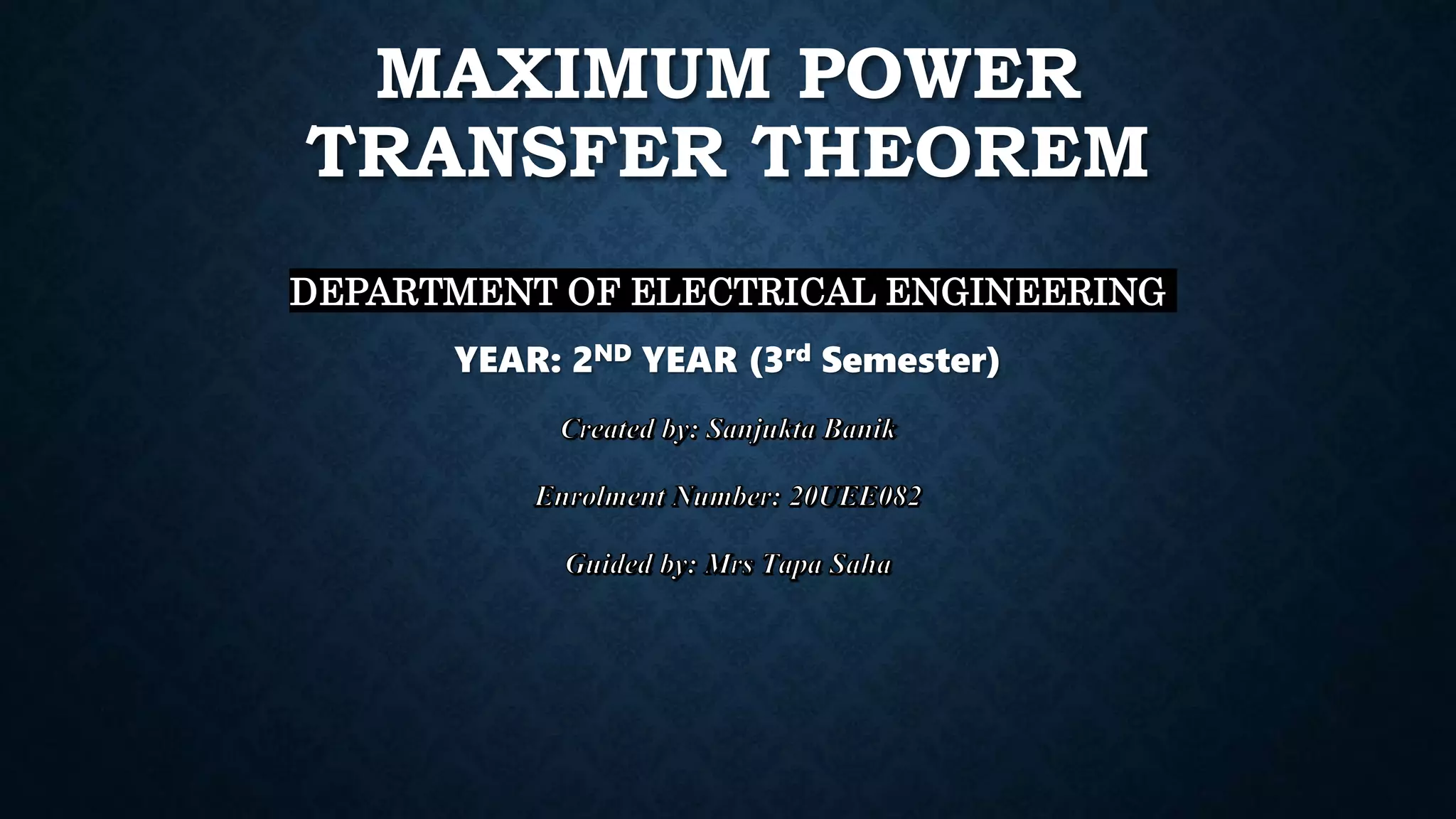
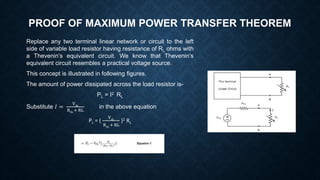
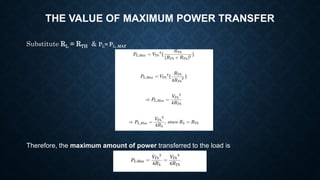
The document explains the maximum power transfer theorem, which states that maximum power is delivered to a load when the load resistance equals the internal resistance of the source in a linear, bilateral DC circuit. It further discusses the proof of the theorem, the condition for maximum power transfer, and provides a practical application involving a speaker and audio amplifier to illustrate the concept. The necessity for impedance matching in situations where load and source resistances differ is also highlighted.