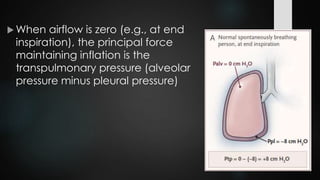
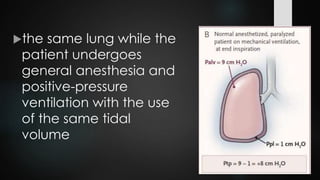
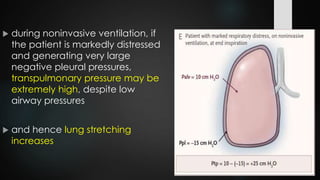
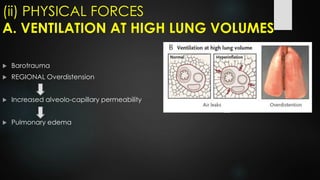
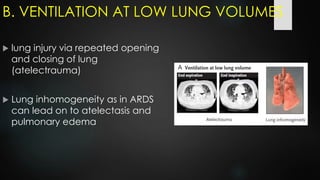
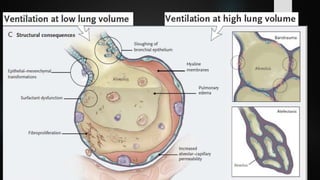
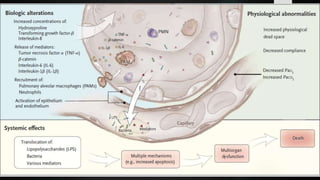
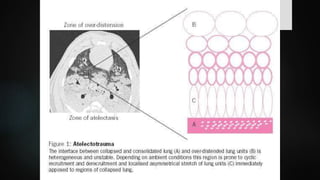
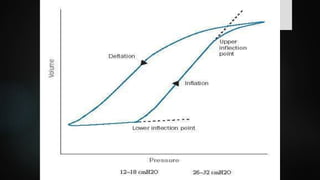
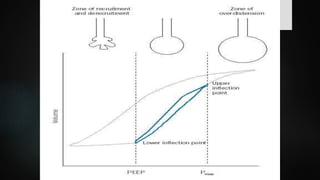
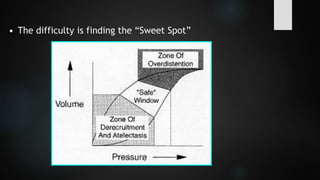
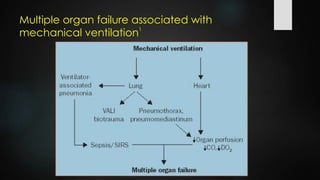
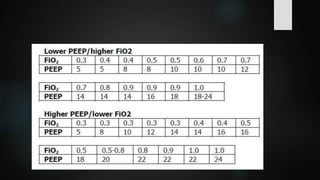
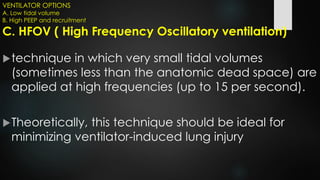
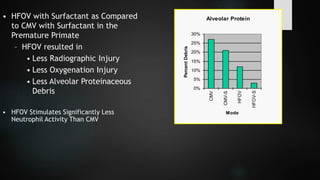
The document discusses ventilator-associated lung injury (VALI), which can result from mechanical ventilation and may occur in normal or previously injured lungs, particularly in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). Complications such as volutrauma, barotrauma, and biotrauma can lead to further lung injury, while various ventilation strategies like low tidal volume and high PEEP aim to minimize such damage. The importance of protective ventilation and adjunctive therapies, including neuromuscular blocking agents and prone positioning, is emphasized to improve patient outcomes.