This document discusses the four main types of hypersensitivity reactions:
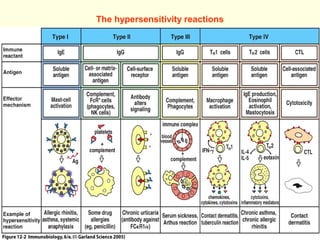
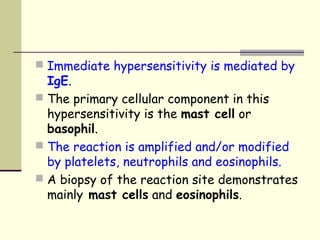
Type I is an immediate reaction mediated by IgE antibodies. It causes conditions like allergic asthma.
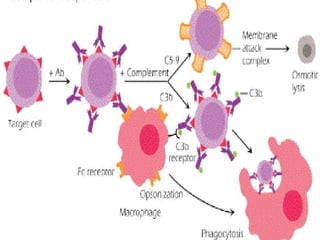
Type II involves antibodies binding to antigens on a person's own cells, activating complement and causing cell lysis. It includes conditions like autoimmune hemolytic anemia.
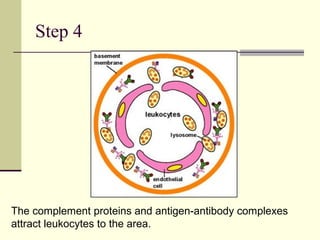
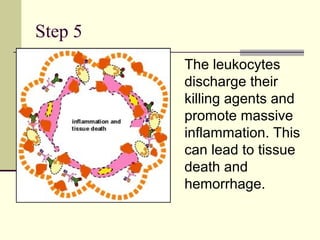
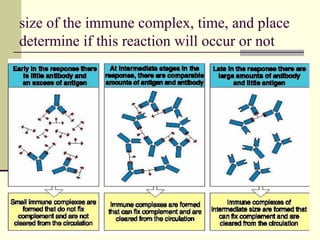
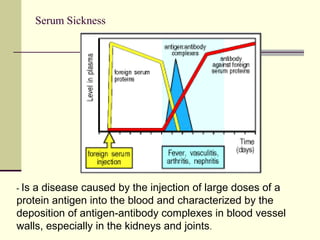
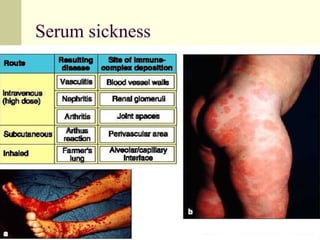
Type III occurs when immune complexes are deposited in tissues, activating complement and causing inflammation and tissue damage. Examples are serum sickness and lupus nephritis.
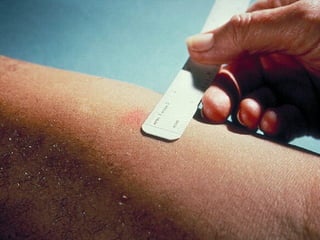
Type IV is a delayed reaction mediated by T cells and monocytes/macrophages. It causes conditions like contact dermatitis and tuberculosis.