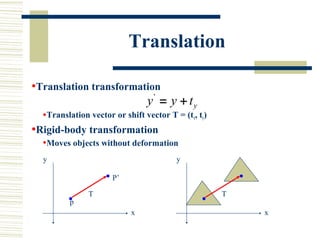
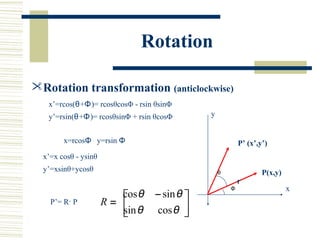
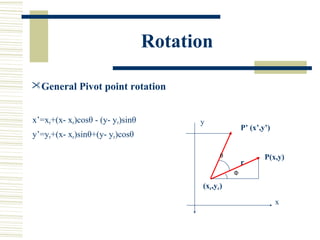
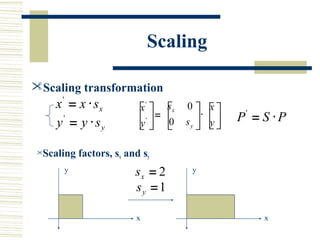
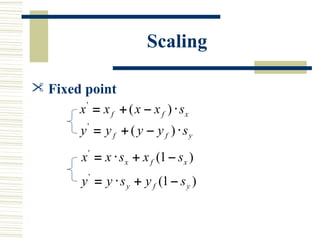
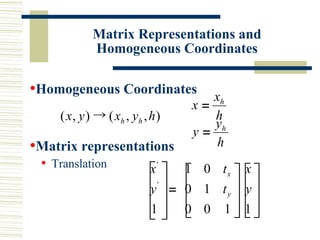
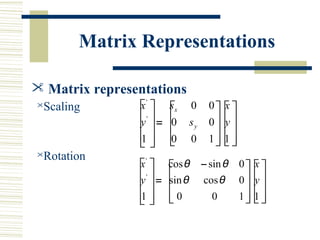
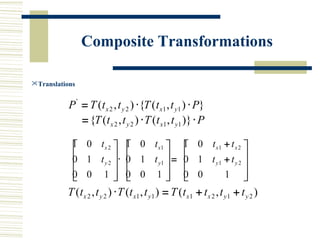
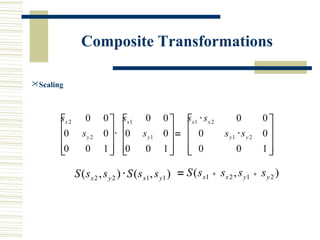
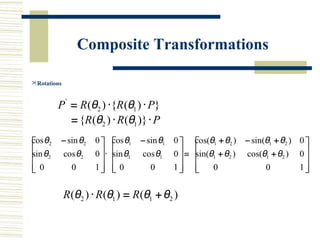
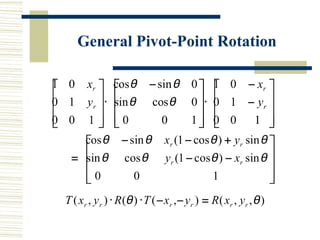
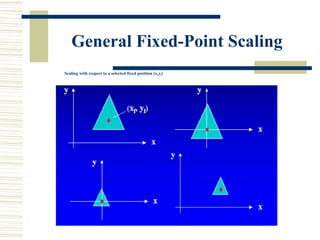
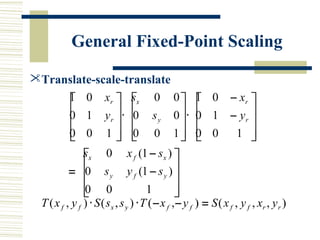
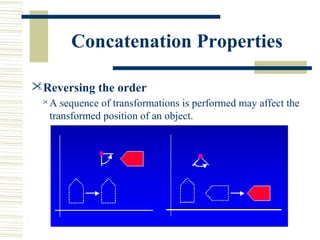
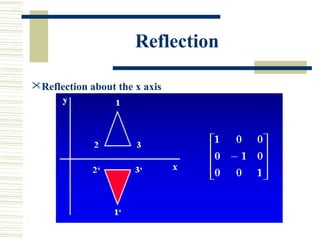
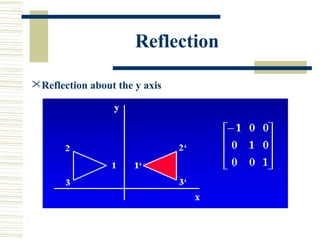
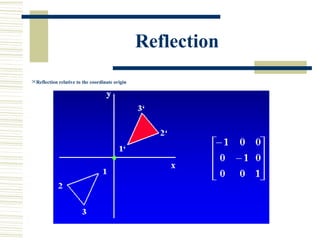
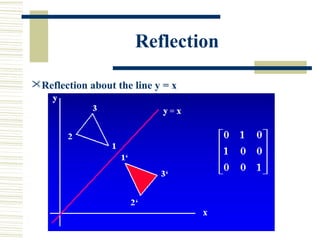
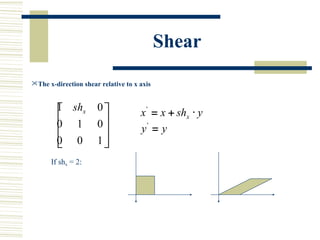
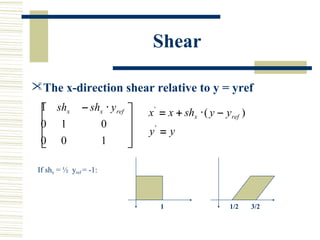
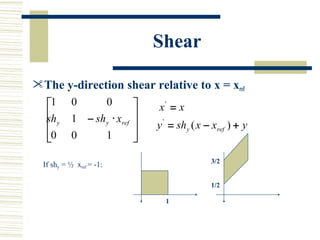
This document discusses various two-dimensional geometric transformations including translations, rotations, scaling, reflections, shears, and composite transformations. Translations move objects without deformation using a translation vector. Rotations rotate objects around a fixed point or pivot point. Scaling transformations enlarge or shrink objects using scaling factors. Reflections produce a mirror image of an object across an axis. Shearing slants an object along an axis. Composite transformations combine multiple basic transformations using matrix multiplication.