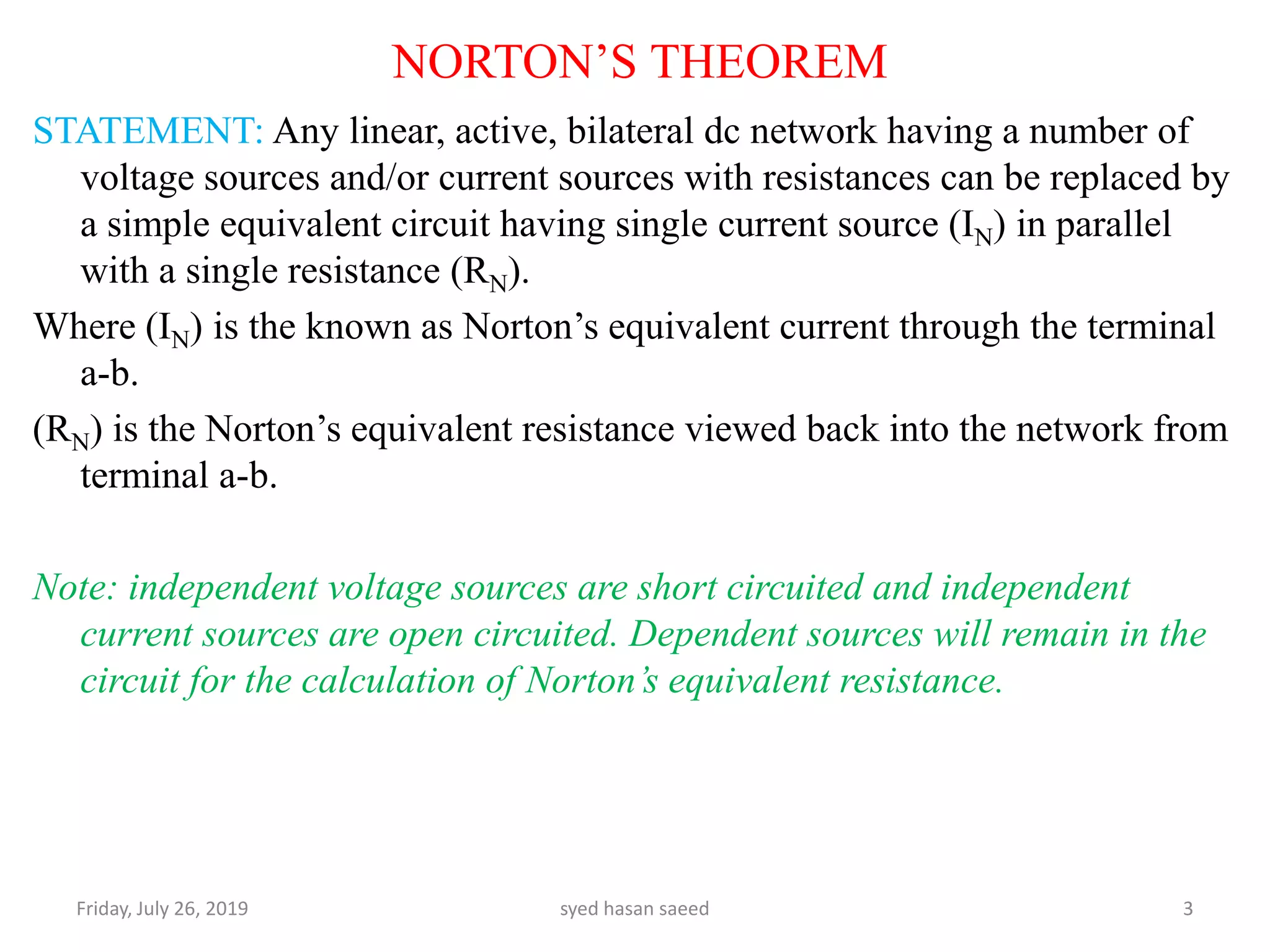
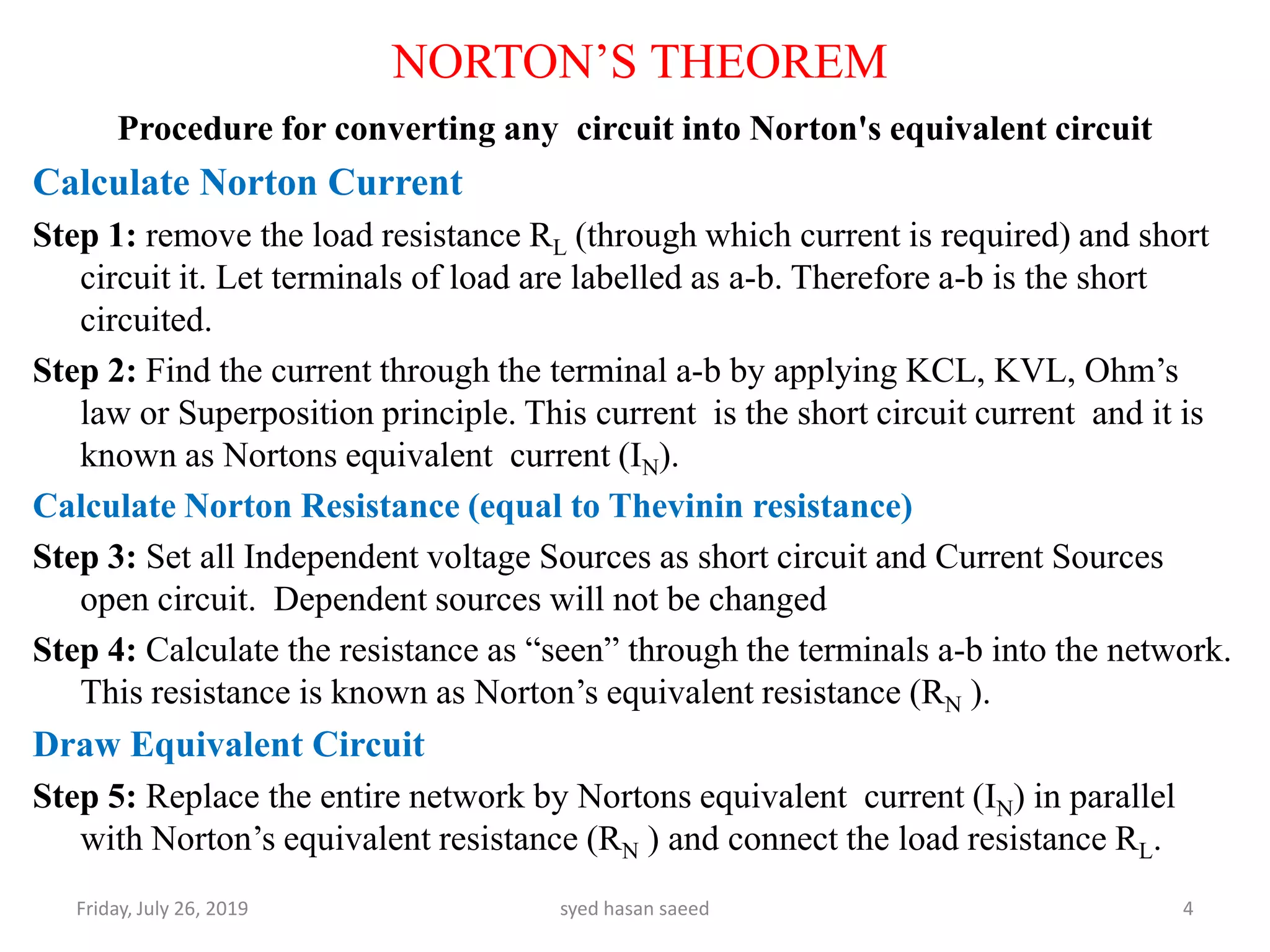
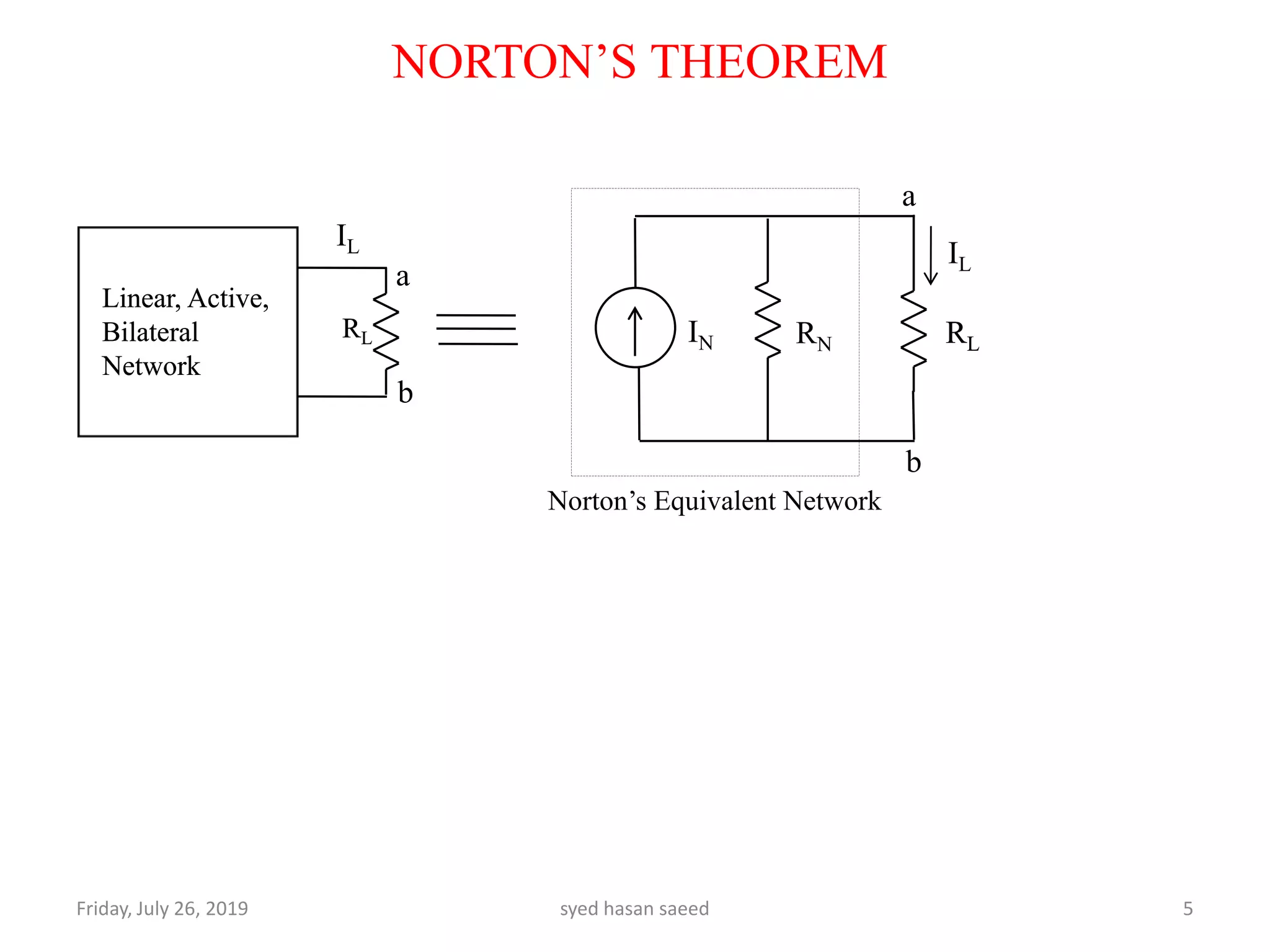
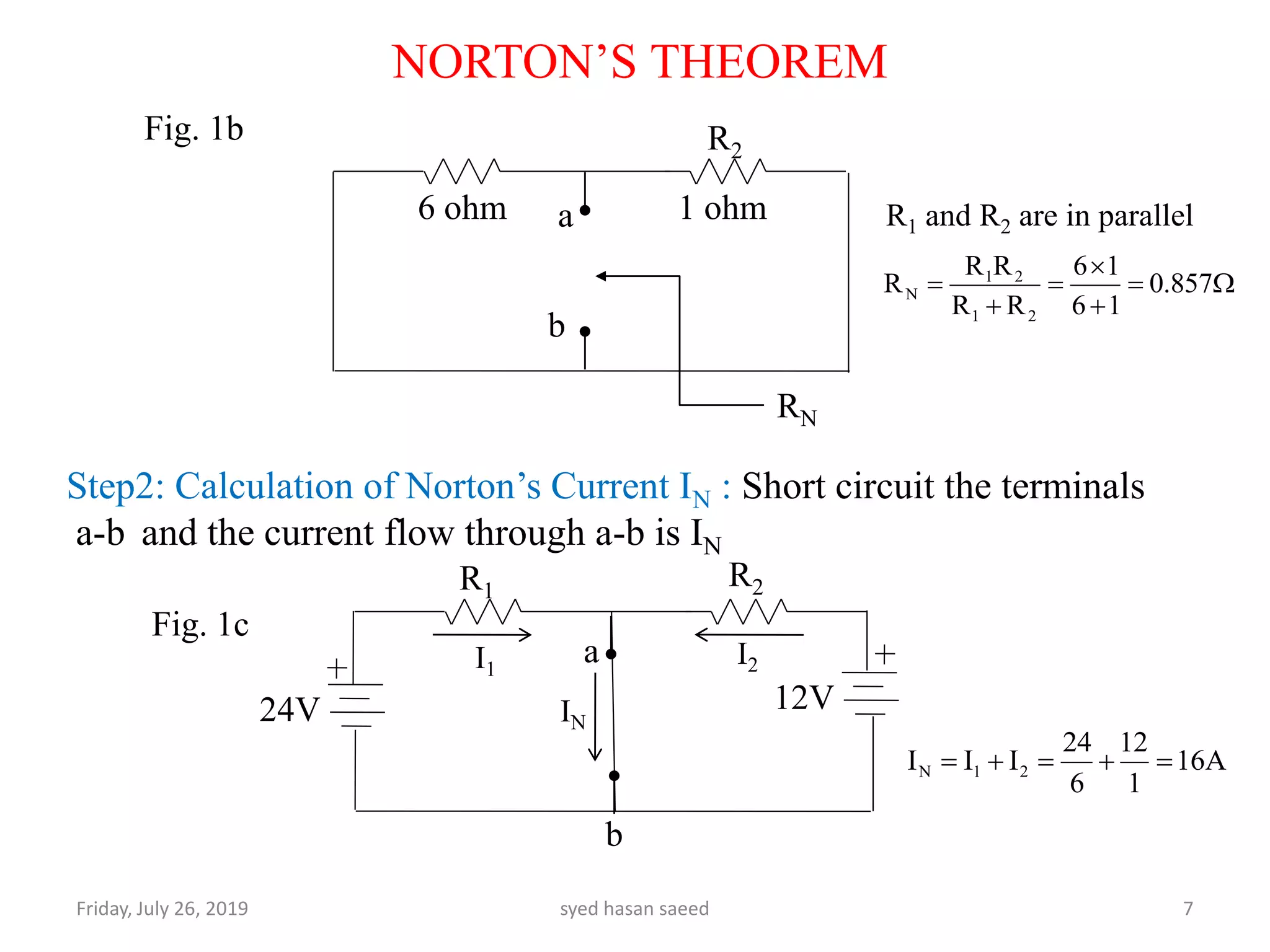
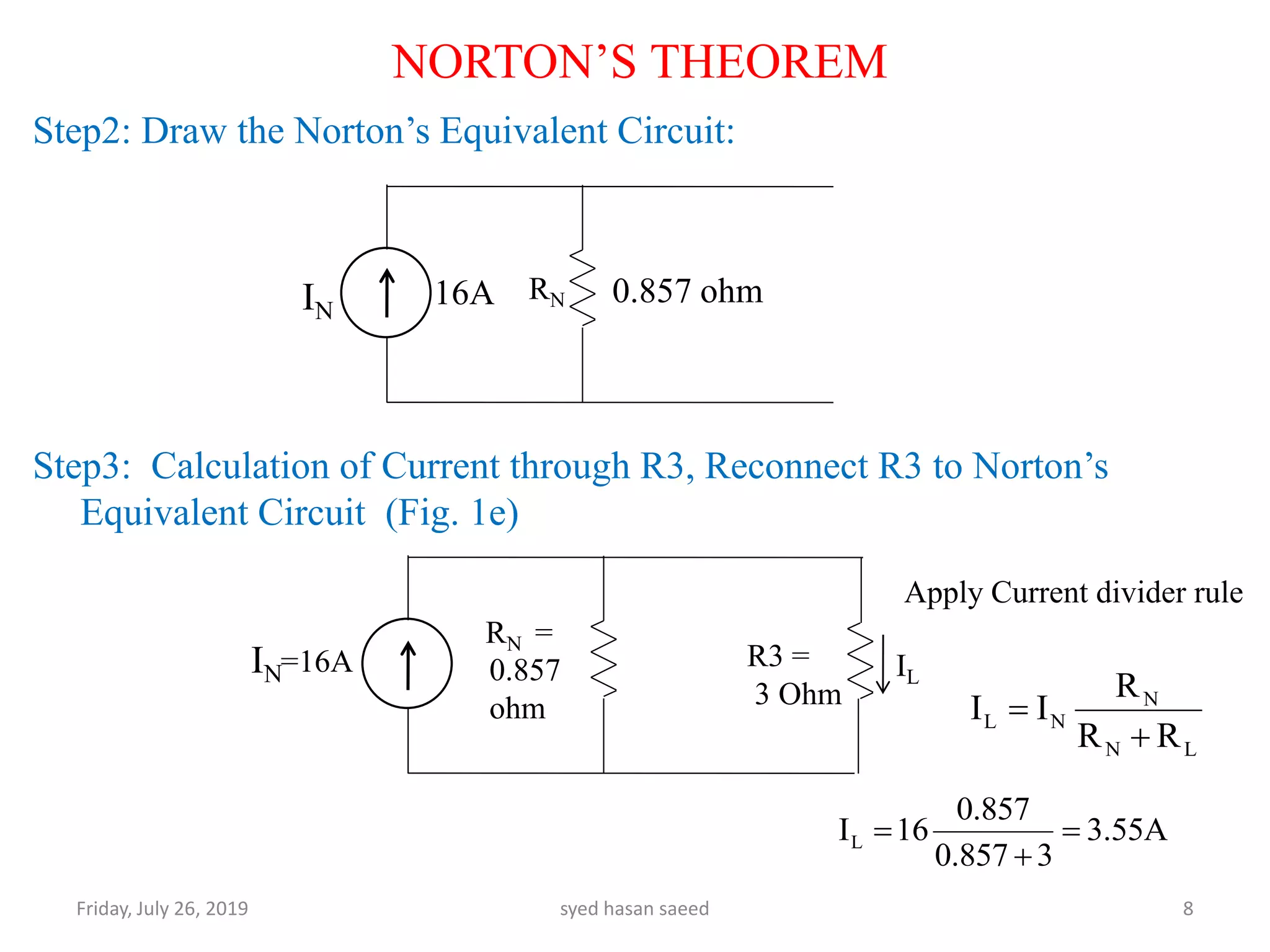
This document discusses Norton's theorem for circuit analysis. It begins by listing reference books on the topic. It then states that Norton's theorem allows any linear DC circuit to be replaced by an equivalent circuit with a single current source (IN) in parallel with a single resistance (RN). It provides the procedure to calculate the Norton equivalent current and resistance by opening independent current sources, shorting independent voltage sources, and calculating the current and resistance as seen by the terminals. An example problem demonstrates finding the current through a 3 ohm resistor using Norton's theorem.