Embed presentation
Downloaded 25 times


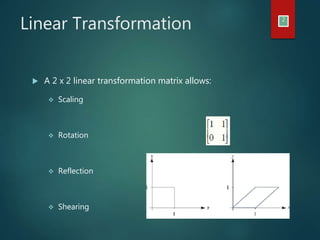


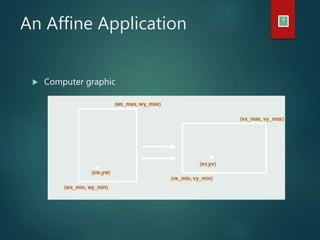



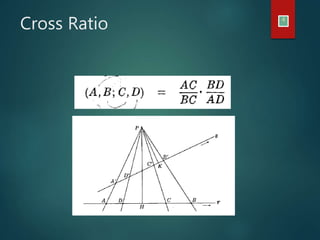

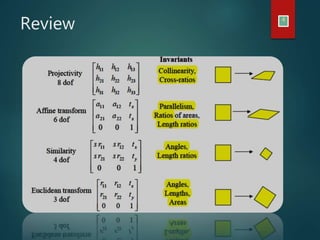


This document discusses different types of geometric transformations including linear transformations, affine transformations, and projective transformations. Linear transformations allow for scaling, rotation, reflection, and shearing using a 2x2 matrix. Affine transformations preserve parallel lines and proportional distances but not lengths and angles. Projective transformations describe how objects appear rather than how they are, distorting lengths, angles, and parallelism. Both affine and projective transformations are important applications in computer graphics and robot recognition.












