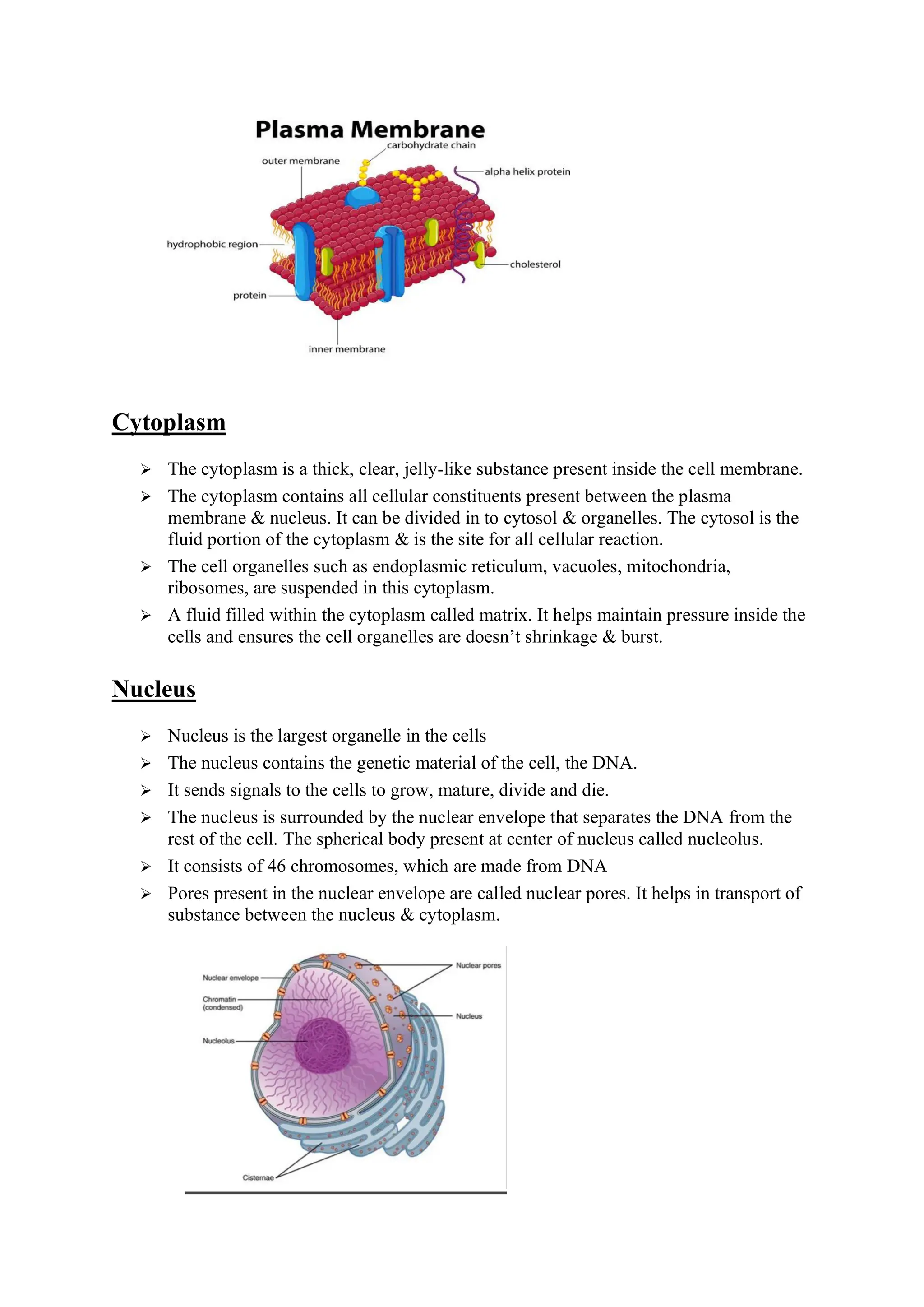
Cells are the basic unit of life and come in two main types - prokaryotic and eukaryotic. Prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus and are smaller, while eukaryotic cells have a nucleus enclosed in a nuclear envelope and are generally larger. All cells contain a cell membrane, cytoplasm, and various organelles that carry out specific functions necessary for life. Key organelles include mitochondria that generate energy, ribosomes for protein synthesis, the endoplasmic reticulum for transport, Golgi bodies for processing and packaging molecules, lysosomes for digestion, and a cytoskeleton for structural support and movement within the cell.