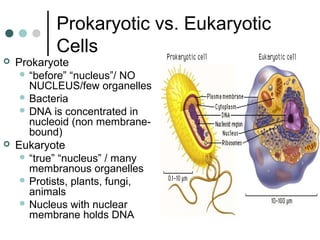
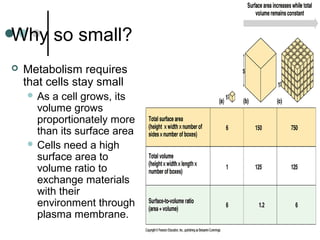
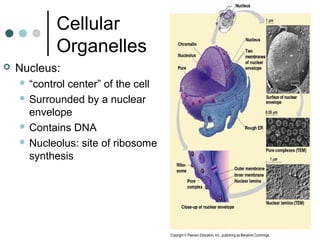
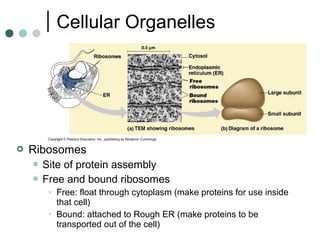
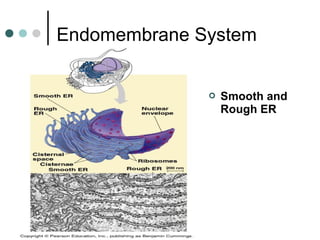
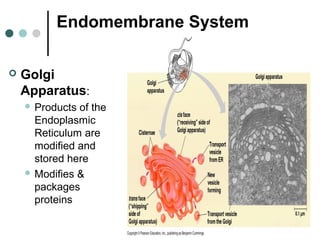
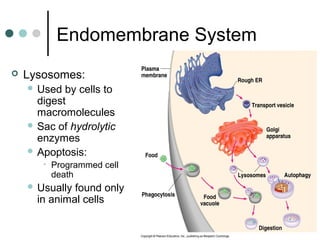
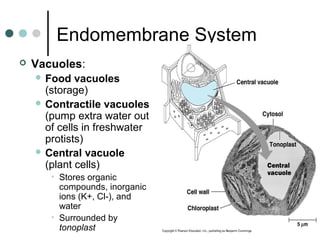
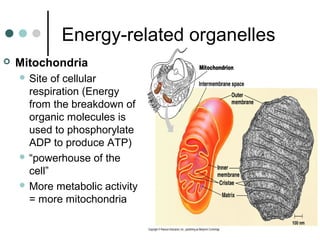
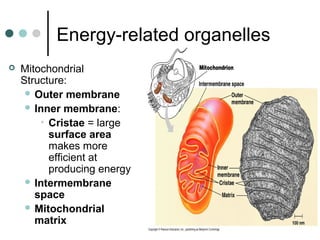
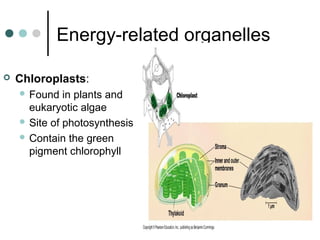
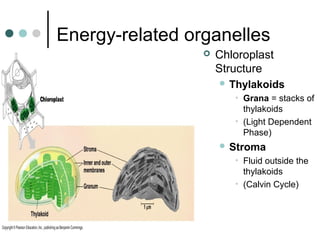
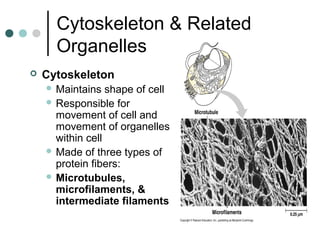
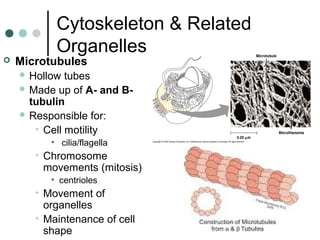
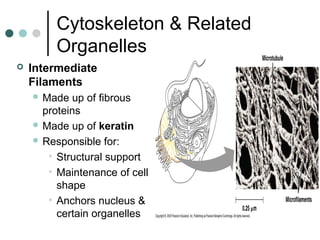
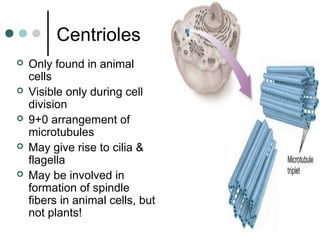
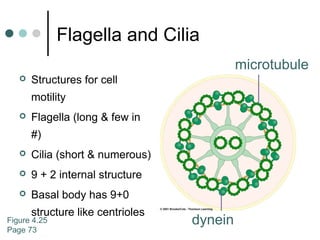
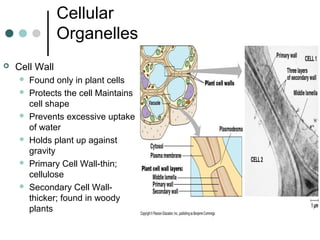
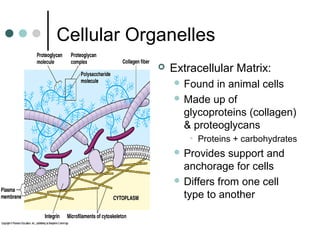
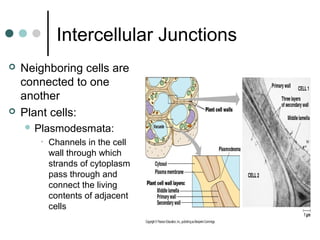
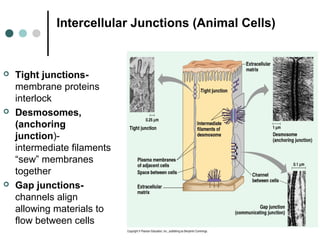
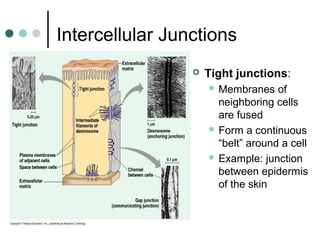
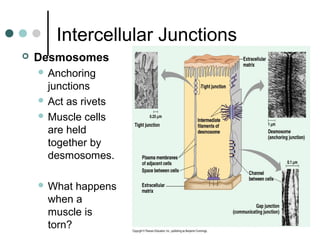
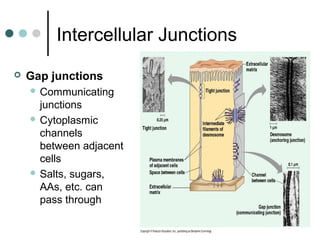
Eukaryotic cells have organelles that compartmentalize functions. Key organelles include the nucleus, which contains DNA; mitochondria and chloroplasts, which generate energy; and the endomembrane system of ER, Golgi, and vesicles, which modifies and transports proteins. The cytoskeleton, including microtubules, microfilaments, and intermediate filaments, maintains cell shape and enables movement. Plant cells have additional structures like cell walls and plasmodesmata between cells.