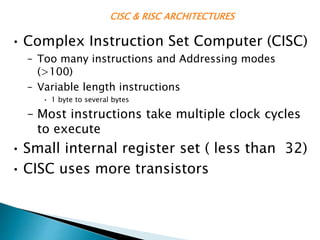
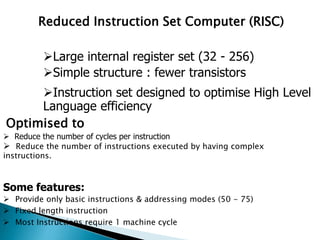
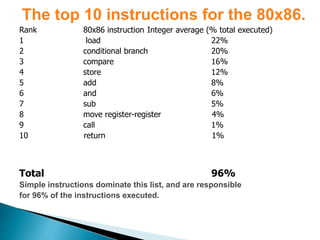
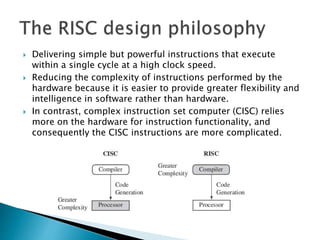
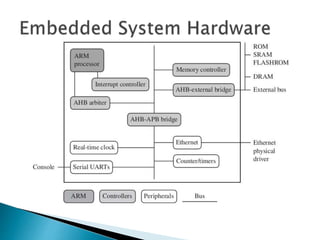
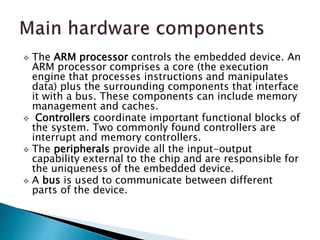
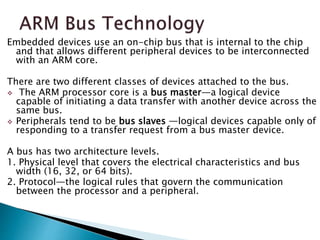
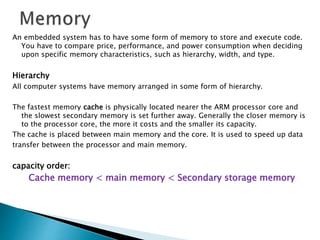
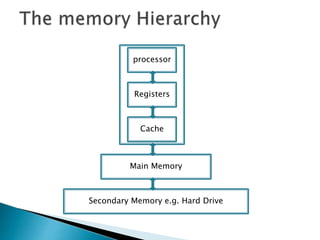
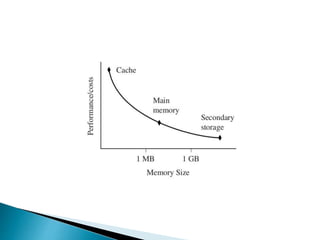
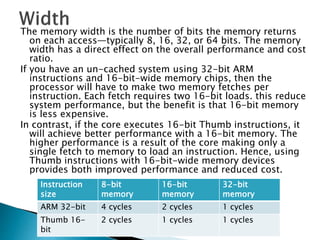
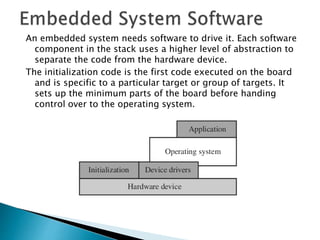
The ARM processor architecture uses either reduced instruction set computing (RISC) or complex instruction set computing (CISC). RISC aims to improve performance by reducing the number of clock cycles per instruction through simpler instructions that execute in one cycle. CISC relies more on hardware for complex instructions. Memory in ARM systems is hierarchical, with cache memory closest to the processor core and secondary storage like hard drives further away. Peripherals allow input/output and are memory mapped through registers. Initialization code configures hardware and runs diagnostics before booting the operating system.