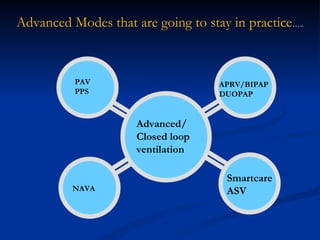
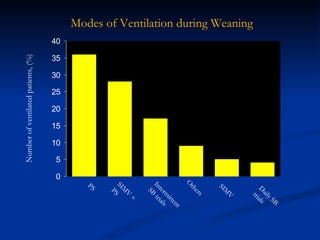
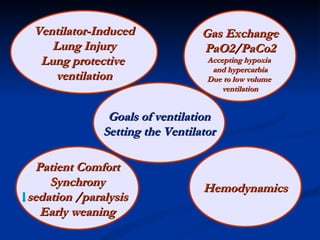
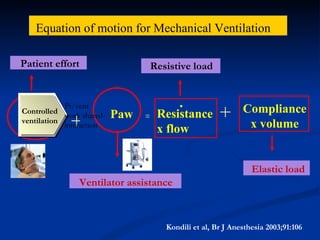
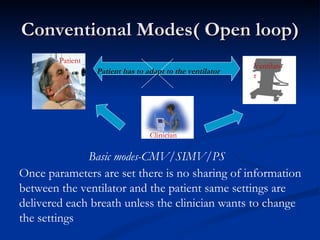
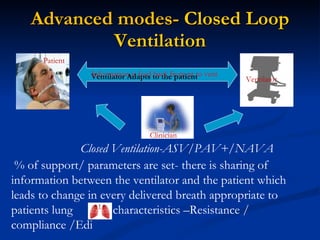
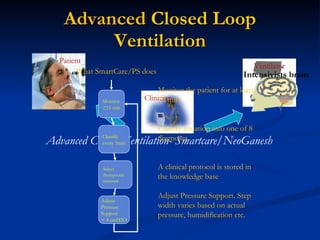
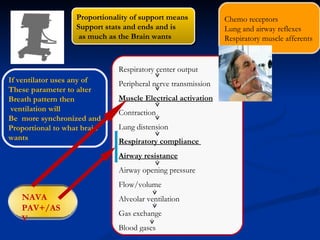
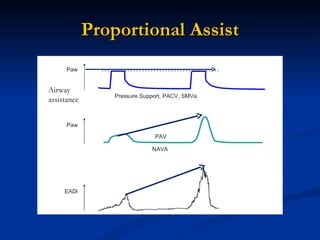
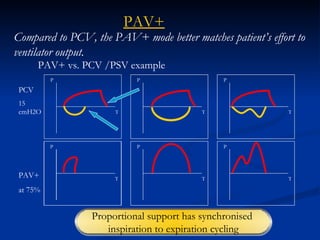
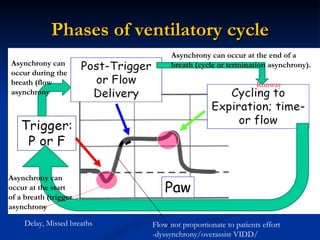
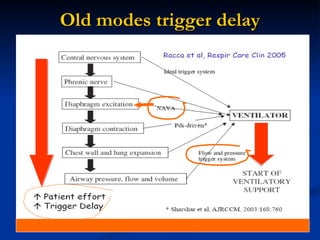
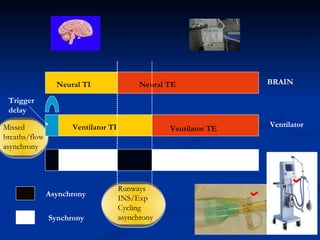
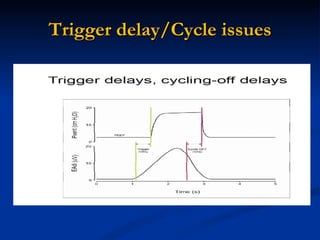
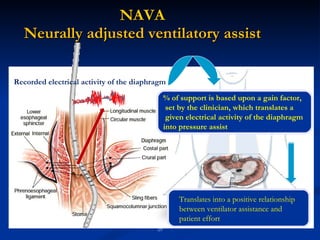
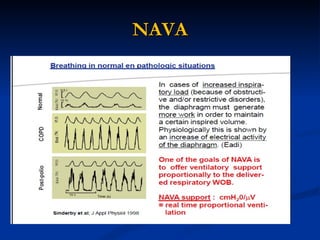
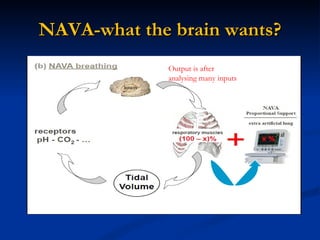
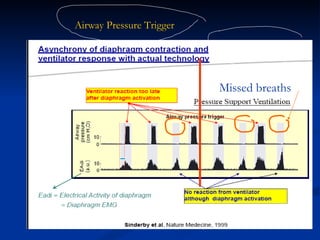
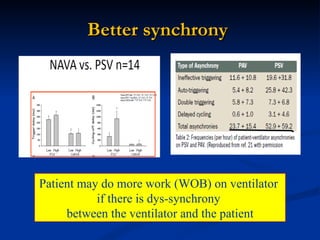
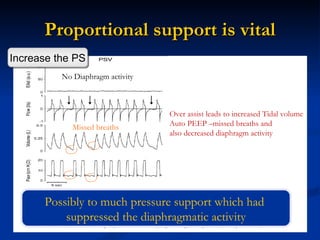
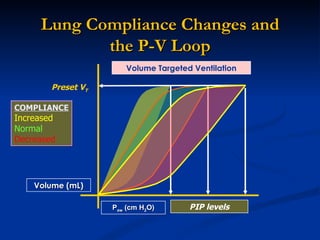
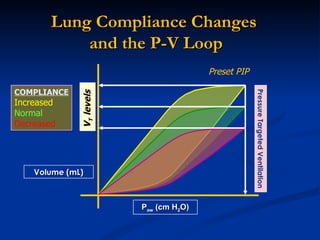
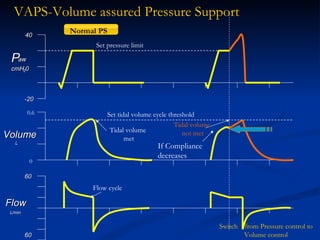
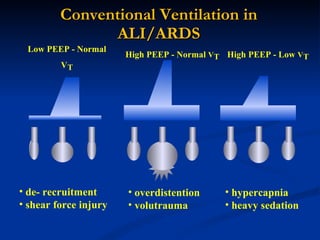
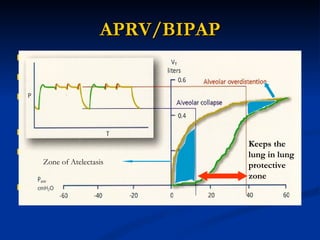
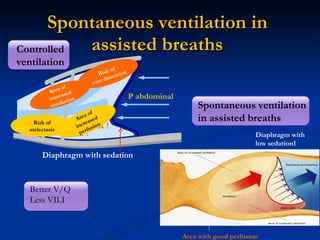
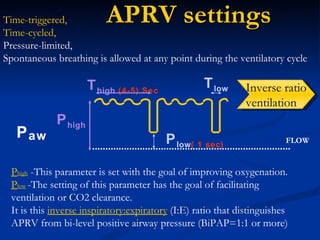
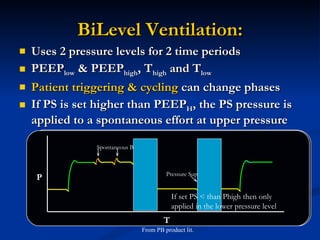
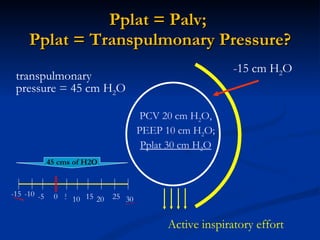
The document discusses advanced modes of mechanical ventilation. It begins by outlining newer modes such as VAPS, APRV/BIPAP, PAV+, Smartcare, and their benefits over basic modes. These advanced modes aim to improve synchrony between the patient and ventilator, reduce asynchrony issues, and make ventilation proportional to patient effort through feedback loops. The document argues that automated closed-loop ventilation is the future as it reduces workload and errors while allowing for quicker weaning and lower costs through greater ease of use and patient safety.