Embed presentation
Downloaded 489 times

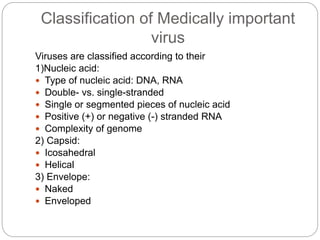



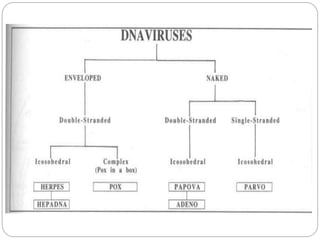


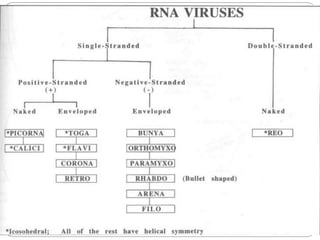

The document classifies viruses according to their nucleic acid, capsid, and envelope. Viruses are classified based on whether they contain DNA or RNA, if it is single or double stranded, segmented or not, and positive or negative stranded for RNA viruses. Capsids are classified as icosahedral or helical. Envelopes are naked or enveloped. DNA viruses like herpes, hepatitis, adeno, papilloma, parvo, and pox viruses are usually double stranded, icosahedral, and replicate in the nucleus, with some exceptions. RNA viruses are generally single stranded, enveloped, helical, and replicate in the cytoplasm, though some are double stranded, non-enveloped, or








