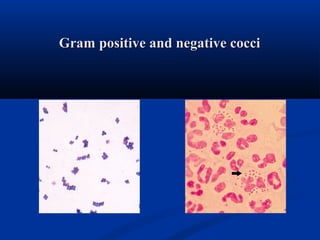
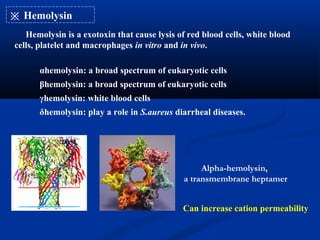
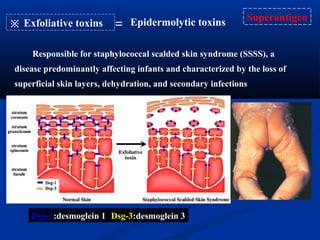
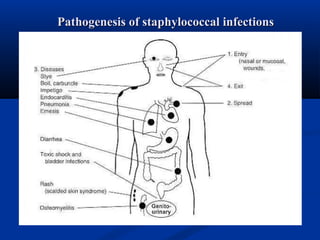
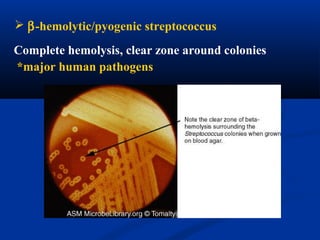
This document summarizes Gram positive cocci, focusing on Staphylococcus and Streptococcus. Staphylococcus is classified based on coagulase production. It is a facultative anaerobe that can cause skin infections and food poisoning through toxins like enterotoxins. Streptococcus is classified by hemolytic activity and cell wall antigens. It attaches to host cells using M protein and hyaluronidase. It produces invasive enzymes and exotoxins like pyrogenic toxins that allow it to spread. Both bacteria cause disease through various virulence factors including toxins, enzymes, and structural components.







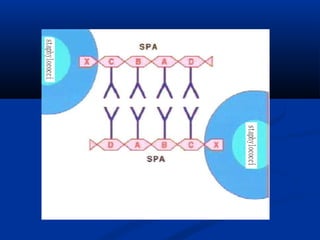
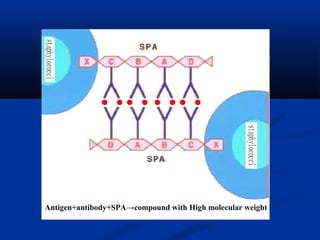








![Formation conditions of staphylococcal
enterotoxin
Mechanism of action :
▲ Acting on the gastrointestinal mucosa, result in
inflammatory changes such as congestion, edema,
erosion and metabolic disturbance of electrolyte
and eventually diarrhea.
▲ stimulate the visceral ['v sərəl] branch of the vagusɪ
nerve, and result in reflex vomiting](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/9-cocci-150727150845-lva1-app6891/85/9-cocci-27-320.jpg)
![Skin (local) infectionSkin (local) infection
※※ Furuncle:Furuncle:Protein A, Leukocidin, HemolysinProtein A, Leukocidin, Hemolysin
※※ Stye:Stye: lipaselipase
※※ Impetigo:Impetigo:contagiouscontagious
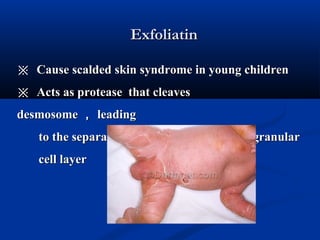
※※ Epidermal necrolysisEpidermal necrolysis
※※ Exfoliative Dermatitis:Exfoliative Dermatitis: Exfoliative toxinExfoliative toxin
※※ MastitisMastitis
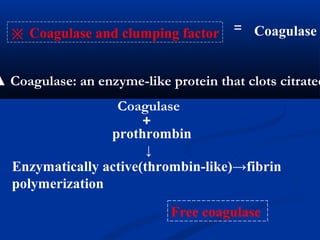
※※ Abscess (deep tissue); granulation:Abscess (deep tissue); granulation: coagulase, hyaluronidasecoagulase, hyaluronidase
(burn, wound)(burn, wound)
Systemic infectionSystemic infection
Bactermia (from abscess, wound, burn)Bactermia (from abscess, wound, burn) ,, Osteomyelitis (tibiaOsteomyelitis (tibia
['t biə])ɪ['t biə])ɪ ,, PneumoniaPneumonia
Clinical findings
Invasive infections](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/9-cocci-150727150845-lva1-app6891/85/9-cocci-29-320.jpg)



![Toxic shock syndrome toxin 1Toxic shock syndrome toxin 1
※※ Cause toxic shockCause toxic shock
◆◆ Tampon['tæmp n]ɑːTampon['tæmp n]ɑː 止血棉塞止血棉塞–– usingusing
menstruating womenmenstruating women
◆◆ Individuals with wound infectionIndividuals with wound infection
◆◆ Patients with nasal packing used to stop bleedingPatients with nasal packing used to stop bleeding
from the nosefrom the nose
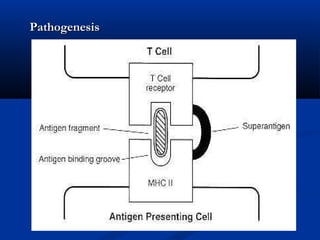
※※ SuperantigenSuperantigen](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/9-cocci-150727150845-lva1-app6891/85/9-cocci-33-320.jpg)





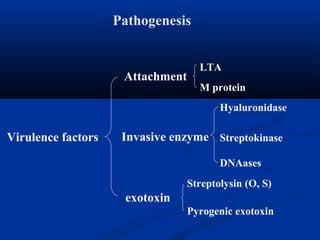
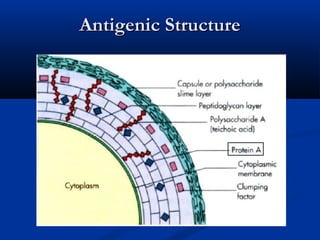
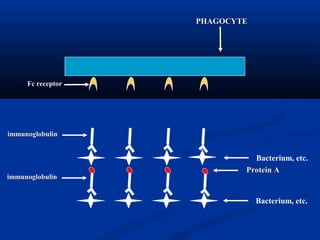
![(1) Attachment: Surface structure
* LTA (lipoteichoic acid) : Adhere to sensitive cell
* M-protein :
◆ Anti-phagocytotic
◆ Common antigen -- heart muscle cell, glomerular basement membrane
cells, etc.
◆ M Ag-Ab complex: type Ⅲ hypersensitivity
Such as: poststreptococcal acute glomerulonephritis, rheumatic fever,
rheumatic heart disease.
There is common antigenicity between M protein and Myocardial
cells, glomerular [ 'l mrj lə] basement membrane cells, so theɡ ɒ ʊ
antibody just against M protein can also combine with these cells,
activate complements and result type Ⅱ hypersensitivity](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/9-cocci-150727150845-lva1-app6891/85/9-cocci-44-320.jpg)
![▲ Hyaluronidase :
Destroy the polysaccharide (hyaluronic acid) that holds animal cells
together, making it easier for the pathogen to spread through the tissues of
the host organism.
(2) Invasive enzyme
▲ Streptokinase (SK) = fibrinolysin [ fa brə'n l s n]ˌ ɪ ɒ ɪ ɪ
▲ Streptodornase (SD):
an enzyme produced by hemolytic streptococci that catalyzes the
depolymerization of deoxyribonucleic [di ksi ra bə nu 'kli k] acidːˌɒ ː ɪ ʊ ː ːɪ
(DNA).
a protein secreted by several species of streptococci which can bind
and activate human plasminogen [plæz'm nəd ən]ɪ ʒ 血浆酶原
plasminogen Streptokinase plasmin digest
Fibrin and other proteins
Spreading factorSpreading factor](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/9-cocci-150727150845-lva1-app6891/85/9-cocci-45-320.jpg)


![Pathogenesis of S. pyogenes infections.
[ er 's p l s]ˌ ə ɪ ə ə](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/9-cocci-150727150845-lva1-app6891/85/9-cocci-48-320.jpg)


![Scarlet fever is characterized by:
▲ Sore throat
▲ Fever
▲ Bright red tongue with a "strawberry" appearance
▲ Forchheimer spots (fleeting small, red spots on the soft palate) may occur
▲ spares the face (although some circumoral [ s kəm'o rəl] pallorˌ ɜː ʊ 口周苍
白 is characteristic)
▲ Characteristic rash:
△ fine, red and rough-textured
△ blanches upon pressure
△ Pastia lines (where the rash runs together in the armpits and groin)
appear and can persist after the rash is gone.
Strawberry tongue
Pastia lines 帕斯蒂亚](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/9-cocci-150727150845-lva1-app6891/85/9-cocci-51-320.jpg)
![(1) acute glomerulonephritis ( group A)
[glə merj lə nef'ra t s]ʊ ʊ ʊ ɪ ɪ
(2) Rheumatic fever
(3) rheumatic heart disease
poststerptococcal diseases (hypersensitive disease)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/9-cocci-150727150845-lva1-app6891/85/9-cocci-52-320.jpg)

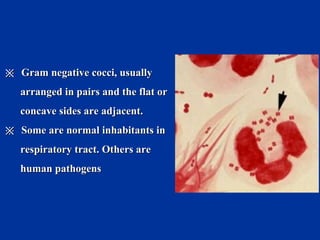






![▲ Porin proteins (Por) : form porins and mediate
resistance to neutrophil and serum killing, allow
intracellular survival of the bacteria[ also called
protein I].
▲ Opacity proteins (Opa) : associated with opaque
colonies; an outer membrane protein functioning
in attachment to host cells[ also called protein Ⅱ].
▲ Reduction-modifiable proteins (Rmp) : stimulates
antibodies that block serum bactericidal
activity [also called protein Ⅲ].
※※ Outer membrane proteins (OMPs):Outer membrane proteins (OMPs):](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/9-cocci-150727150845-lva1-app6891/85/9-cocci-62-320.jpg)

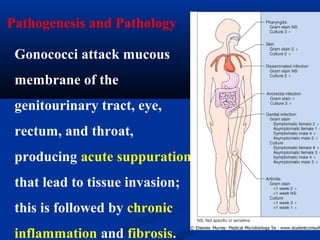

![※ Gonorrhea (sexually transmitted disease STD)
in male: acute urethritis
in female: pelvic inflammatory
※ Ophthalmia [ f'θælm ə]ɒ ɪ
neonatorum [ni næ't r m]ːɒ ɔː ʌ →blindness](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/9-cocci-150727150845-lva1-app6891/85/9-cocci-66-320.jpg)
![Symptoms
1. Male: urethritis with yellow, creamy pus and
painful urination. The process may extend to
the epididymis [ epə'd dəm s]ˌ ɪ ɪ .
As suppuration subsides in untreated
infection, fibrosis occurs, sometimes leading to
urethral strictures (sterility).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/9-cocci-150727150845-lva1-app6891/85/9-cocci-67-320.jpg)
![2. Female: infection starts from the endocervix, and
results in vagina discharge, dysuria, and abdominal
pain. Uterine ['ju təra n]ː ɪ tubes may be involved,
causing salpingitis , fibrosis, and obliteration of the
tubes (20% may become infertile). When
gonococcal cervicitis is either asymptomatic or
unrecognized, the patient may progress to pelvic
inflammatory disease (PID).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/9-cocci-150727150845-lva1-app6891/85/9-cocci-68-320.jpg)

![4. Gonococcal bacteremia (1-3% of infected women
and much lower percent of infected men) can lead
to fever, pustular rash over the extremities,
tenosynovitis [ teno s nə'va t s]ˌ ʊˌ ɪ ɪ ɪ 腱鞘炎 and
suppurative arthritis.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/9-cocci-150727150845-lva1-app6891/85/9-cocci-70-320.jpg)

![Prevention and treatment
Penicillin, Spectinomycin 奇霉素 ,
Ceftriaxone[seftra' æksn]ɪ 头孢三嗪 , and so on
※ Treatment
△ neonatorum ophthalmia - silver nitrate
△ Strengthen health education and prohibit dirty sex
△ No vaccine
※ Prevention](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/9-cocci-150727150845-lva1-app6891/85/9-cocci-72-320.jpg)
![Infection rate can be reduced by:
1. avoiding multiple sexual partners;
2. early diagnosis and treatment;
3. finding cases and contacts through education
and screening of population at high risk.
4. combined with doxycycline 强力霉素 or azithromycin
[e z θrə'ma s n]ɪ ɪ ɪ ɪ 阿奇霉素 for dual infections with
Chlamydia
※ Prevention](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/9-cocci-150727150845-lva1-app6891/85/9-cocci-73-320.jpg)





![2. Pathogenesis:2. Pathogenesis:
Epidemic cerebrospinal meningitisEpidemic cerebrospinal meningitis
Clinical typing: common, outbreak, septicemic typeClinical typing: common, outbreak, septicemic type
(1) Organisms(1) Organisms →→ attach to epithelial cells of nasoparynxnasoparynx with the aid of
pili ( nasopharyngeal infection : asymptomatic , most are carriers,( nasopharyngeal infection : asymptomatic , most are carriers,
only 2~3% go to next stage )only 2~3% go to next stage )
(2) Blood stream <fever, skin ecchymosis[ ekə'mo s s] >ˌ ʊ ɪ(2) Blood stream <fever, skin ecchymosis[ ekə'mo s s] >ˌ ʊ ɪ →→cross the braincross the brain
barrier <severe headache ,vomitting, stiff neck > (meningococcemia.barrier <severe headache ,vomitting, stiff neck > (meningococcemia.
bacteremia or septicemia. blood contain cocci )bacteremia or septicemia. blood contain cocci )
(3) Meninges [mə'n nd i z] (meningitis. meninges pyogenic inflammation.ɪ ʒ ː(3) Meninges [mə'n nd i z] (meningitis. meninges pyogenic inflammation.ɪ ʒ ː
spinal fluid contain cocci )spinal fluid contain cocci )
Clinical cause: 3 stagesClinical cause: 3 stages](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/9-cocci-150727150845-lva1-app6891/85/9-cocci-79-320.jpg)
![※※ Immunity:Immunity:
Group-specific antibody(subclinicalGroup-specific antibody(subclinical and
symptomaticsymptomatic infection).infection).
※※ Prevention and treatmentPrevention and treatment
1. Polysaccharide vaccine (group A, C)1. Polysaccharide vaccine (group A, C)
2. Penicillin; cefotaxime [sefə 'tæksa m]ʊ ɪ2. Penicillin; cefotaxime [sefə 'tæksa m]ʊ ɪ
头孢噻肟头孢噻肟 ; chloramphenicol; chloramphenicol](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/9-cocci-150727150845-lva1-app6891/85/9-cocci-80-320.jpg)

