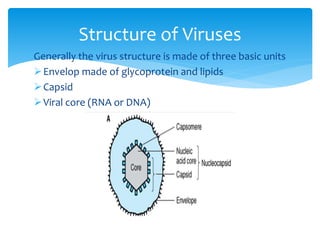
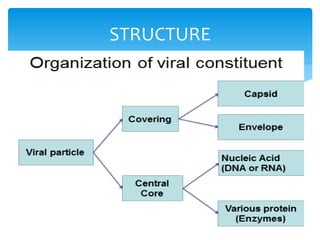
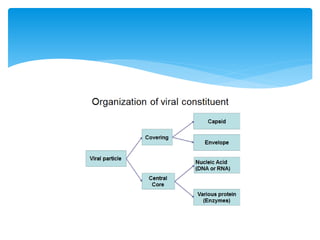
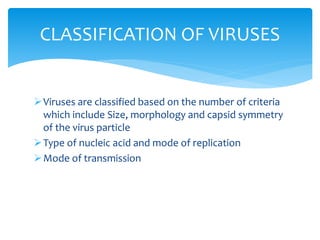
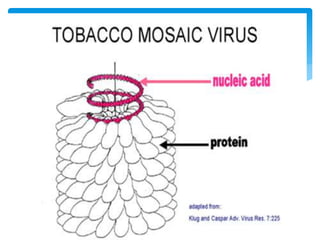
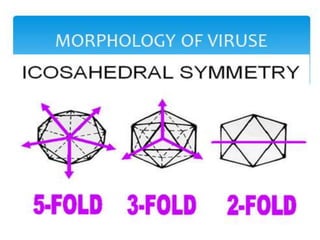
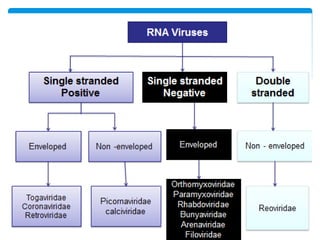
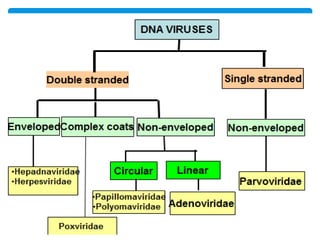
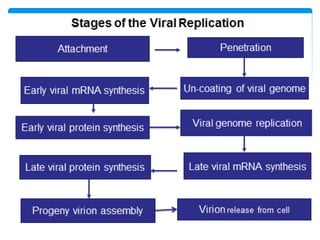
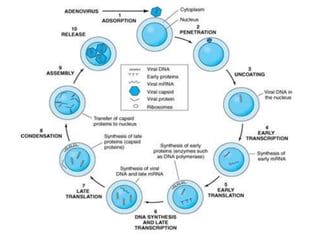
Viruses are the smallest infectious agents ranging from 20-300nm. They contain either RNA or DNA as their genome and have a protein coat called a capsid that protects the genetic material. Viruses are classified based on their structure, nucleic acid content, and replication strategy. The typical virus structure includes an envelope, capsid, and core containing the genetic material. Viruses replicate only inside living cells by hijacking the host cell's machinery to produce new virus particles.