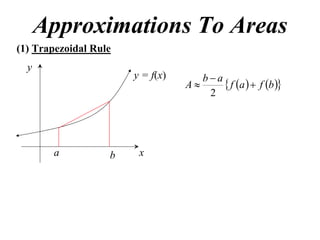
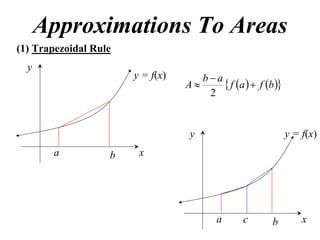
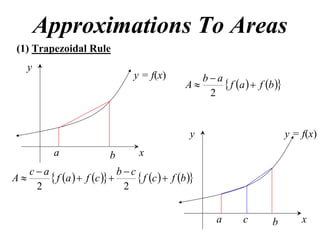
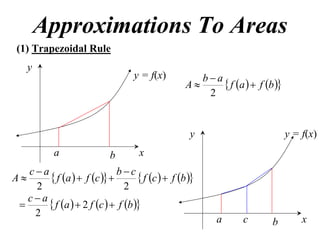
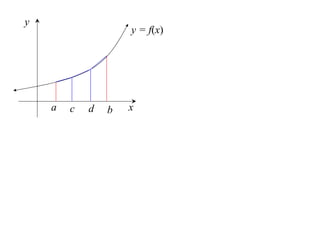
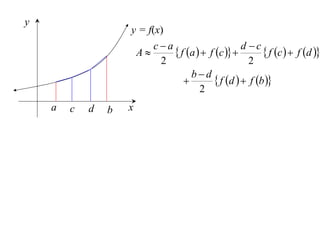
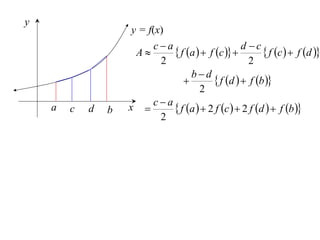
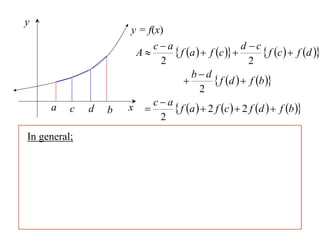
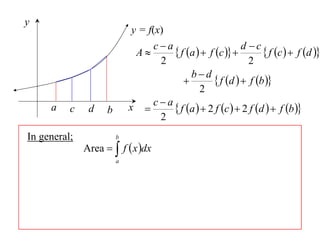
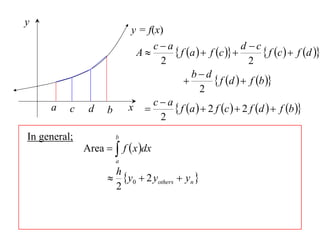
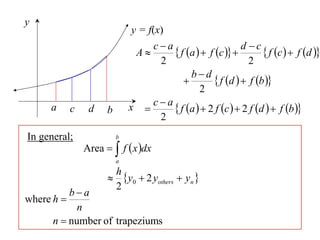
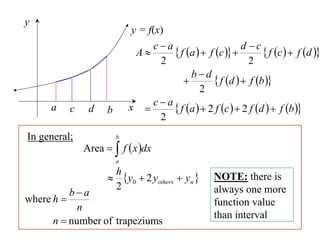
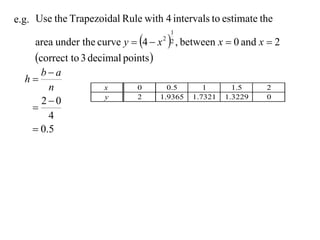
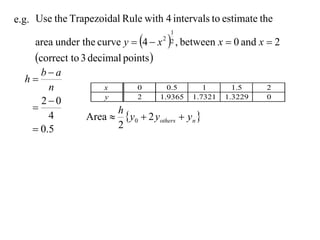
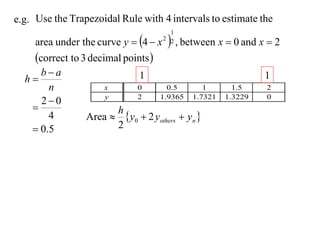
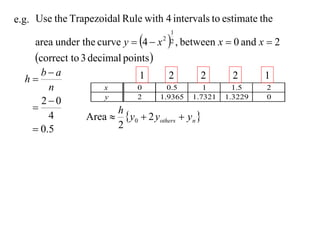
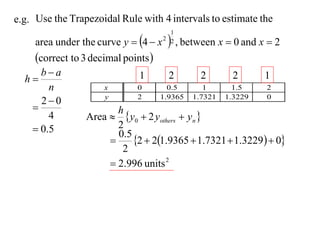
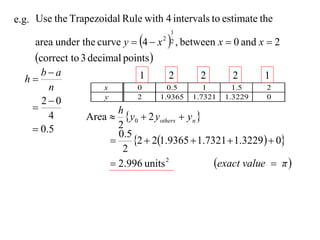
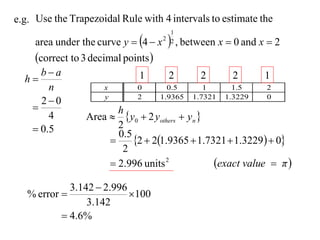
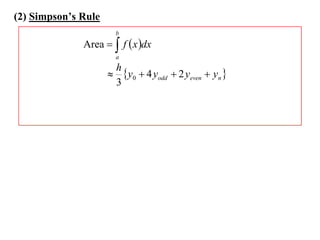
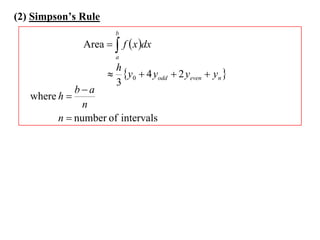
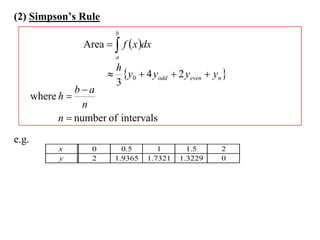
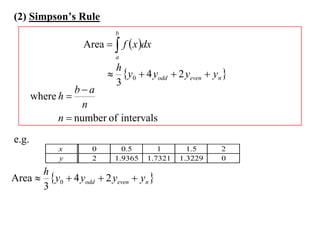
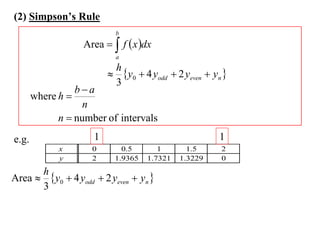
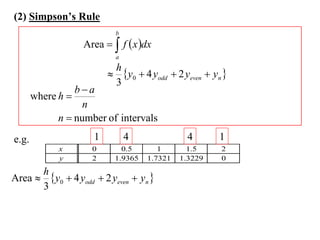
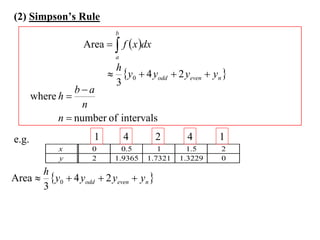
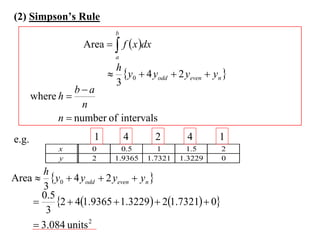
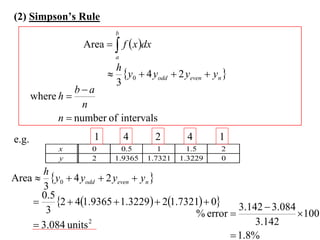
The document describes the trapezoidal rule for approximating the area under a curve. The trapezoidal rule works by dividing the area into trapezoid sections and summing their individual areas. In general, the area is approximated as the average of the initial and final y-values plus twice the sum of the internal y-values, divided by the number of sections. An example applies this to estimate the area under a given curve divided into 4 intervals.