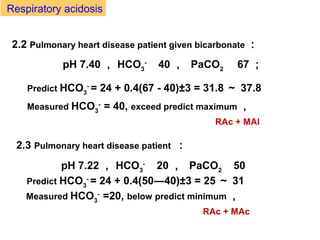
The document discusses acid-base balance and disturbances, detailing concepts related to respiratory and metabolic acidosis and alkalosis. It covers causes, compensation mechanisms, blood gas changes, and effects on the organism, with specific examples and treatment principles for each condition. The document also includes guidelines for diagnosing acid-base disturbances based on pH changes and historical patient data.










![H+
Loss ↑ from the stomach : bad vomiting and/or
gastric suction
H+
Loss ↑ from the
kidneys
Long term use of diuretics:
primary or secondary
hyperaldosteronism
Cushing Syndrome
(↑ cortisol →↑ glucocorticoid
[similar to ADS])
Hypokalemia: H+
exchanged into cells
ADS↑:
1) Acids
too little
Metabolic alkalosis
Ammonia (NH3) poisoning during hepatic failure
NH3 + H+
→ NH4
+](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/03acidbasedisturbanceptii-150710124843-lva1-app6892/85/03-acid-basedisturbance_ptii-12-320.jpg)









![§6. Principles of prevention and treatment :
1) Saline-responsive MAl
Saline (NaCl or KCl) infusion
2) Saline-resistant MAl
Carbonic anhydrase (CA) inhibitor
- Acetazolamide (diamox)
- Inhibits generation and secretion of H+
ADS inhibitor
- Spironolactone [ 螺内脂 ]
- Inhibits reabsorption of Na+
and H2CO3
+
Metabolic alkalosis](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/03acidbasedisturbanceptii-150710124843-lva1-app6892/85/03-acid-basedisturbance_ptii-22-320.jpg)











![Example :
A 45-year-old women was admitted to the local hospital with nausea,
vomiting, anorexia. She has suffered a 5-year history of hypertension
and a 3-year history of albuminuria. Doctor told her kidneys damaged
one year ago. Now edema and hypertension has been checked out. Her
laboratory results were as follows: pH 7.30 , PaCO2 20
mmHg , HCO3
–
9 mmol/ L , Na+
127 mmol/L , K+
6.7 mmol/L , Cl-
88
mmol/L , BUN 1.5g/L [0.09 – 0.2] 。
1 , Is there acid-base disorders?
2 , Why does PaCO2 decrease too ?
3 , Why her AG ↑ ?
[acids not eliminated from damaged kidneys]
4 , Is there any other acid-base disorders except metabolic
acidosis ?
Equation : predict PaCO2
= 1.5×[HCO3
-
] + 8±2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/03acidbasedisturbanceptii-150710124843-lva1-app6892/85/03-acid-basedisturbance_ptii-34-320.jpg)


