The document provides an overview of the Linux architecture including:
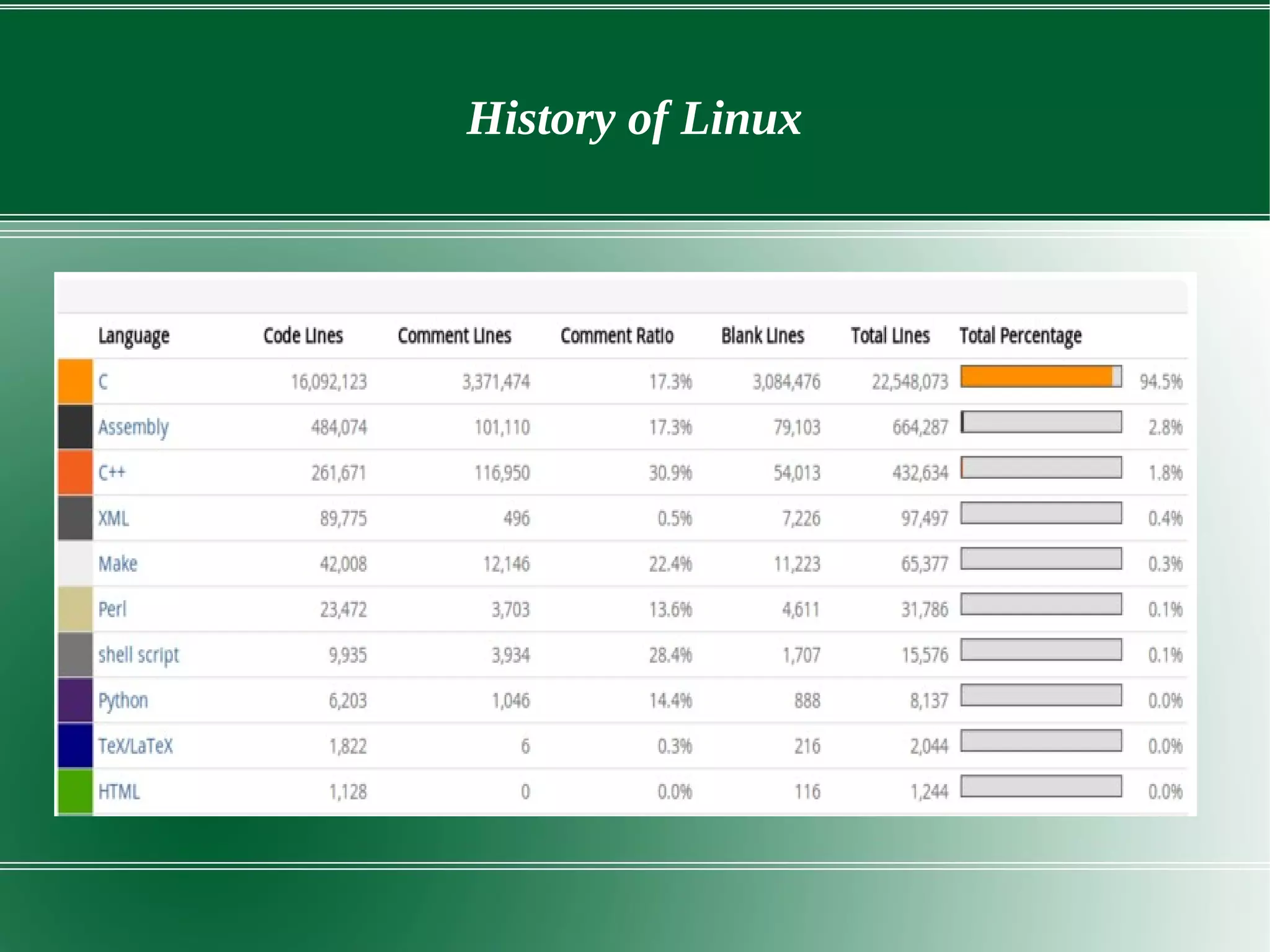
1) It discusses the history of Linux from its origins as a free UNIX-like operating system developed by Linus Torvalds to the over 18 million lines of code it contains today.
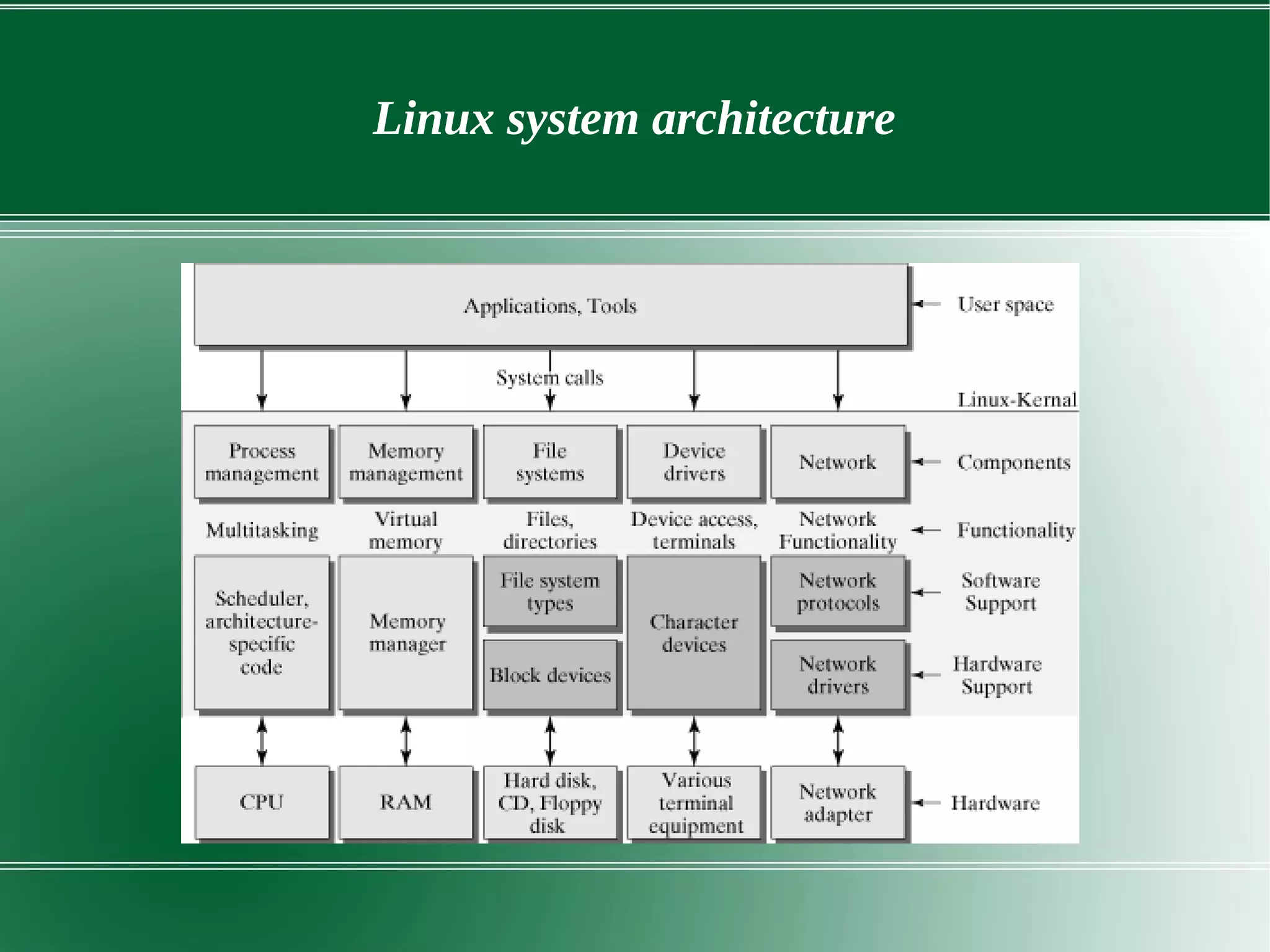
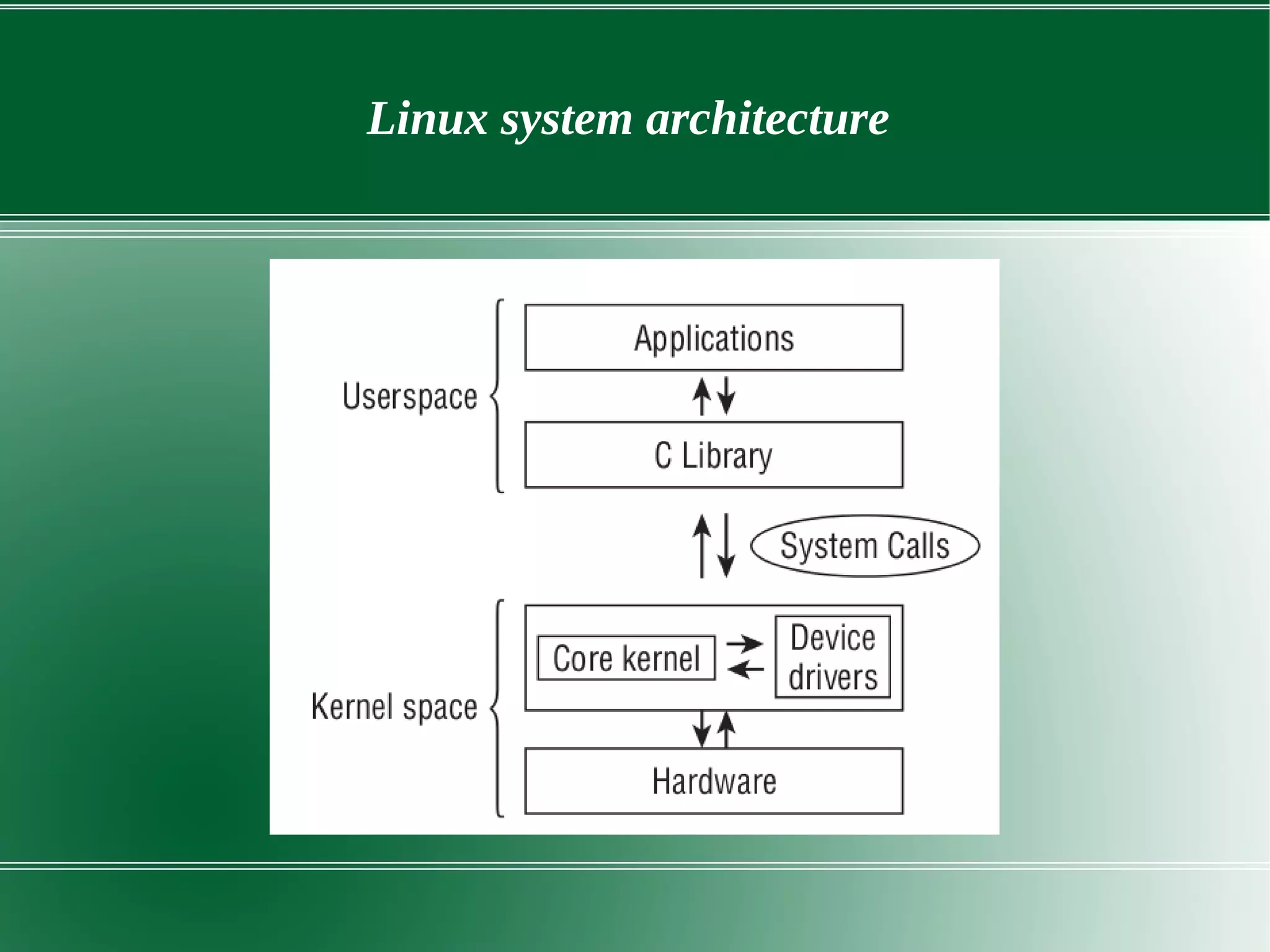
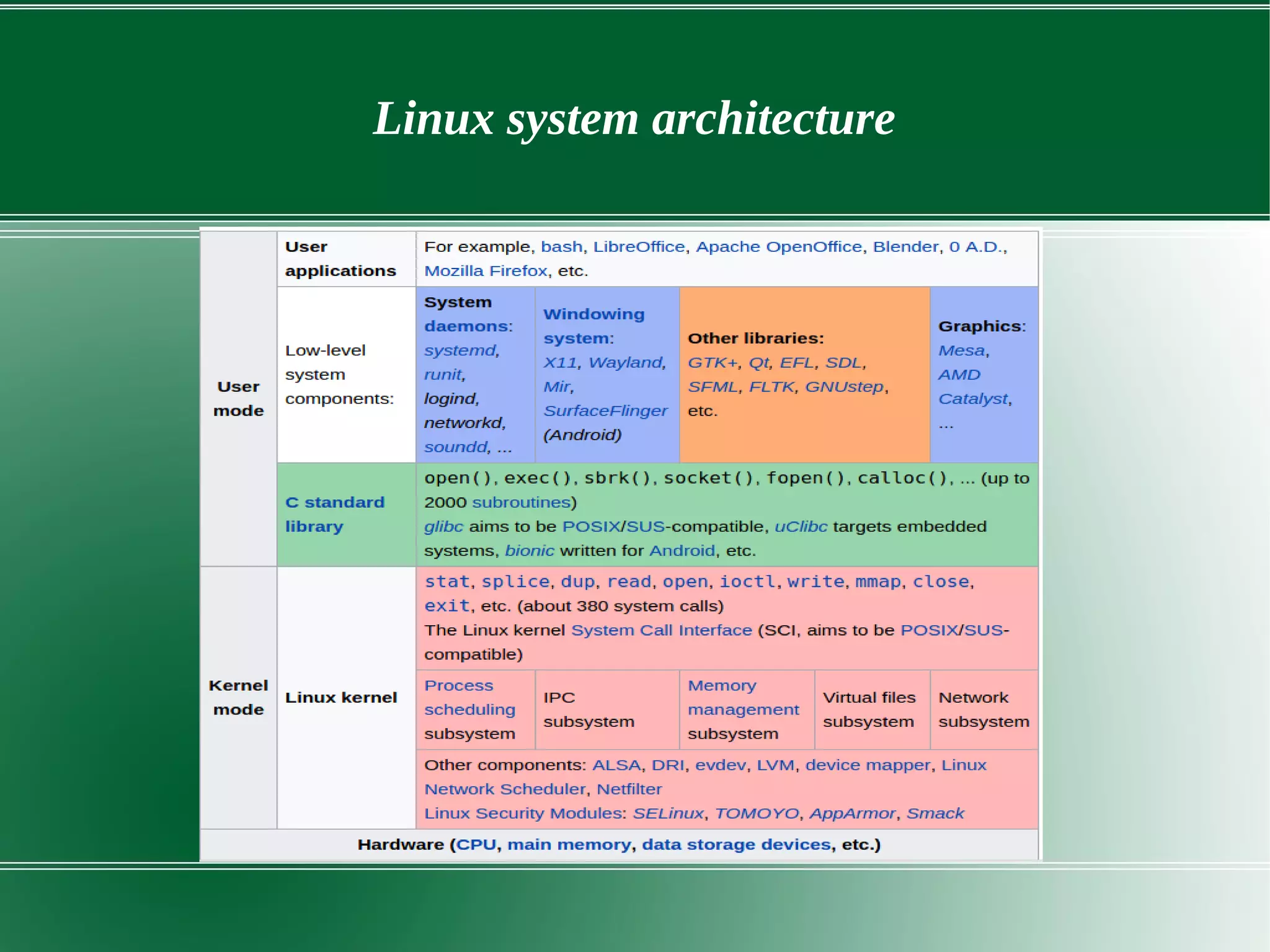
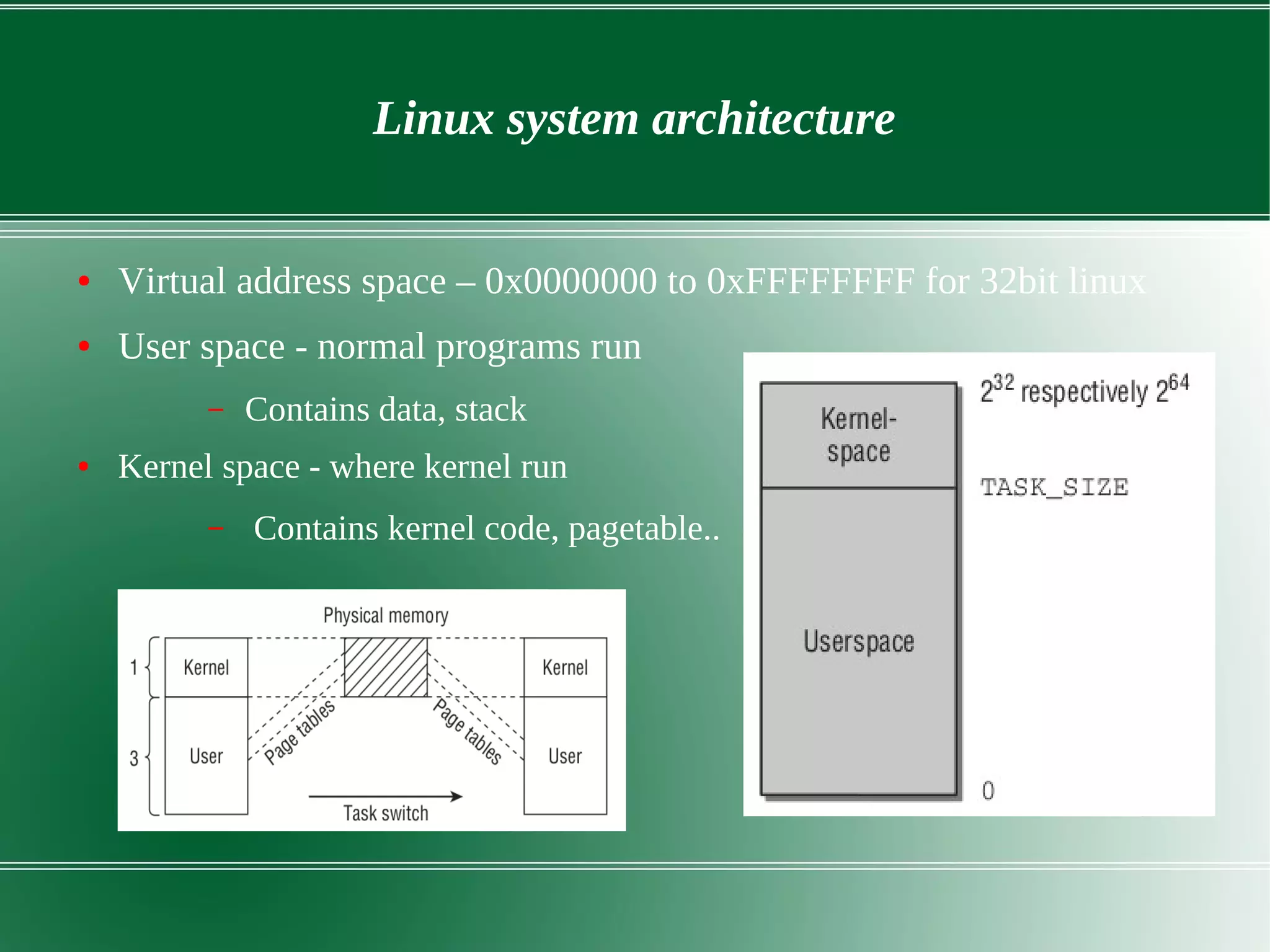
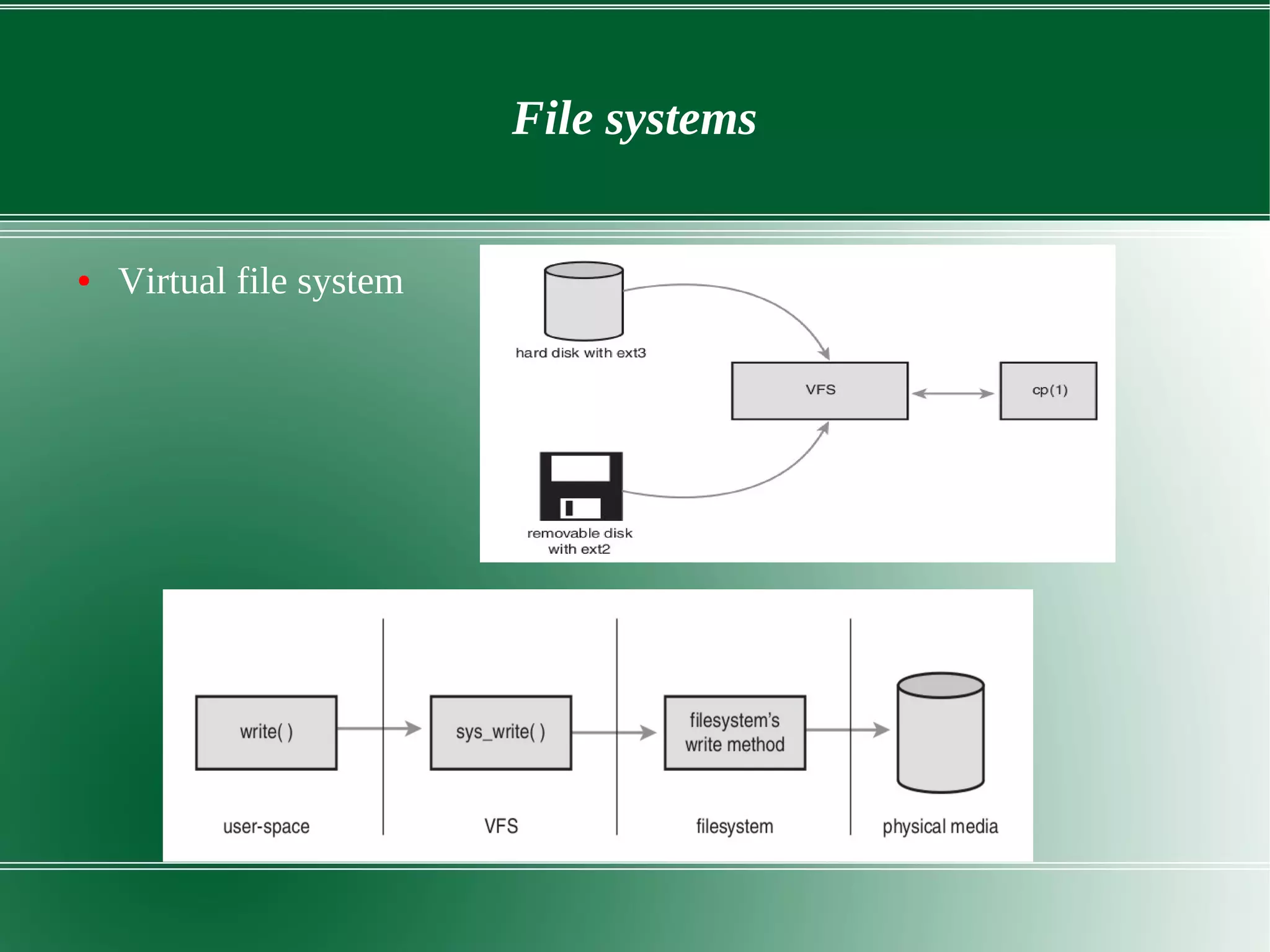
2) It describes the key components of the Linux system architecture including the hardware layer, kernel, shell, and utilities. The kernel acts as the core of the OS and interacts with hardware to perform low-level services.
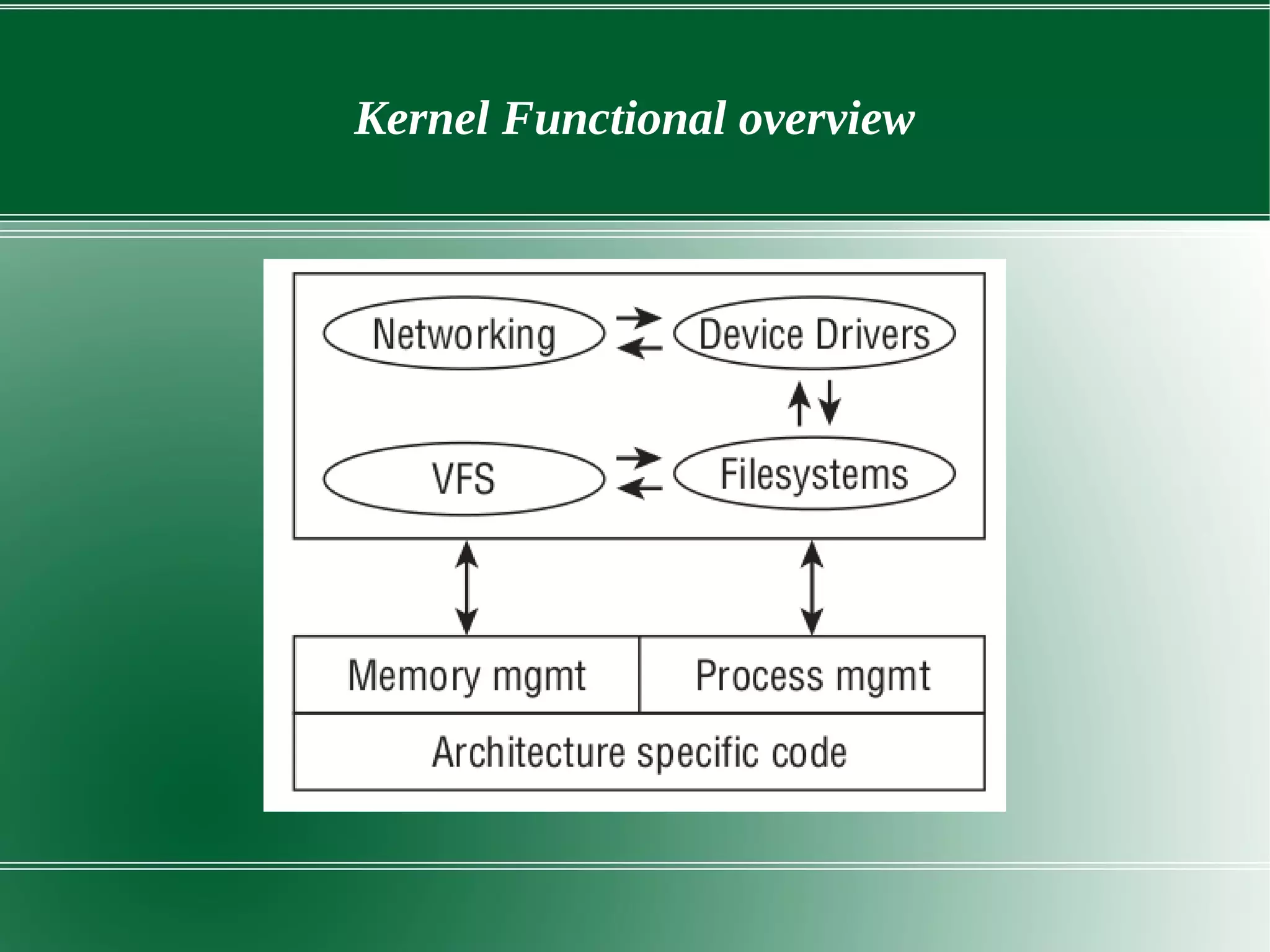
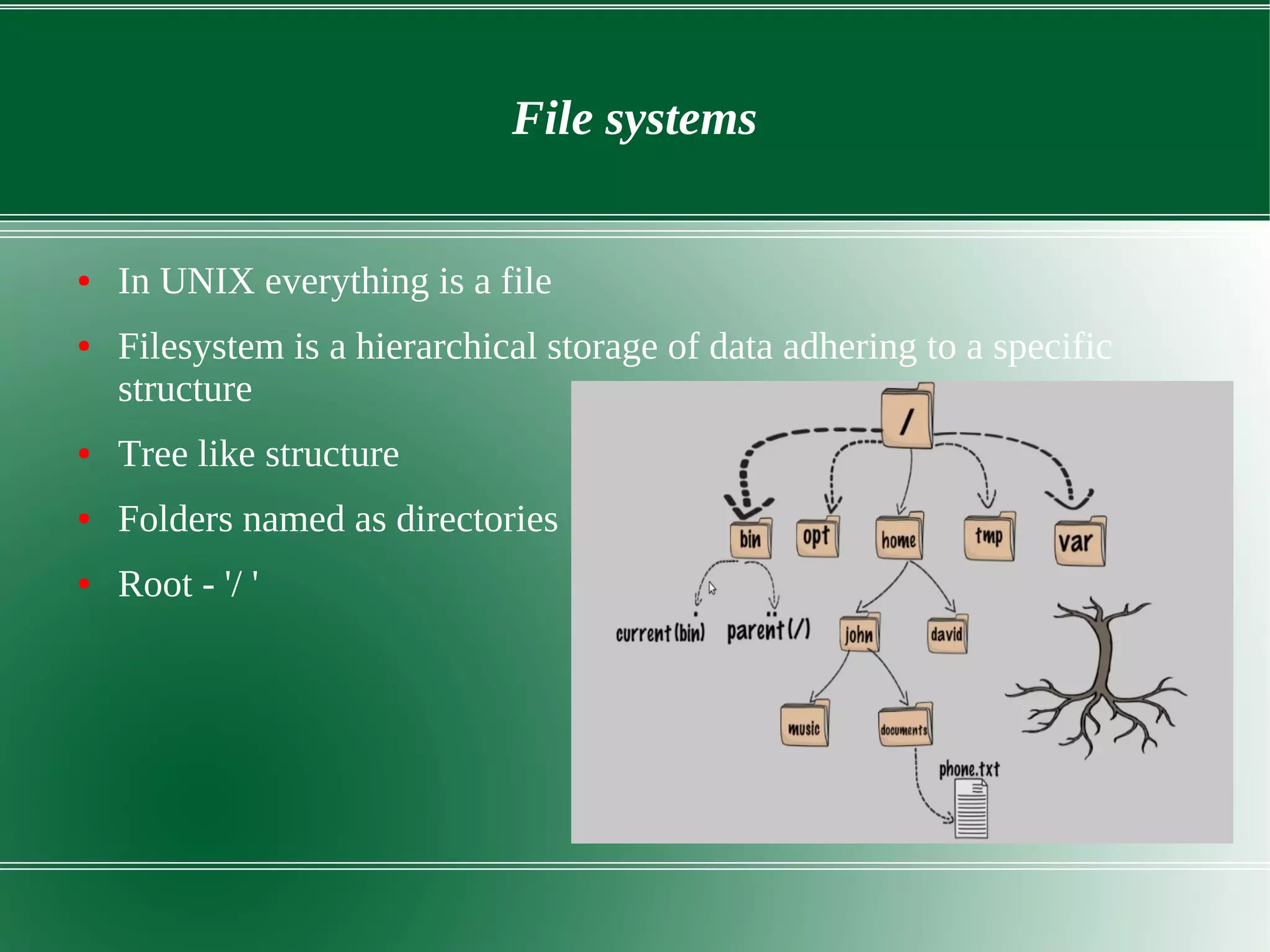
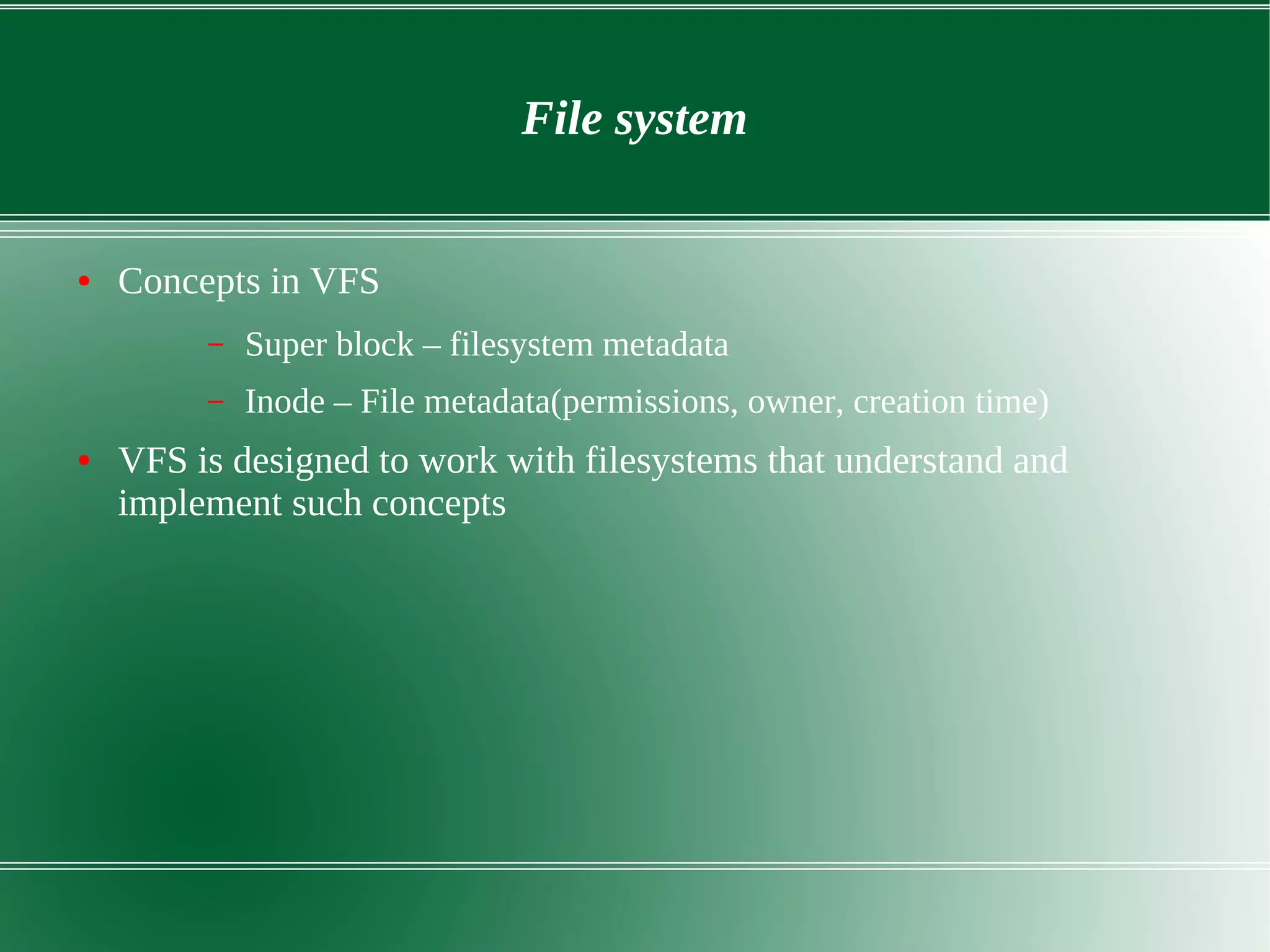
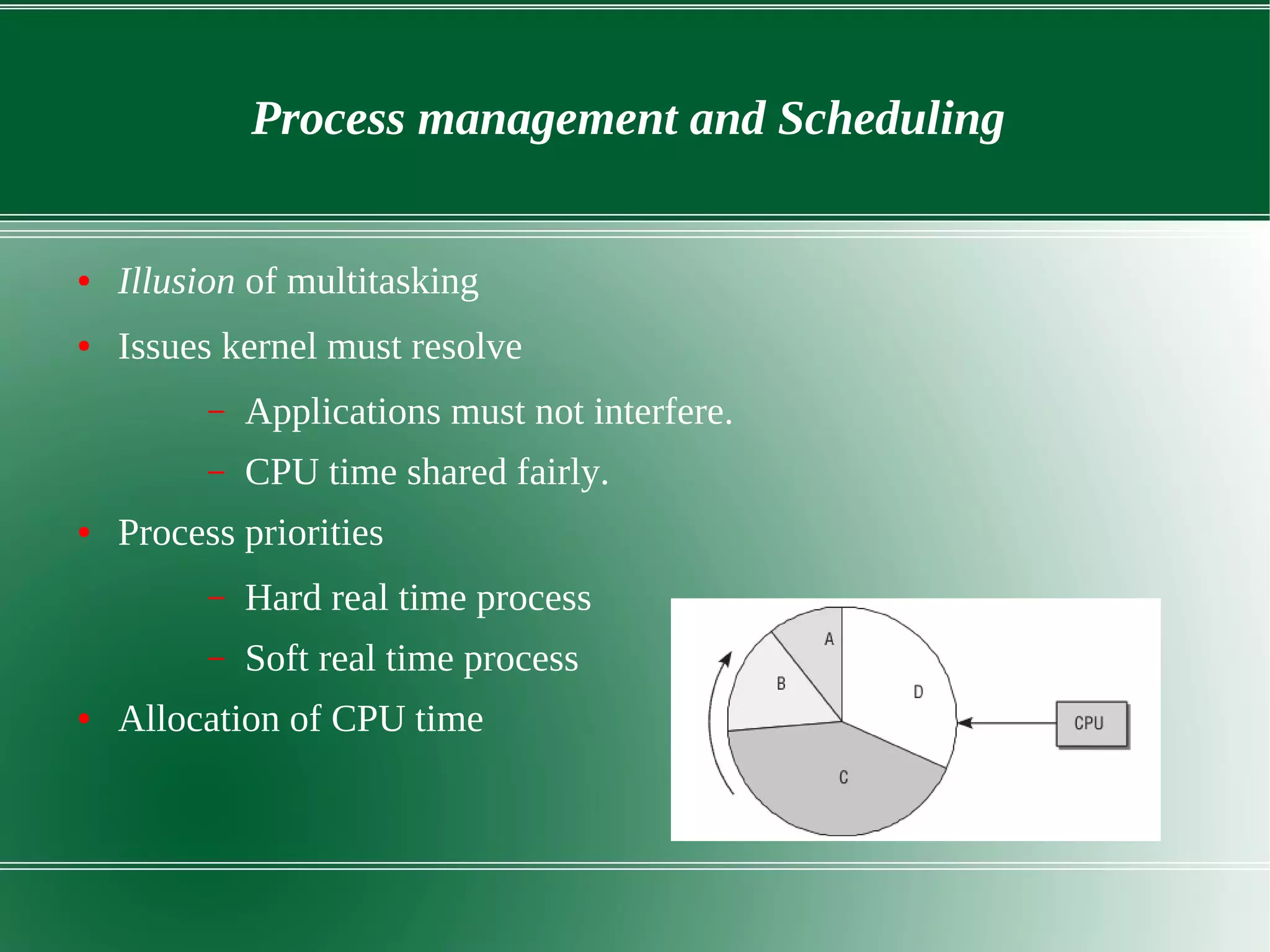
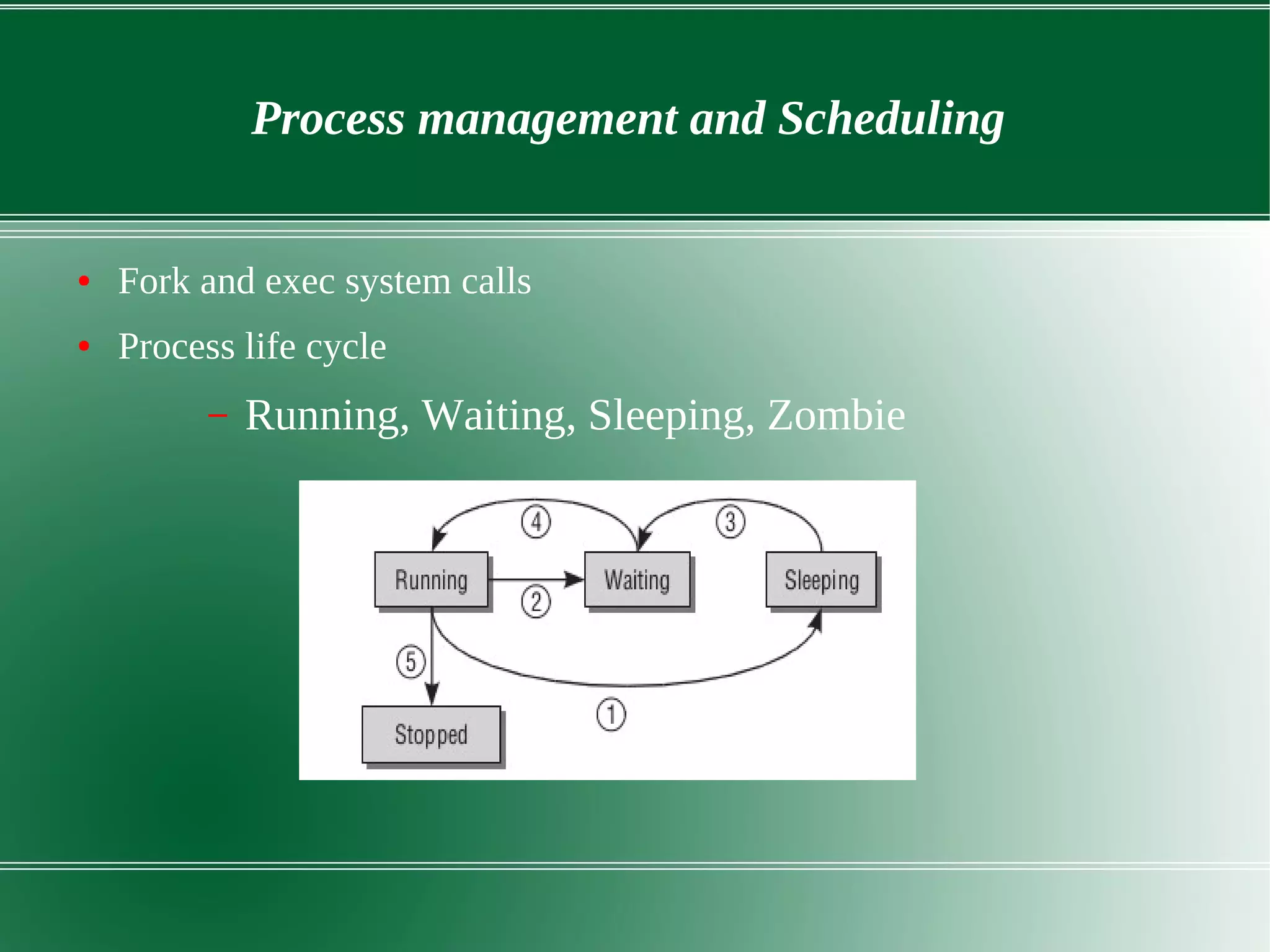
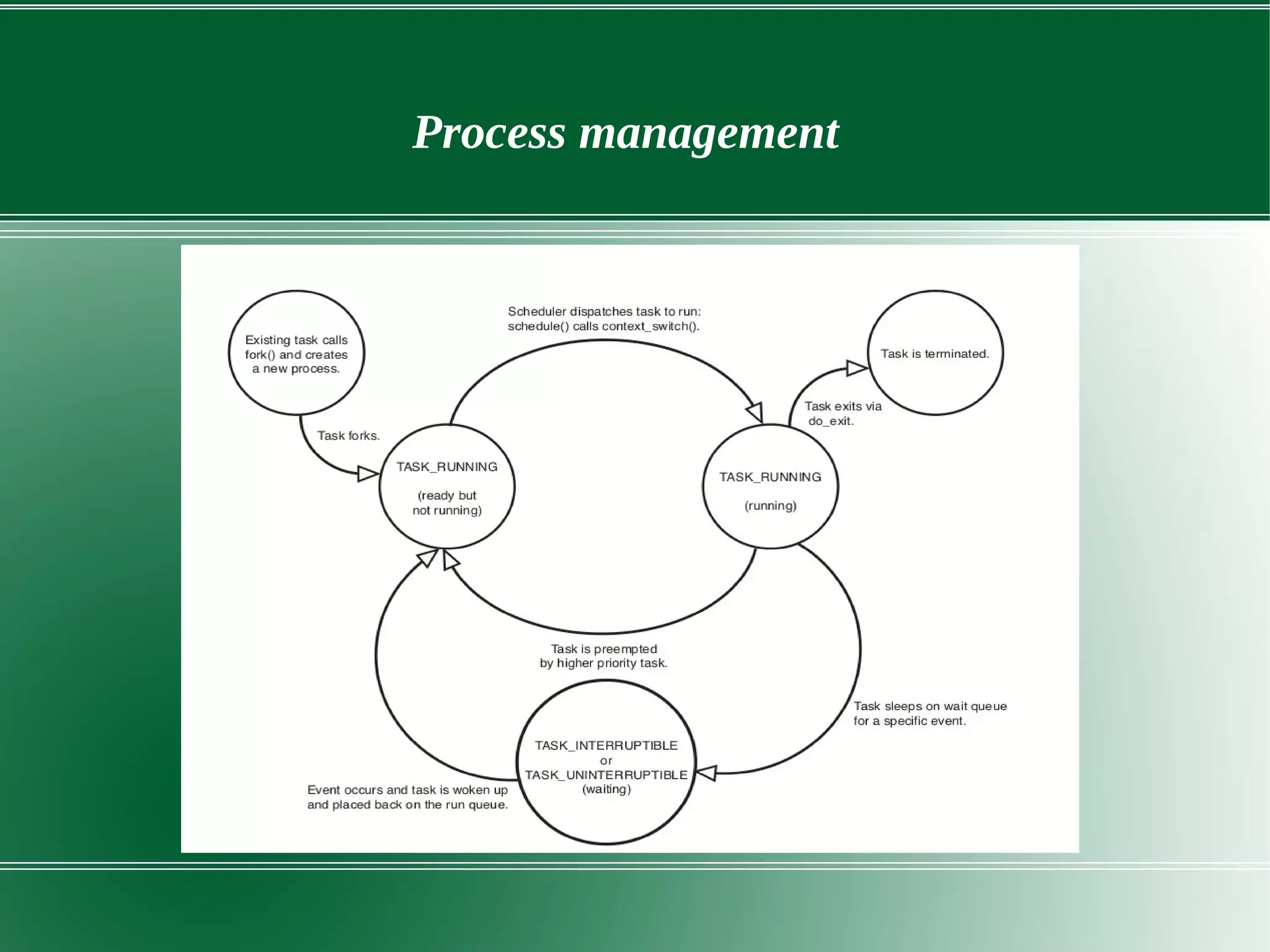
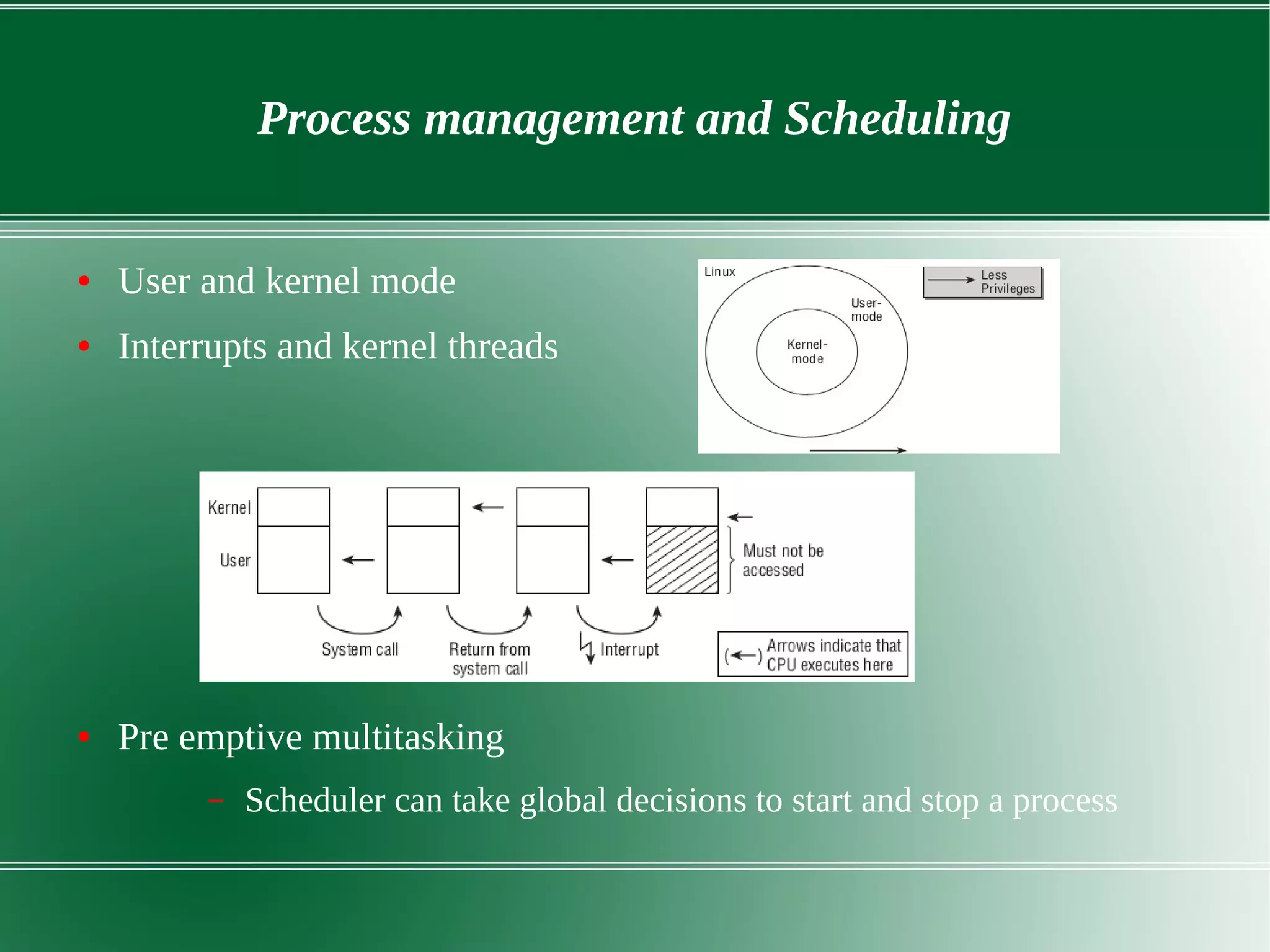
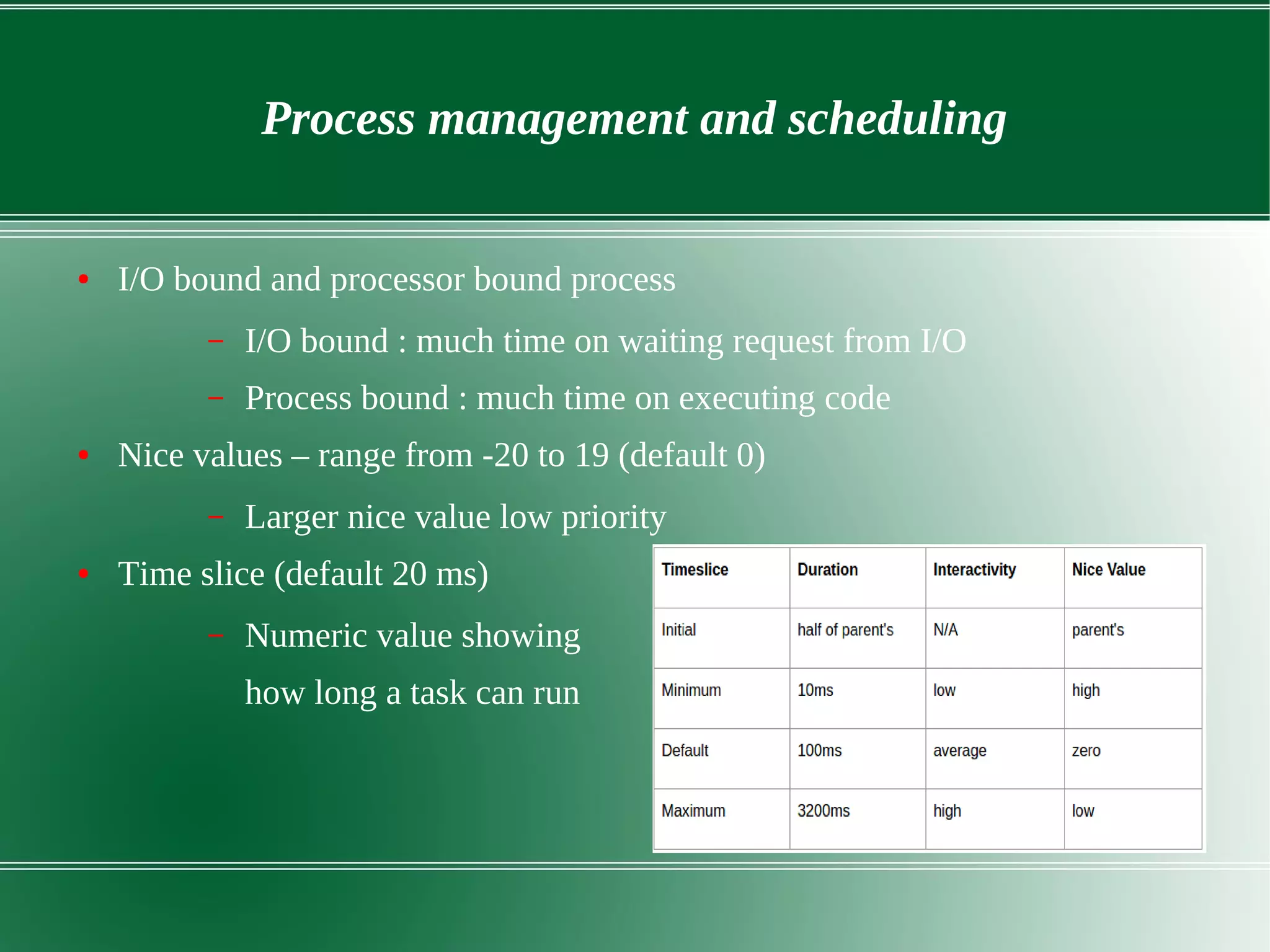
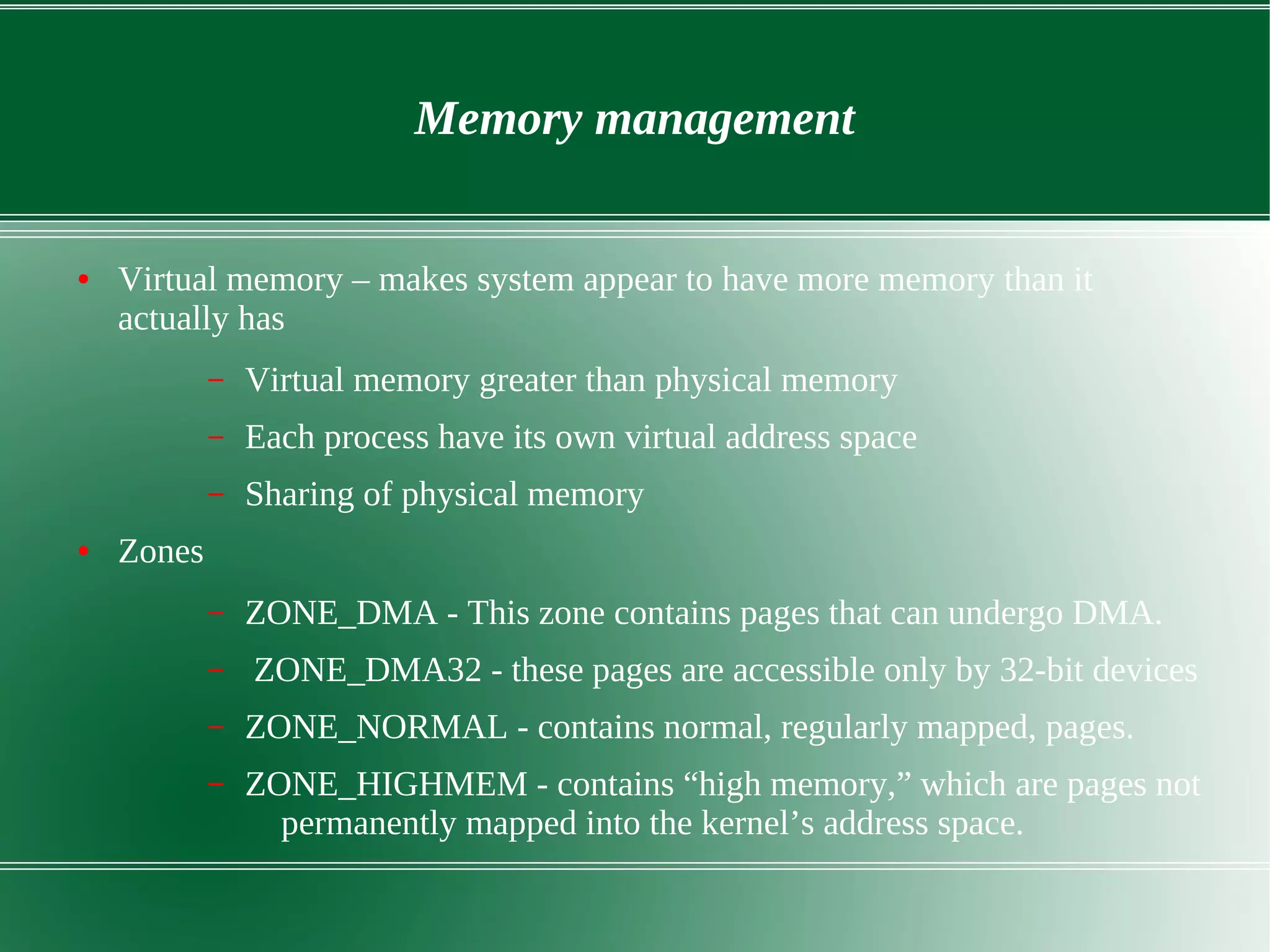
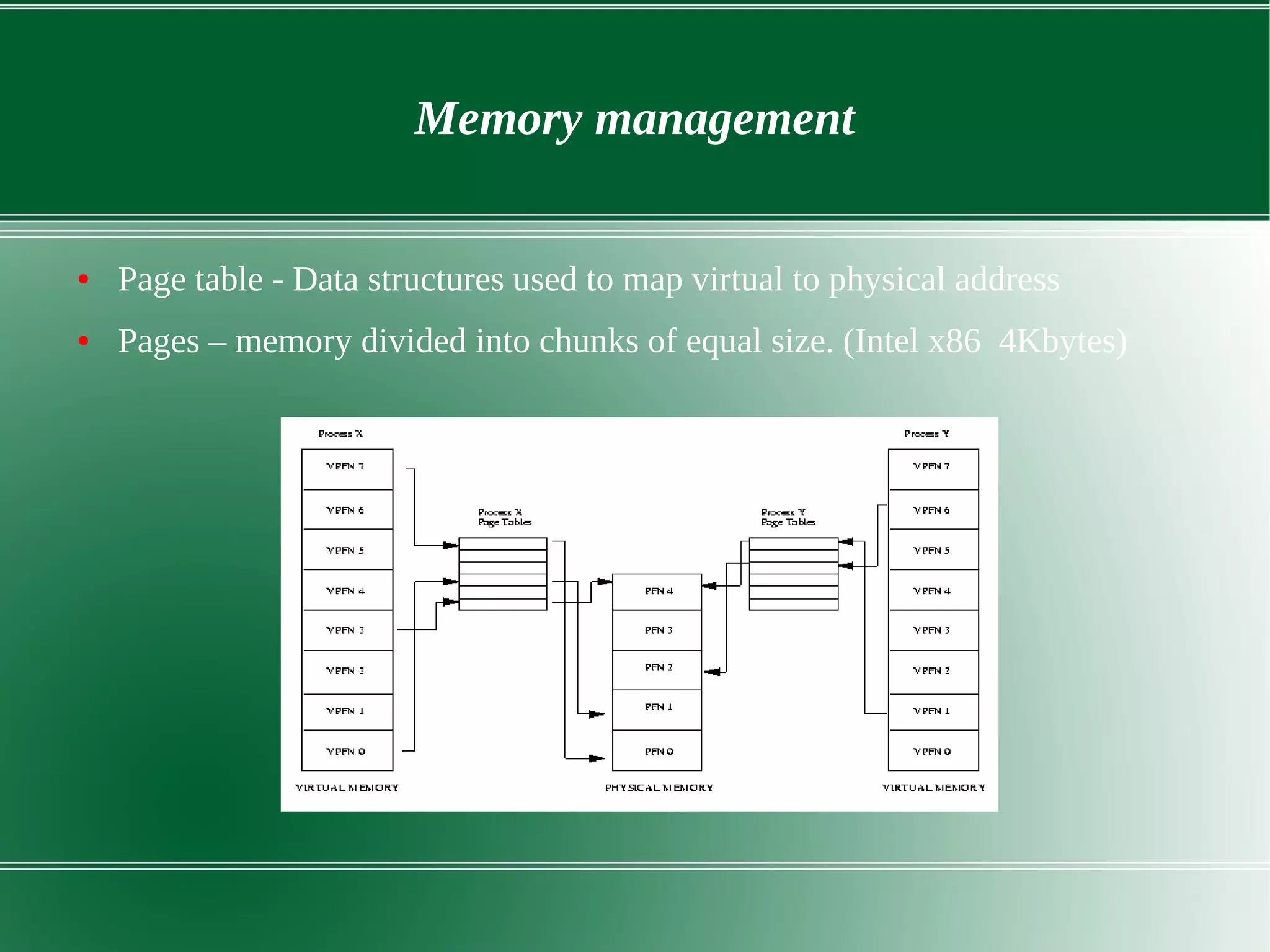
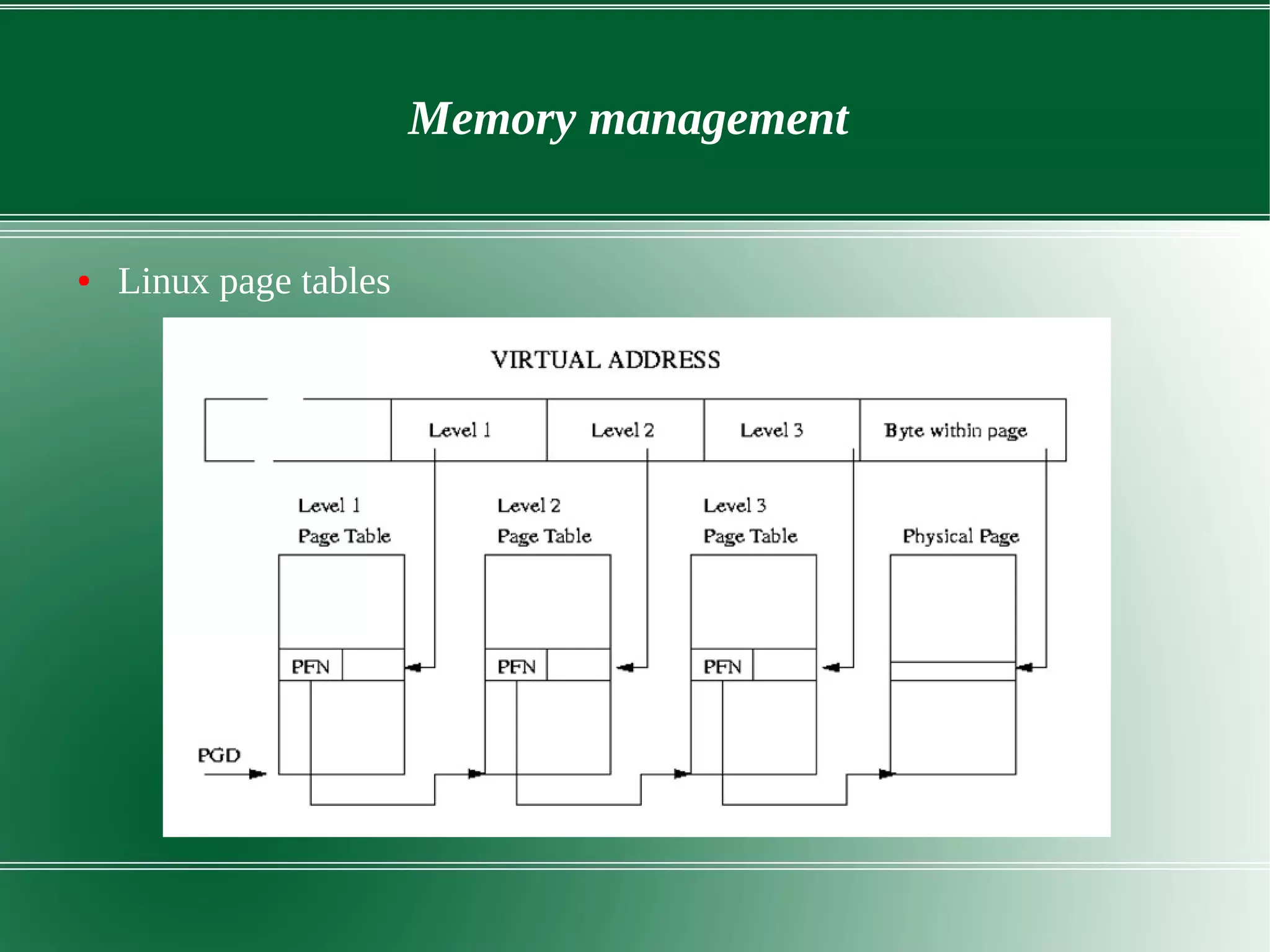
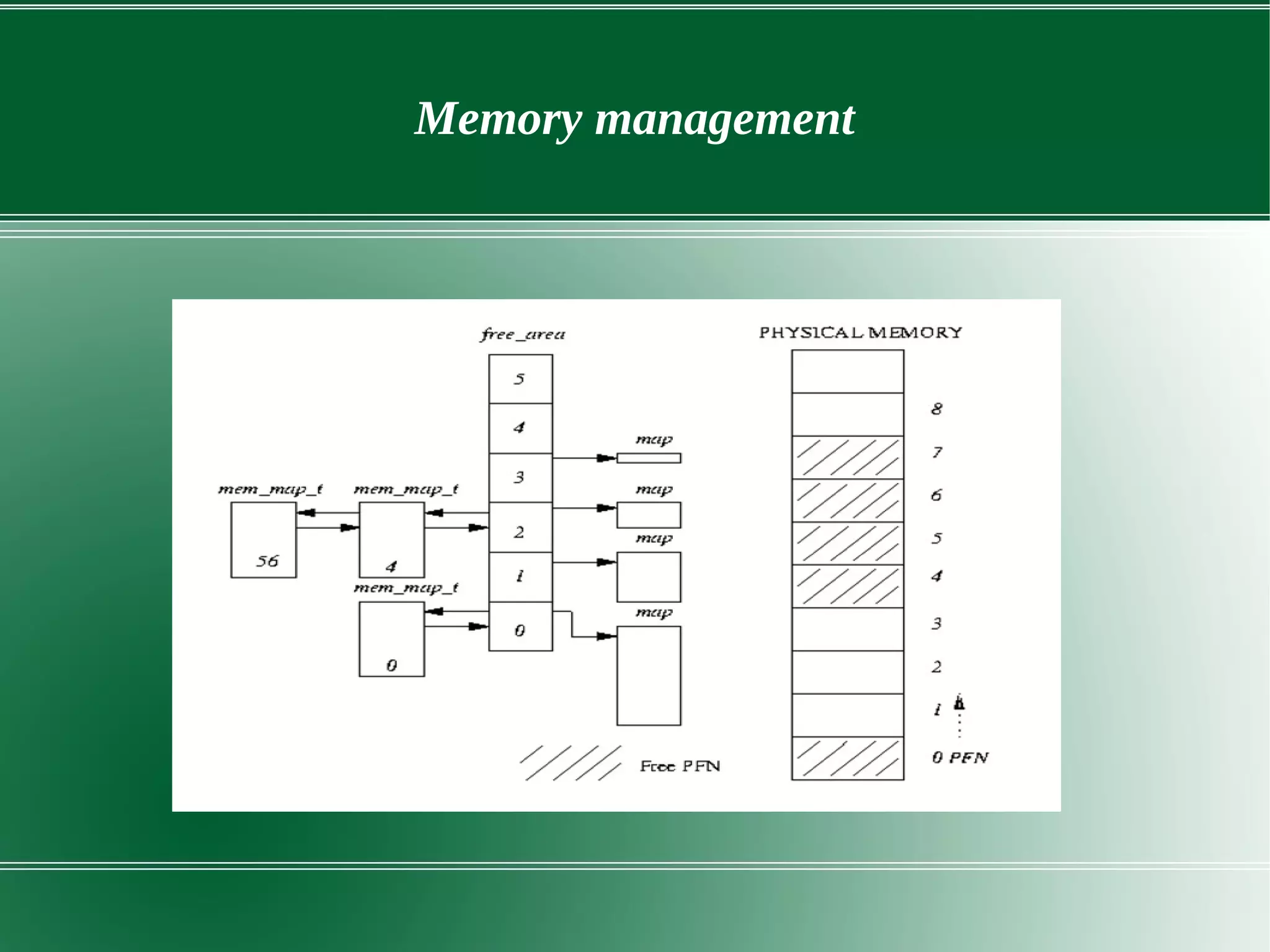
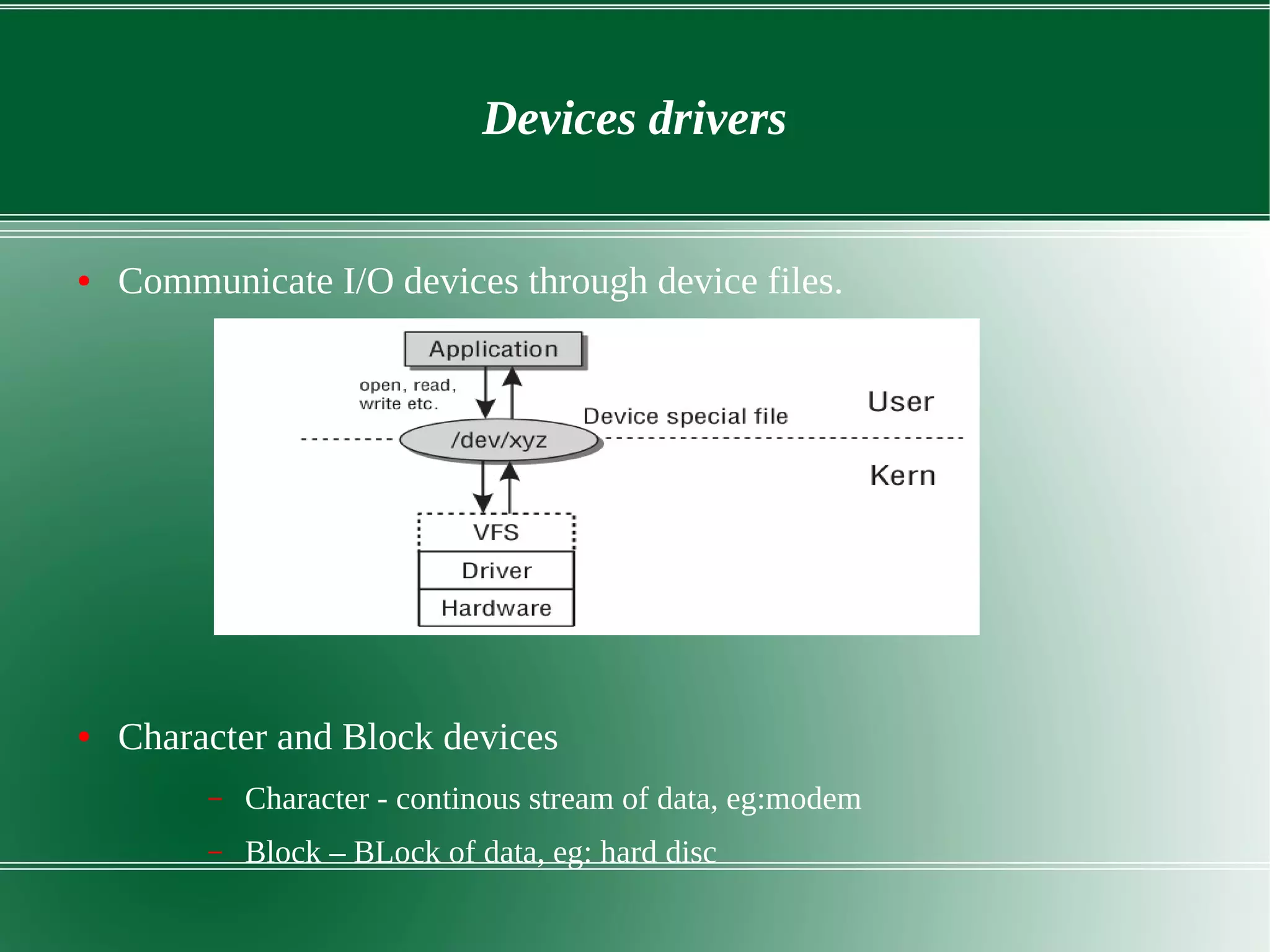
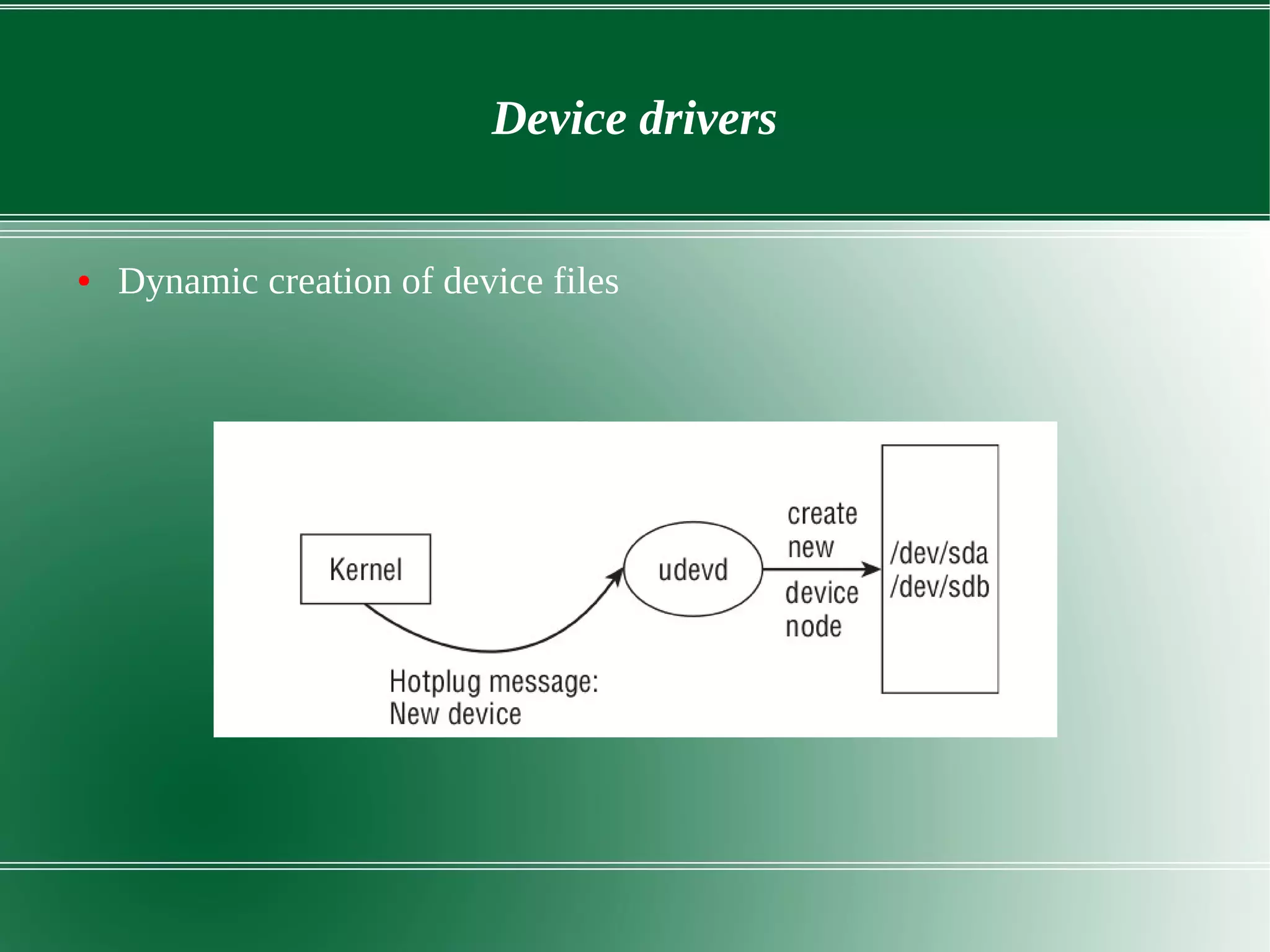
3) It outlines several important kernel functions including file system management, process management and scheduling, memory management, and device drivers which allow communication with I/O devices through device files.