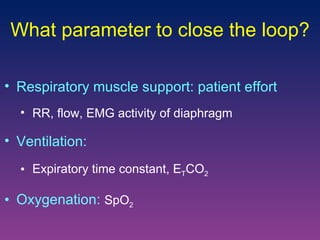
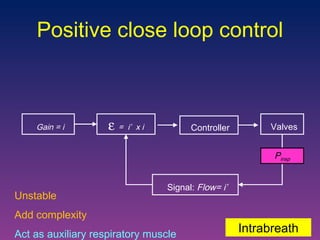
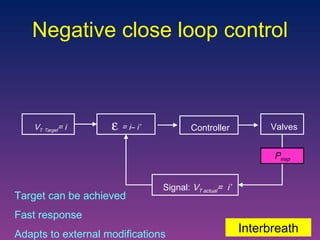
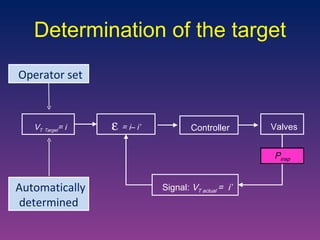
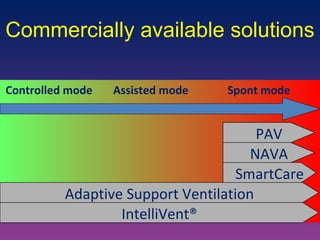
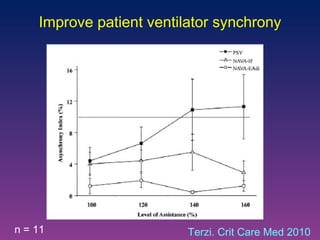
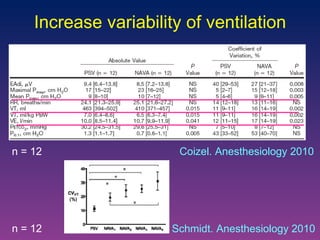
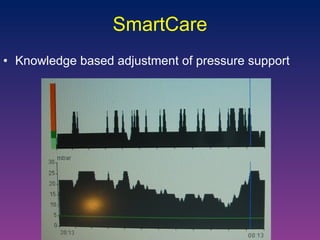
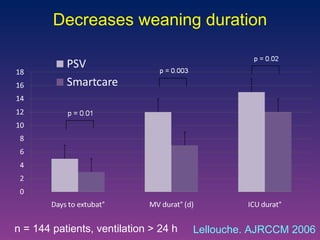
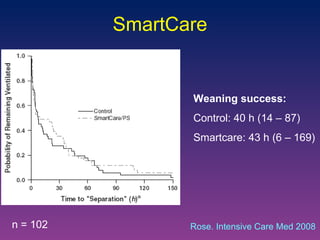
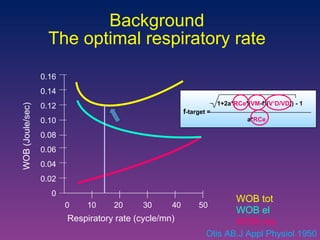
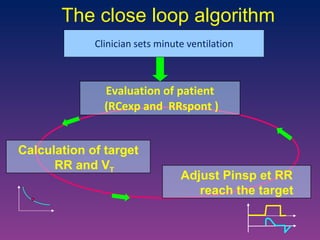
The document discusses closed-loop ventilation in intensive care units. It defines closed-loop ventilation as using automated adjustments to certain ventilator settings based on monitored patient parameters. Potential parameters for closed-loop control include respiratory muscle support, ventilation, and oxygenation. Both positive and negative closed-loop control are described. Commercially available closed-loop solutions aim to improve patient-ventilator synchrony, decrease workload, and reduce weaning duration. While offering advantages, closed-loop ventilation also presents technical and implementation challenges that require further study.
![Dr Jean-Michel Arnal Intensive Care Unit. Hôpital Font Pré Toulon France [email_address] Close loop ventilation in the ICU](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/closeloopventilation-110428090432-phpapp01/85/Close-loop-Ventilation-1-320.jpg)








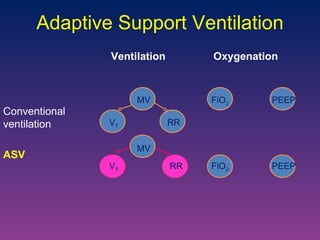
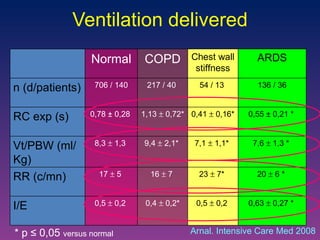
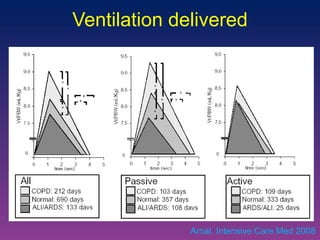
![ASV in ARDS patients Study on model reproducing 108 simulated scenario: ASV delivers around 6 mL/Kg PBW for most of cases Same plateau pressure than ARDSnet strategy Lower V T for the most severe cases with lower Pplat Clinical study on 51 ARDS patients: V T delivered are in line with recommendations Pplat was ≤ 28 cmH 2 O Sulemanji. Anesthesiology 2009 Arnal. AJRCCM 2007 [abstract]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/closeloopventilation-110428090432-phpapp01/85/Close-loop-Ventilation-25-320.jpg)
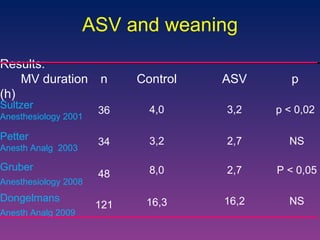
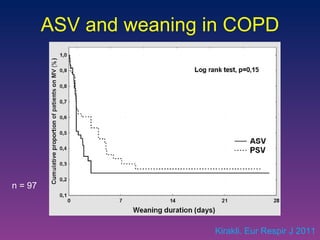

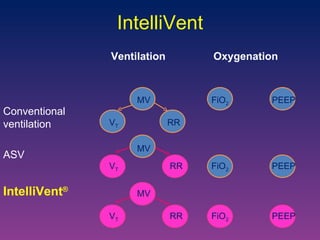
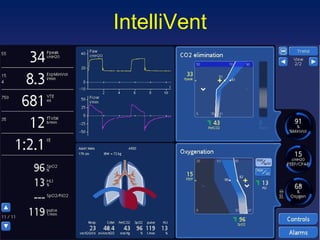

![Randomized control trial: Provide an automatic weaning in post cardiac surgery patients with less manipulations and more time spent in optimal ventilation zones than PS. Randomized cross-over study: Safe in ICU patients with less inspiratory pressure and V T than ASV with same gas exchanges. IntelliVent Arnal. Intensive Care Med 2010 [abstract] Lellouche. Intensive Care Med 2010 [abstract]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/closeloopventilation-110428090432-phpapp01/85/Close-loop-Ventilation-32-320.jpg)



