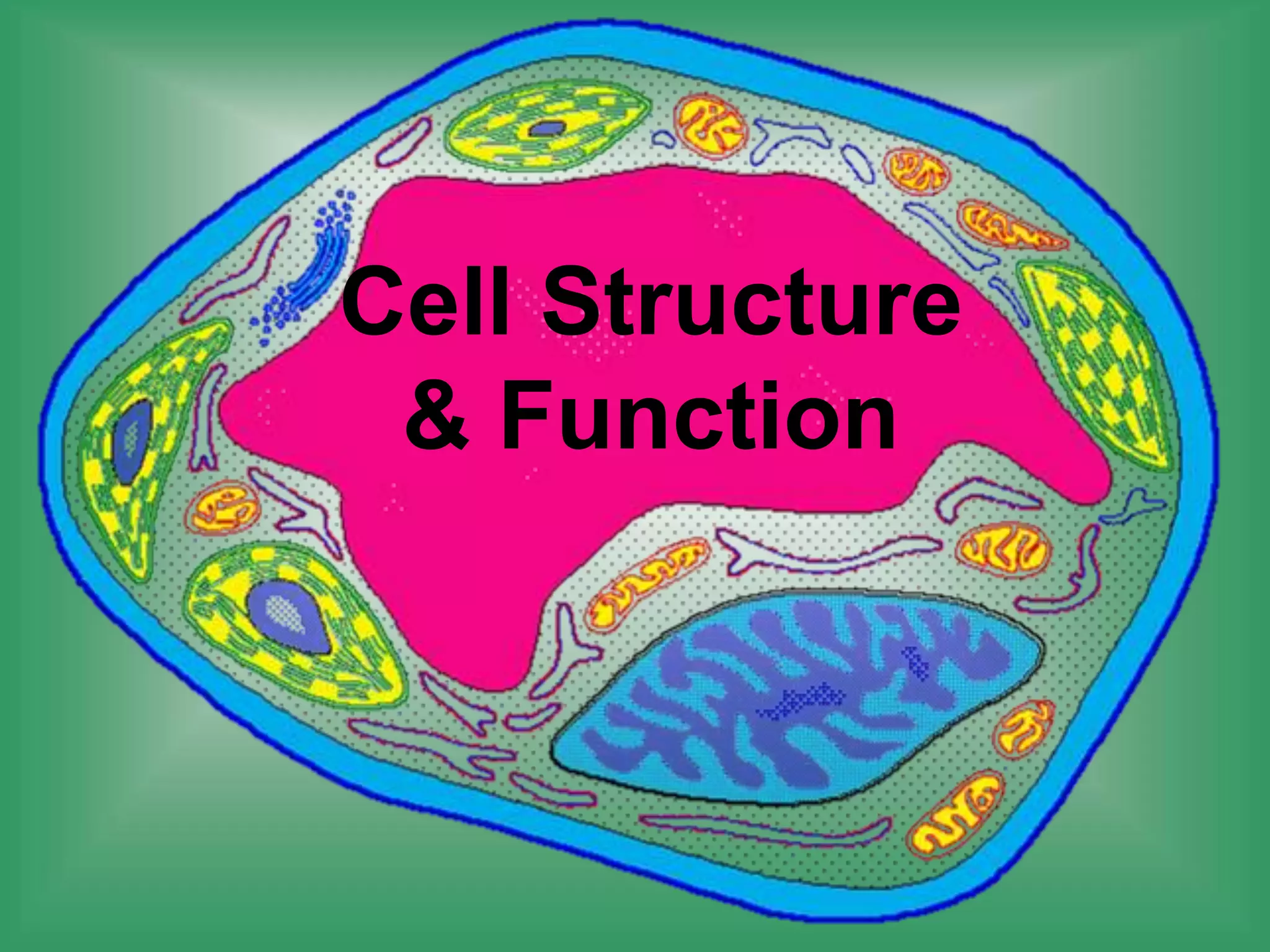
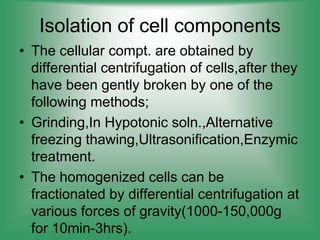
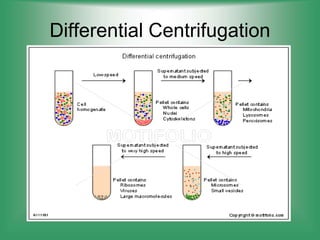
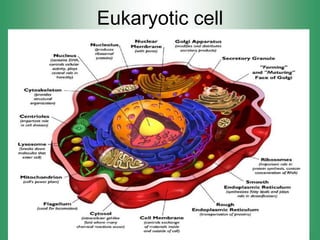
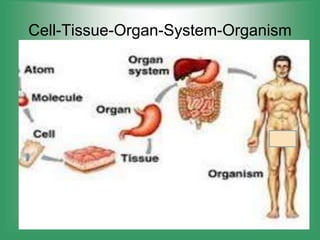
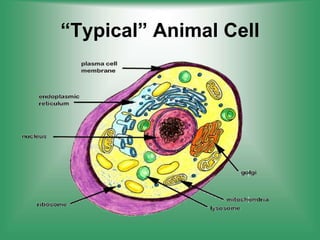
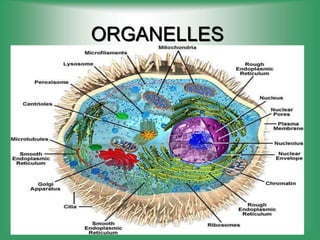
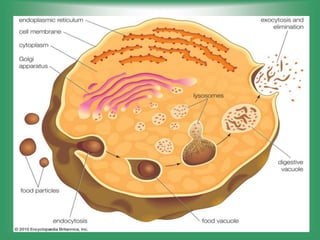
Here are the main parts of the cell labeled:
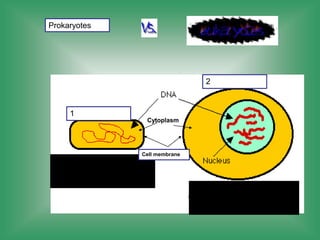
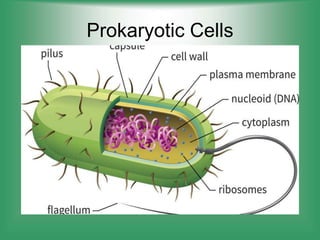
1. Cell membrane - The outer boundary of the cell that regulates what enters and exits.
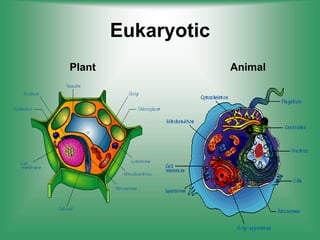
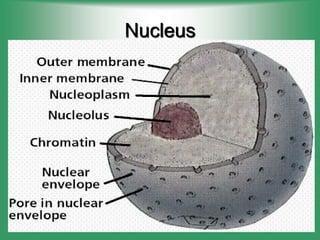
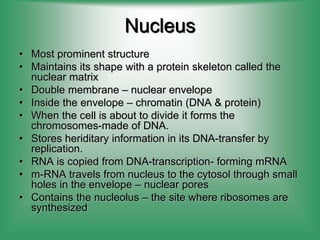
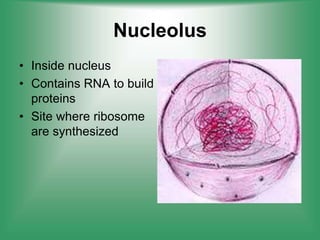
2. Nucleus - Contains genetic material (DNA) and directs cell activities.
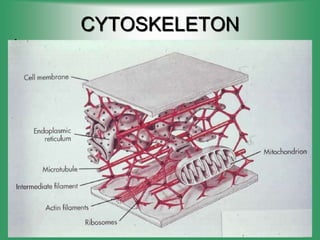
3. Cytoplasm - Jelly-like material inside the cell that contains organelles and allows cell processes.
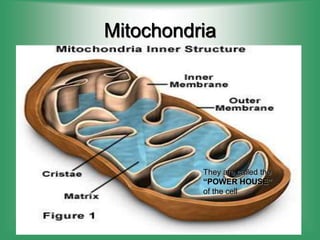
4. Mitochondria - Produces energy (ATP) for cell activities through cellular respiration.
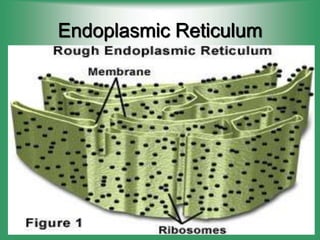
5. Endoplasmic reticulum - Modifies and transports molecules within the cell.
6. Golgi apparatus - Modifies and packages proteins and lipids for export from the cell.
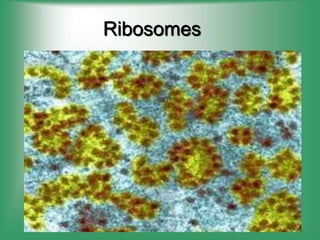
7. Ribosomes - Site of protein synthesis using