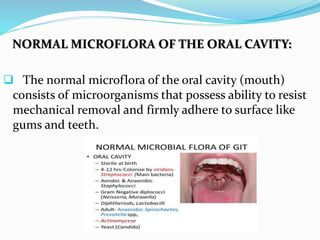
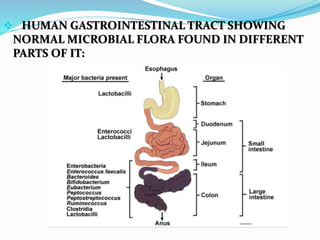
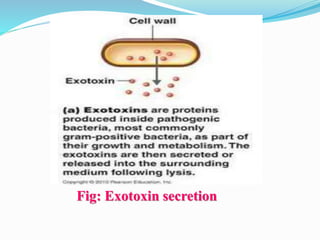
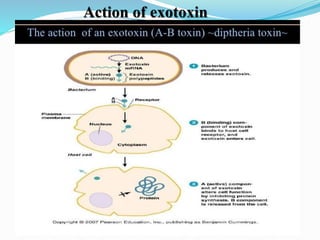
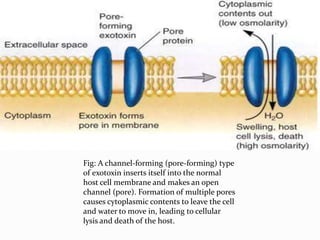
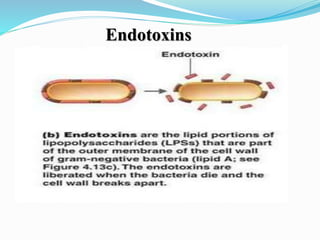
This document discusses various types of symbiotic relationships between organisms, including parasitism, commensalism, and mutualism. It provides examples of each type of relationship. It also discusses the definitions and characteristics of hosts, parasites, normal flora, pathogens, toxins, and infections. The key types of symbiosis are defined as commensalism, mutualism, and parasitism. Commensalism benefits one organism without affecting the other. Mutualism benefits both organisms, while parasitism benefits the parasite at the expense of the host.