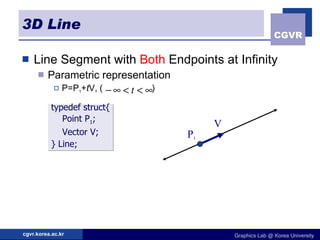
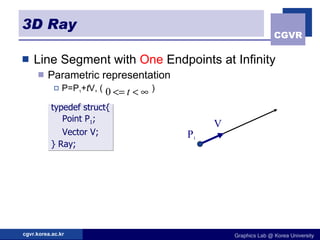
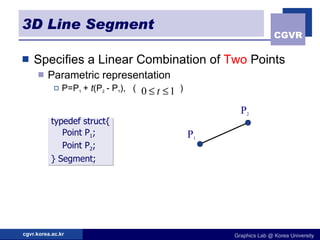
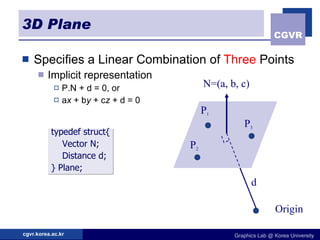
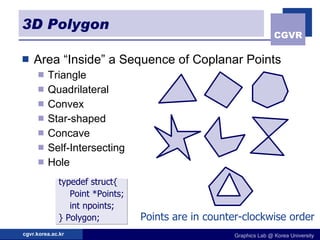
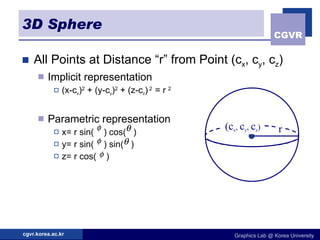
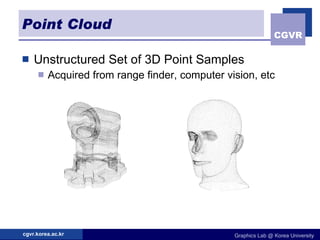
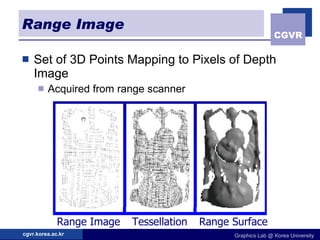
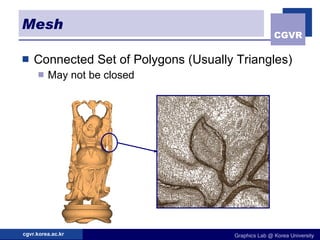
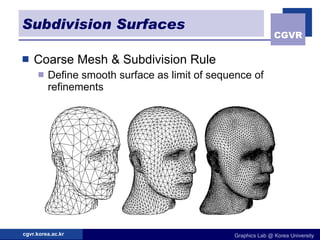
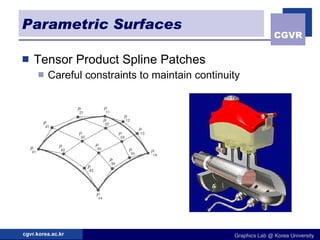
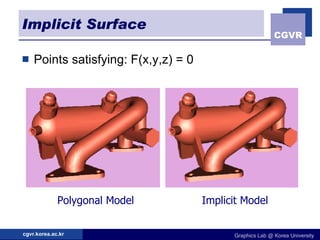
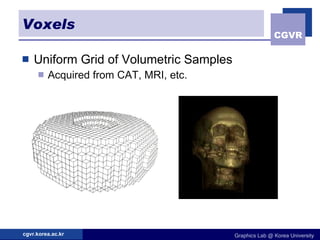
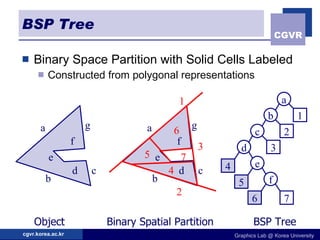
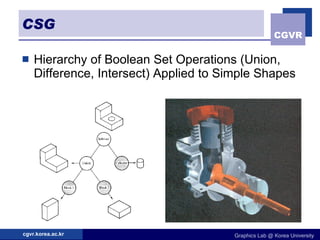
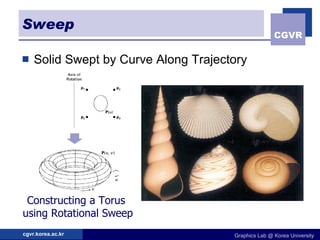
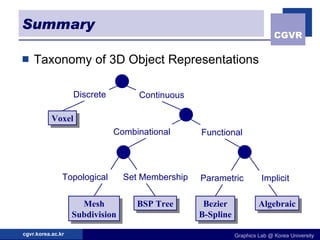
3D objects can be represented in several ways including point clouds, surfaces, and solids. Surfaces include meshes composed of polygons, subdivision surfaces defined by rules, and parametric or implicit surfaces with mathematical equations. Solids include voxel grids, binary space partition trees, constructive solid geometry using boolean operations, and swept volumes along trajectories. Each representation has advantages for different applications like rendering, modeling, or 3D scanning.