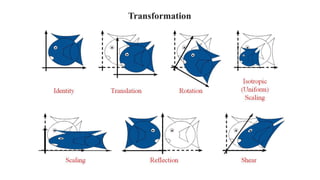
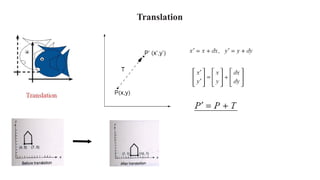
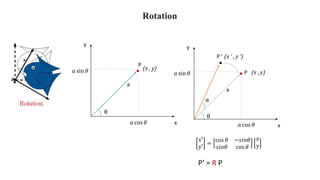
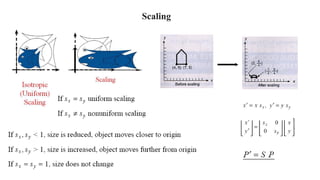
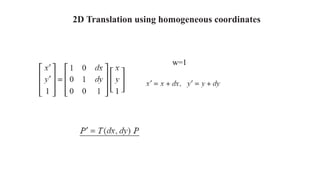
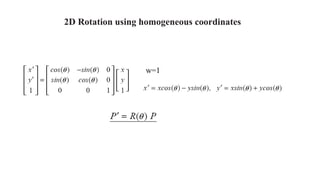
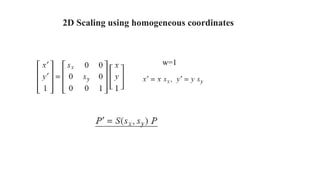
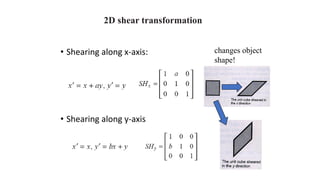
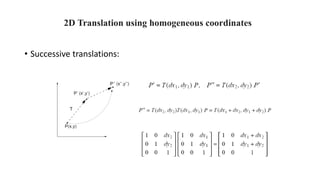
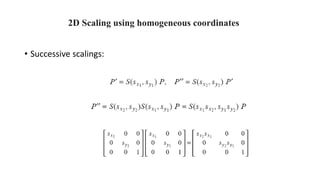
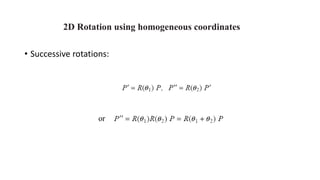
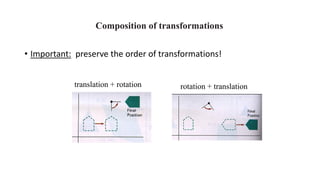
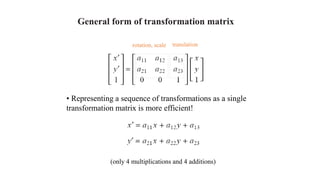
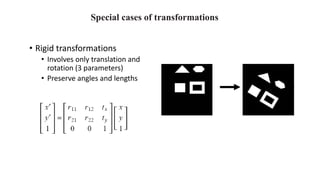
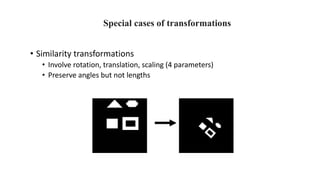
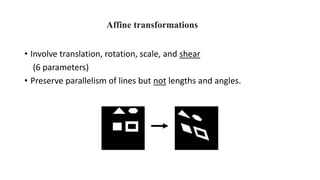
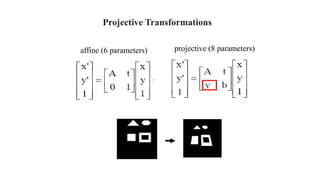
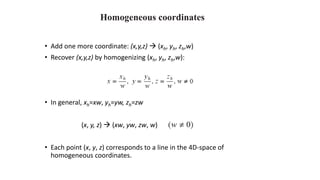
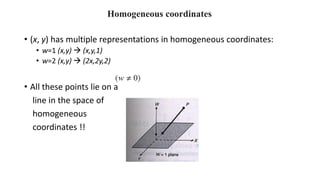
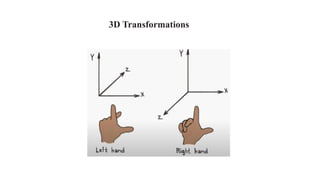
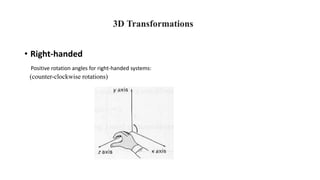
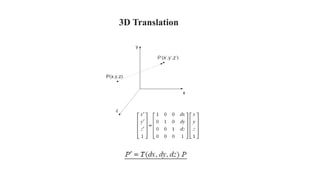
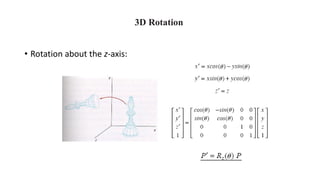
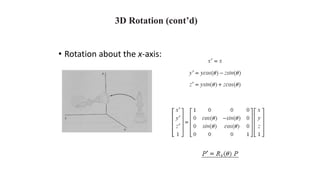
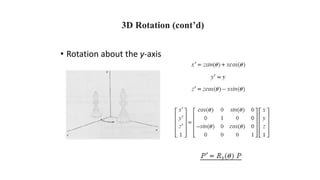
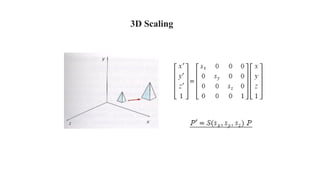
Geometric transformations change an object's position, orientation, or size. There are several types of 2D and 3D transformations, including translation, rotation, scaling, shearing, and their composition. Transformations can be represented using transformation matrices in homogeneous coordinates, where each point corresponds to a line. Special cases include rigid, similarity, and affine transformations that preserve certain properties like angles, lengths, and parallelism.