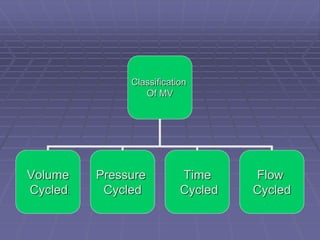
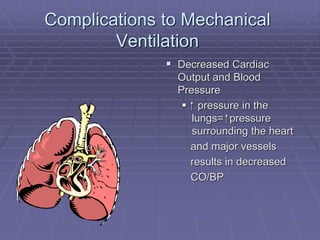
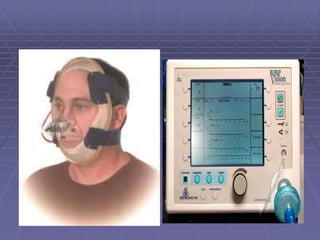
Mechanical ventilators generate a controlled flow of gas into a patient's airways using various modes of ventilation. There are both positive and negative pressure machines that can be either invasive or non-invasive. Modes include volume cycled, pressure cycled, time cycled, and flow cycled. Ventilators aim to provide oxygenation through settings like FIO2 and PEEP, and ventilation through tidal volume and respiratory rate. They are indicated for conditions causing respiratory failure and can have complications like lung injury, infection, and decreased blood pressure. Settings must be adjusted based on blood gas results and the patient's condition. Weaning involves gradually reducing support as the patient improves. Non-invasive ventilation