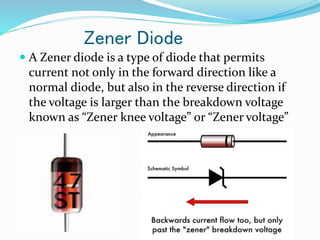
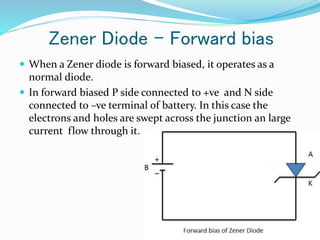
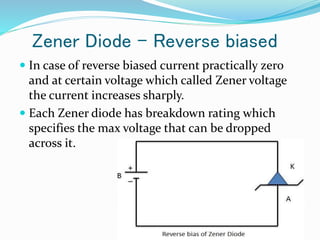
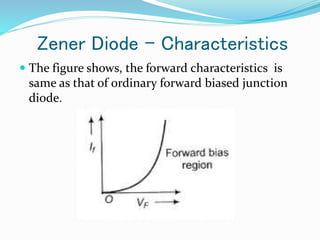
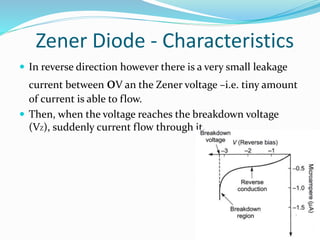
A diode is an electronic component with anode and cathode electrodes, commonly made from semiconductor materials. The Zener diode, a specific type of diode named after physicist Clarence Melvin Zener, allows current to flow in both forward and reverse directions when the voltage exceeds a certain threshold. Key characteristics and applications of Zener diodes include voltage regulation, comparison, and limitations, with operation dictated by parameters like Zener voltage, tolerance, and power handling capability.