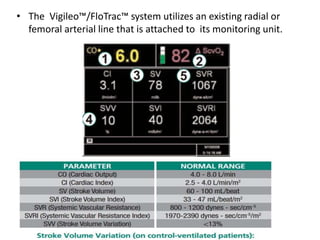
The document discusses the FloTrac system, which uses an existing arterial line to continuously monitor cardiac output (CO) and other hemodynamic values through advanced arterial waveform analysis. While the trends provided by FloTrac can be useful for estimating hemodynamic status, its specific CO and cardiac index values may not correlate exactly with pulmonary artery catheter measurements. FloTrac requires good arterial signal quality and its values could be affected by factors like arrhythmias, hemodynamic instability, or ventilator settings like PEEP. Clinical judgment is still needed to interpret the data from FloTrac.