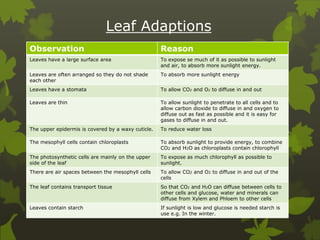
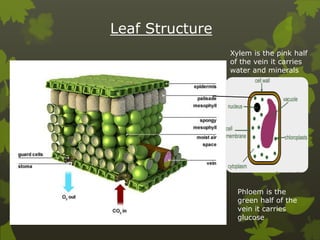
Plants undergo photosynthesis, a process where sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water are converted into glucose and oxygen. Chlorophyll in the leaf absorbs sunlight, which is then used along with carbon dioxide from the air and water from the soil to produce glucose and oxygen through a chemical reaction. The glucose is used for plant growth and any excess is stored as starch. Minerals absorbed from the soil like nitrogen, potassium, and magnesium are also required to support plant growth and production of chlorophyll. Leaves are adapted for efficient photosynthesis through features like a large surface area, thinness to allow for gas exchange, and specialized cells containing chloroplasts where the reaction occurs.