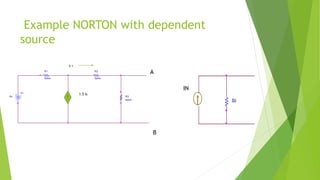
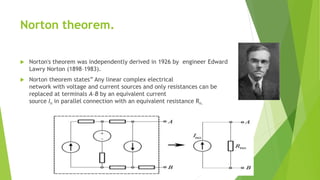
The document discusses Thevenin's and Norton's theorems. Thevenin's theorem states that any linear circuit can be reduced to an equivalent circuit with one voltage source in series with a single resistance. Norton's theorem states any linear circuit can be reduced to an equivalent circuit with one current source in parallel with a single resistance. The document provides examples of applying both theorems to complex circuits to find the equivalent Thevenin or Norton components. It also compares the two theorems noting Thevenin uses a voltage source in series with a resistance while Norton uses a current source in parallel with a resistance.


















![Step 1
remove the R(Load)
short the Vs
Open the Is
Rn=(15//15)+(20//20)
= [(15x15)/(15+15)]+[(20x20)/(20+20)]
= 7.5 + 10
Rn = 17.5Ω
20ohm
20ohm15ohm
15ohm](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thevninandnorton-191228080409/85/Thevnin-and-norton-21-320.jpg)