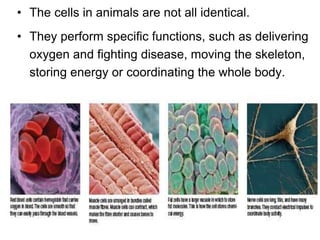
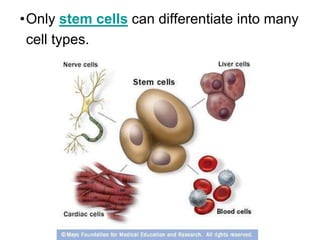
The document discusses specialized cells in the human body. It notes that while the human body contains 50-75 trillion cells total, only 220 of those cells are specialized to perform specific functions. Some examples of specialized cells include heart cells, nerve cells, blood cells, sperm cells, and more. The document explains that specialized cells have unique shapes, sizes, and features that allow each cell type to perform its designated job accurately. Both animal and plant cells contain specialized cell types tailored to their specific functions.