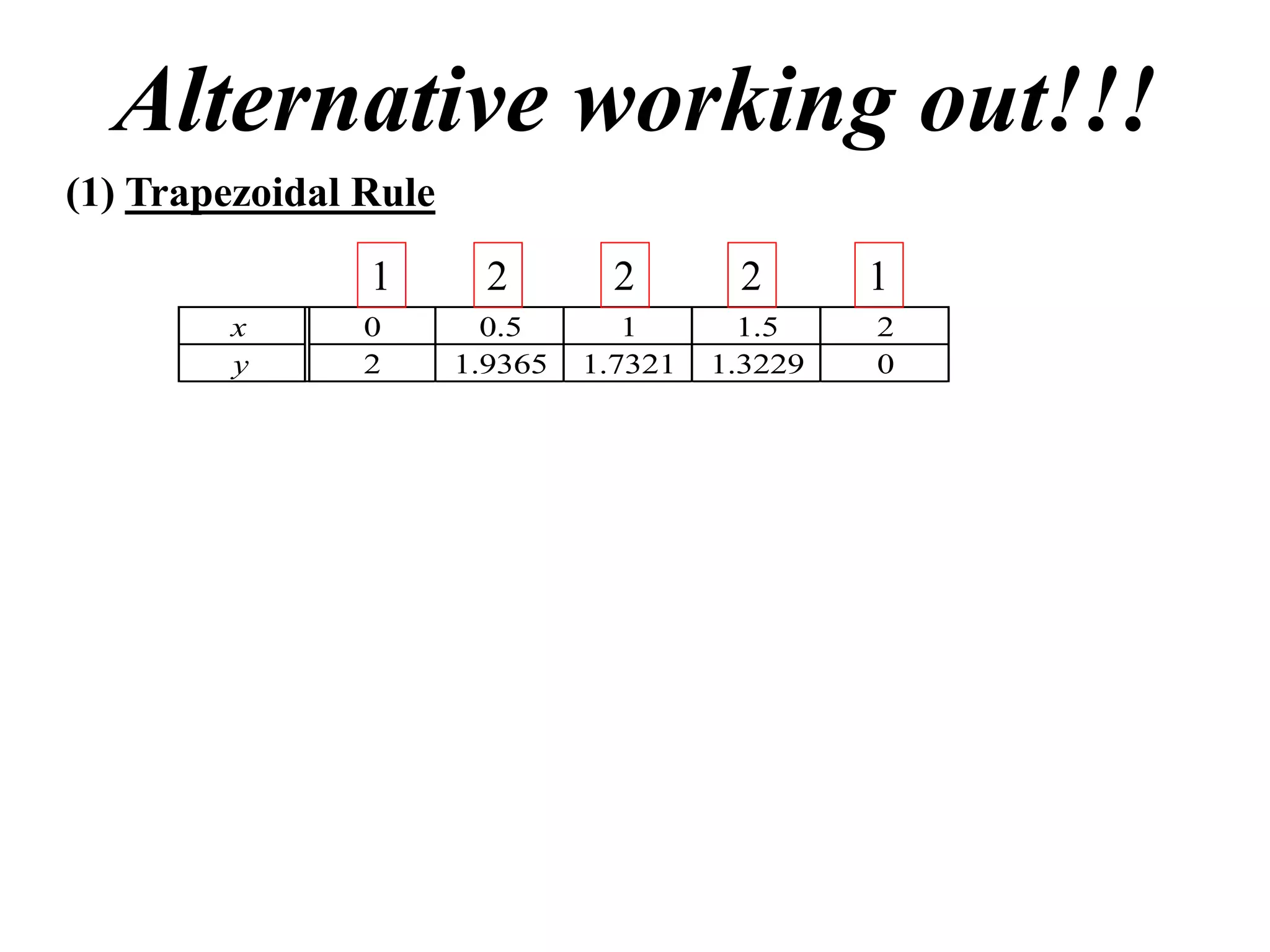
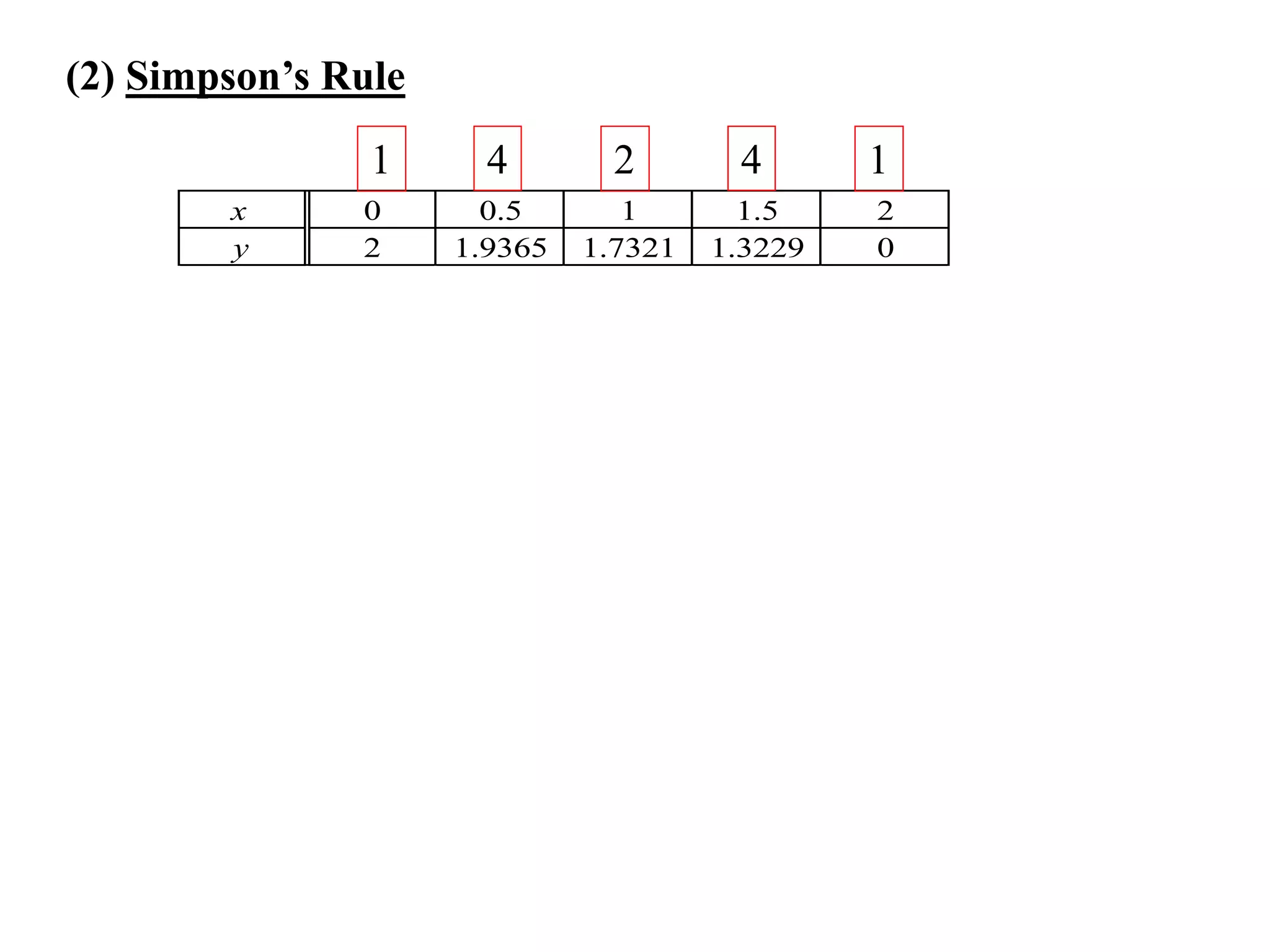
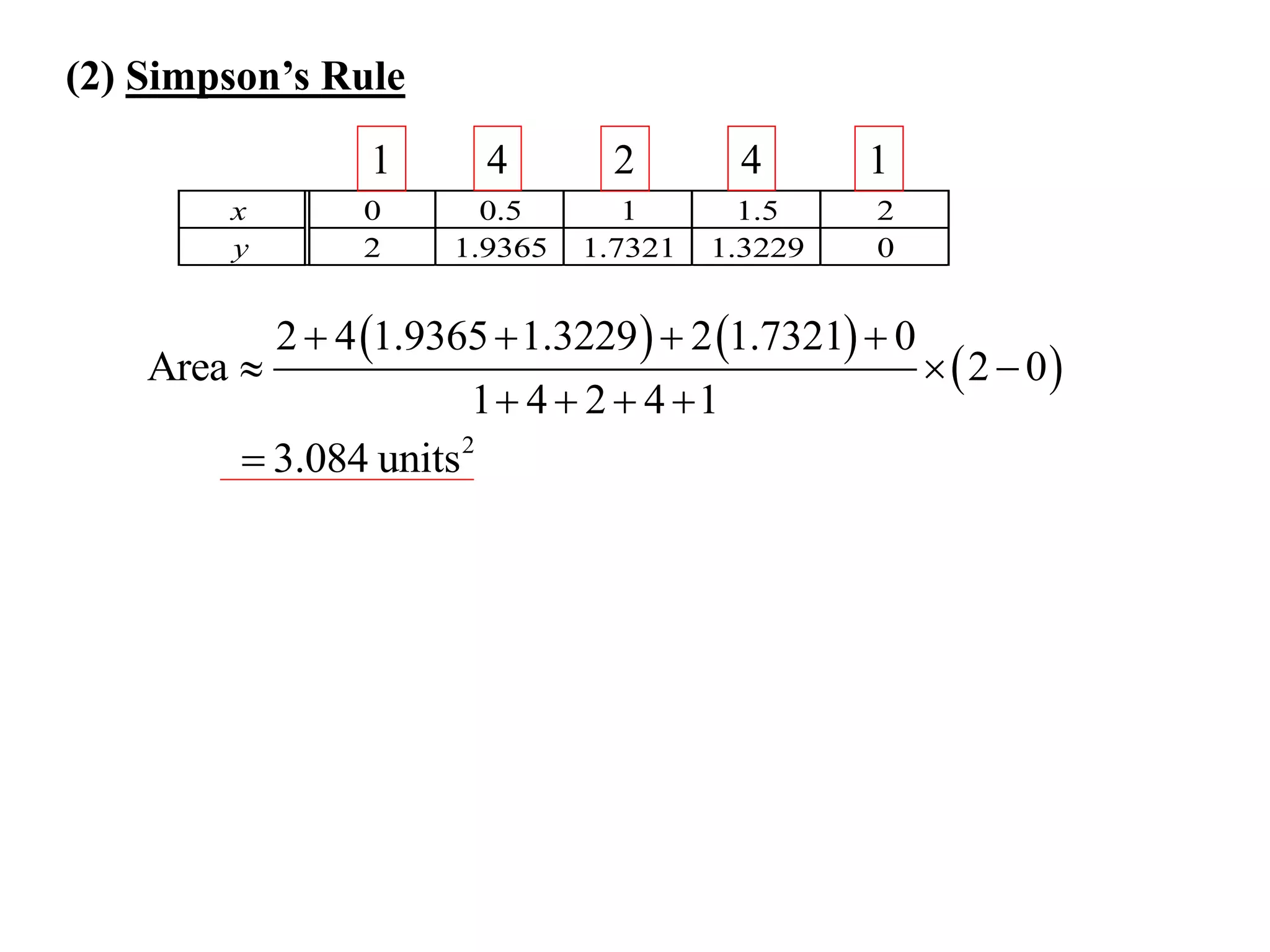
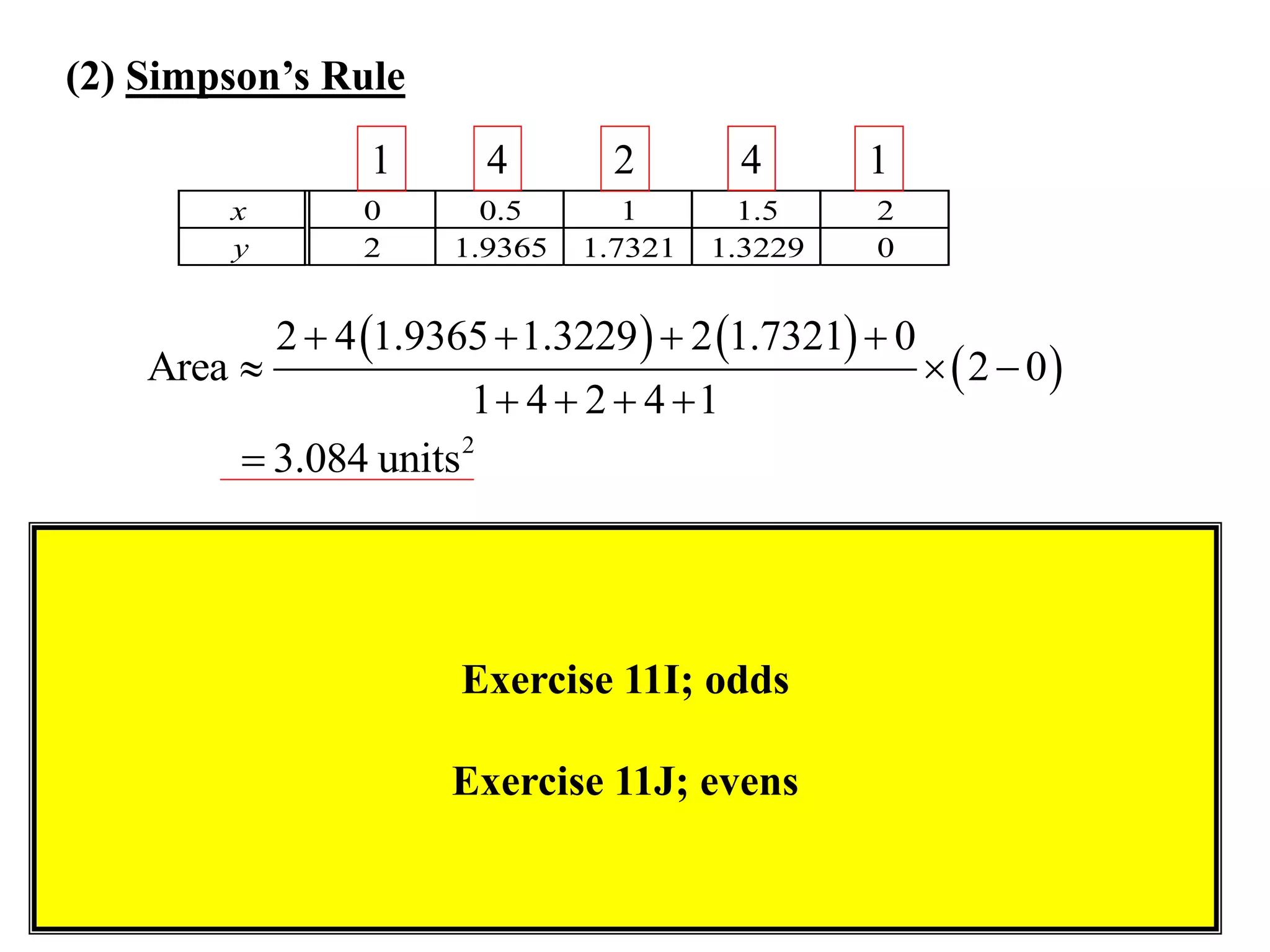
The document discusses approximations of areas under curves using the trapezoidal rule. It introduces the trapezoidal rule formula and shows how it can be used to approximate areas with multiple intervals by summing the areas of individual trapezoids. In general, the area is approximated as the average of the initial and final y-values plus twice the sum of the other y-values, divided by two. An example demonstrates applying the rule to approximate the area under a curve between 0 and 2 using 4 intervals.