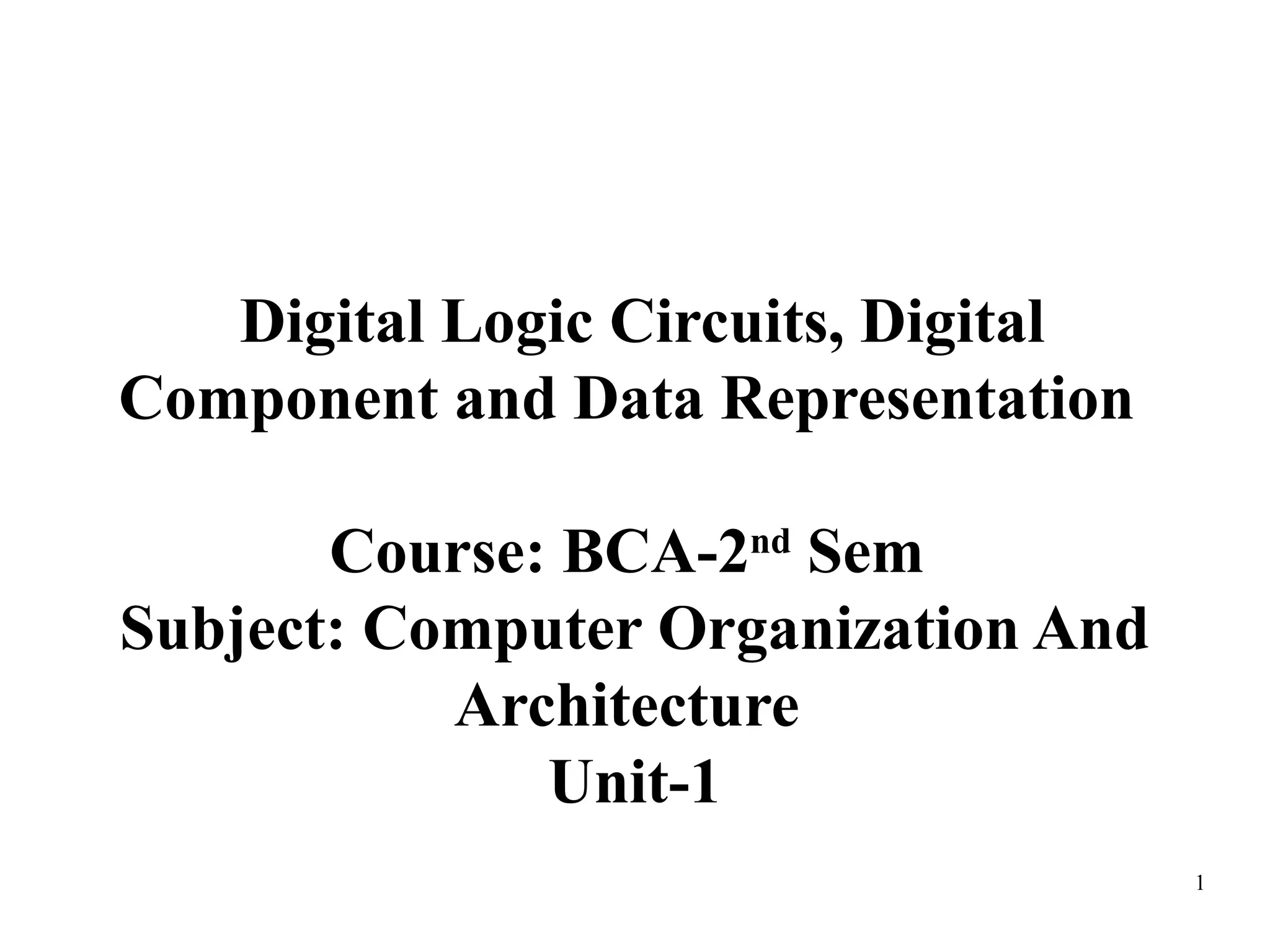
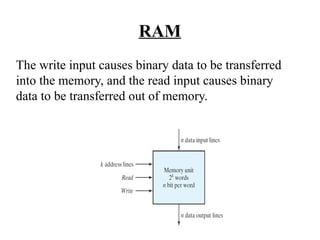
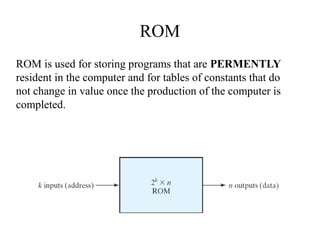
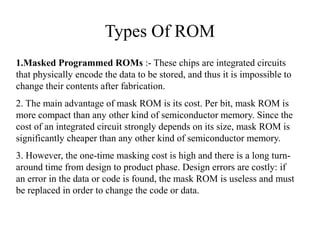
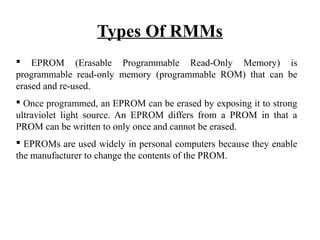
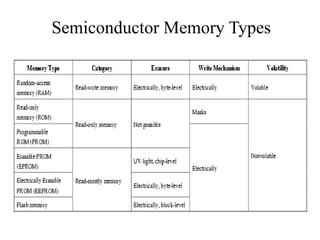
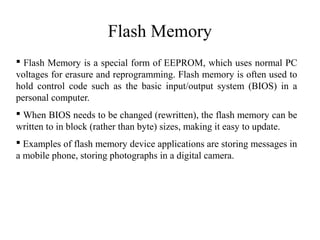
The document discusses different types of computer memory. It defines memory as a device that stores binary data for processing. There are two main types: random access memory (RAM), which allows data to be accessed randomly at the same speed; and sequential access memory, where access time varies. RAM is further divided into static, dynamic, read-only memories (ROM), read-write memories (RWM), and read-mostly memories (RMM). Examples of ROM include mask programmed ROM and PROM, while examples of RMM include EPROM and EEPROM. Flash memory is a type of EEPROM that uses standard voltages.