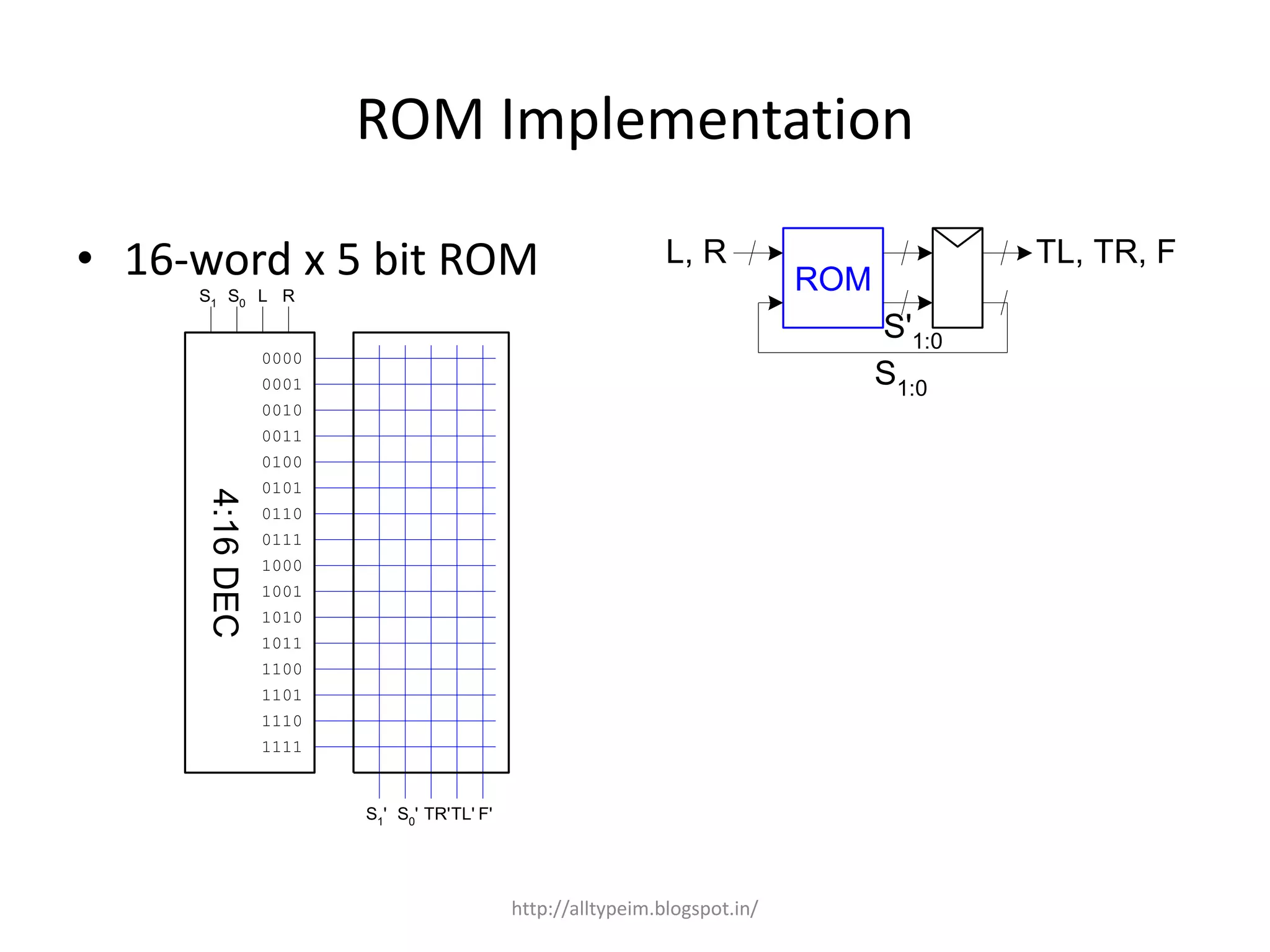
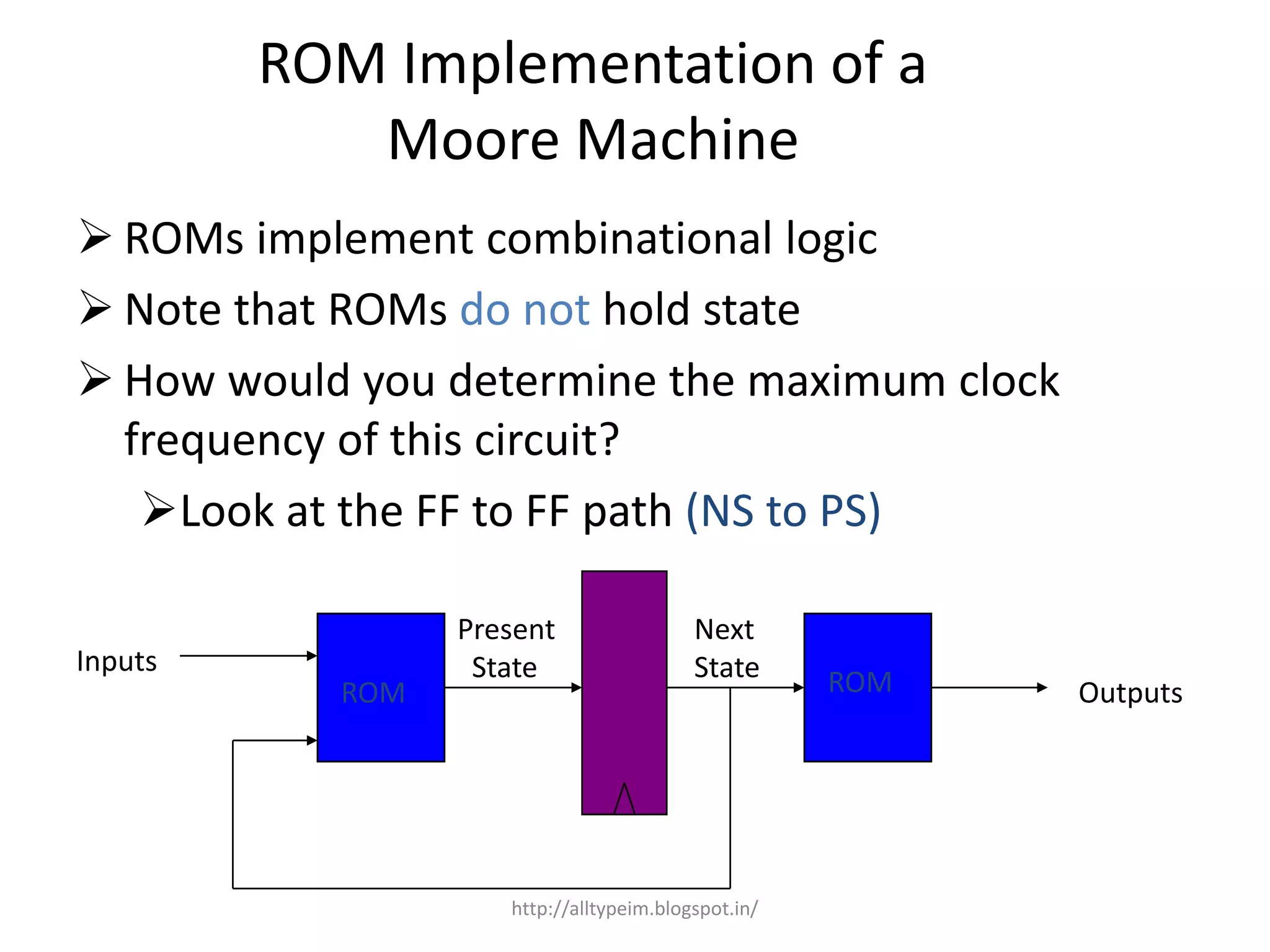
This document discusses Read Only Memory (ROM) including its concept, characteristics, types, internal structure, implementation in Moore and Mealy machines, array layout, row decoders, and complete layout. ROM is read-only memory that does not lose its data when power is lost. It is commonly used to store firmware like the BIOS and can implement truth tables for combinational logic in finite state machines.