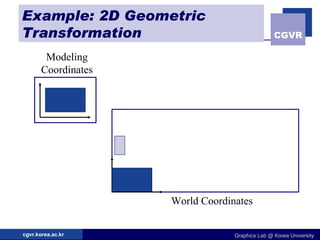
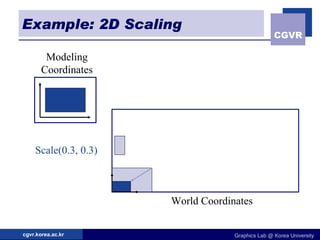
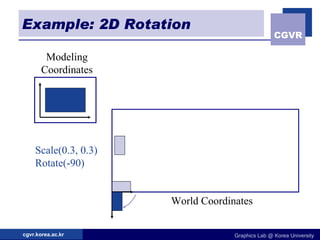
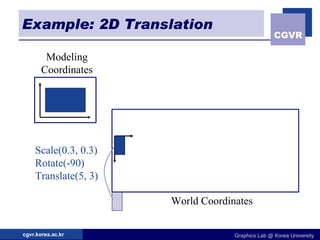
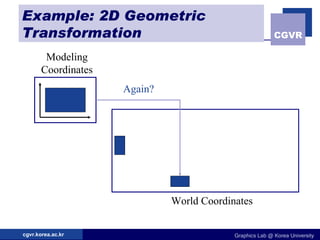
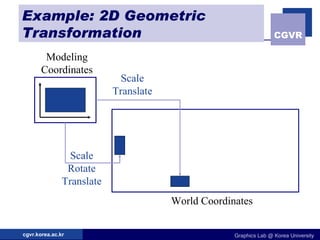
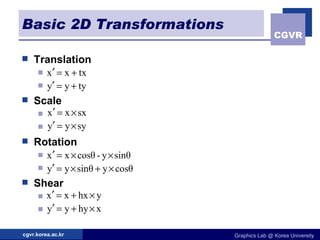
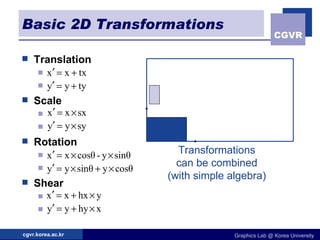
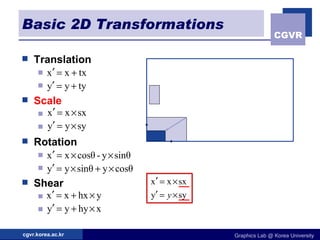
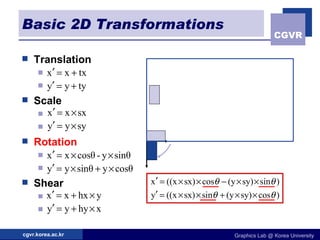
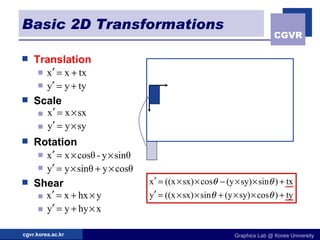
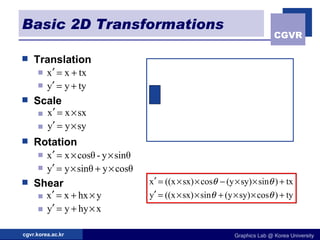
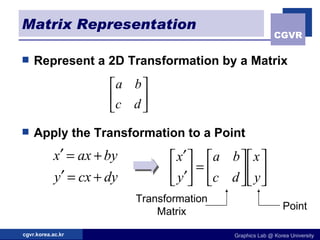
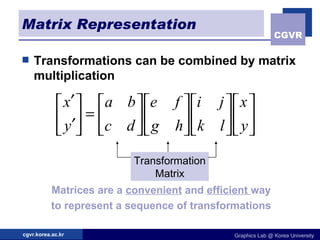
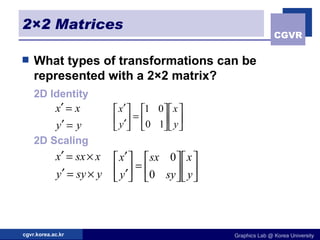
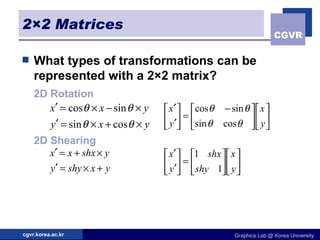
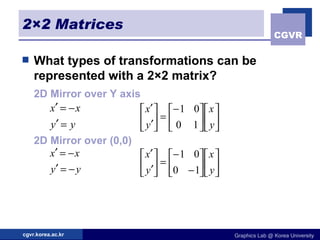
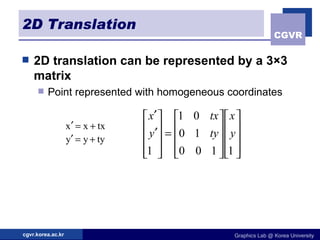
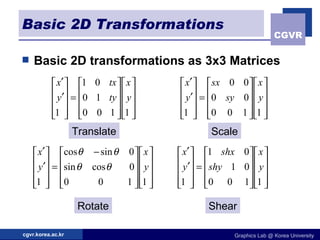
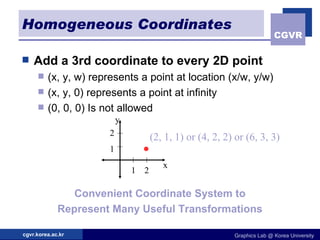
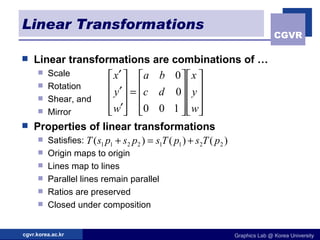
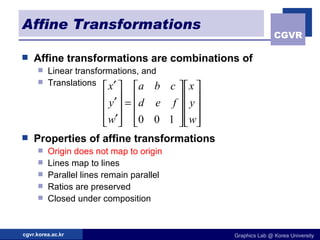
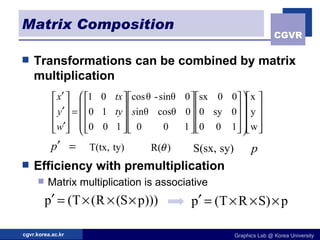
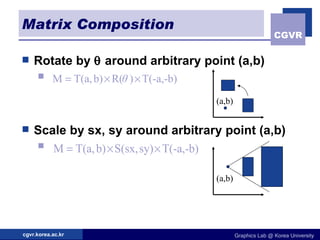
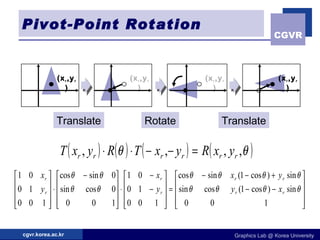
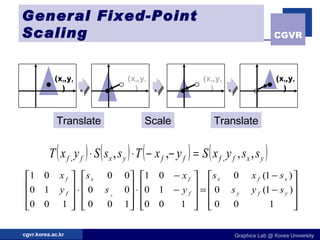
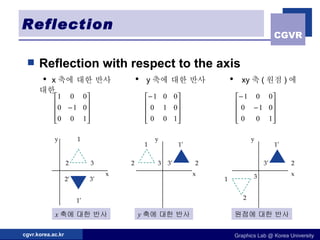
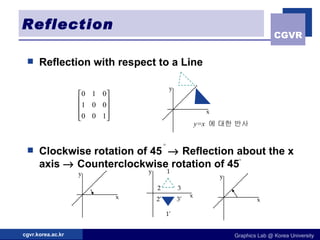
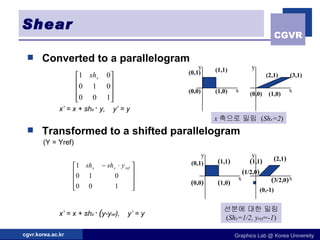
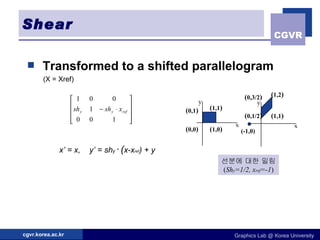
The document discusses 2D geometric transformations including translation, rotation, scaling, and their matrix representations. It explains that transformations can be combined through matrix multiplication and represented as sequences of transformations applied to modeling coordinates to obtain world coordinates. Basic transformations include translation, scaling, rotation, and shearing, which can be expressed as 3x3 matrices using homogeneous coordinates.