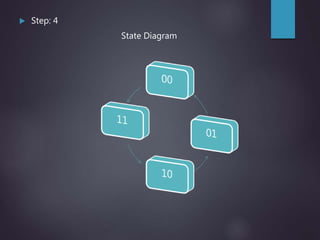
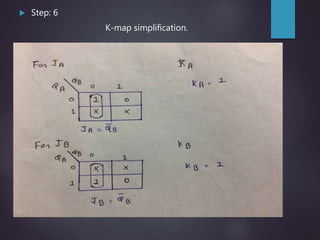
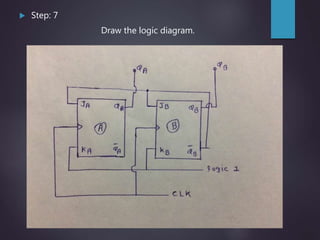
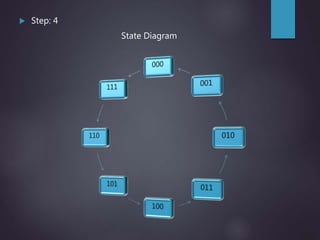
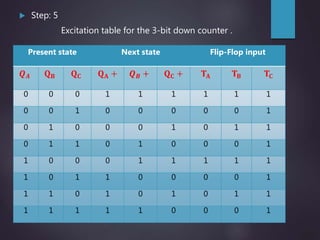
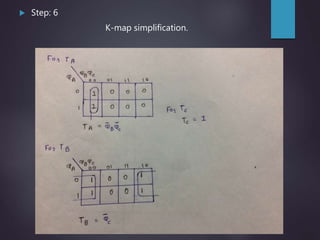
The document outlines the introduction and functioning of synchronous and asynchronous counters, focusing on the operation of flip-flops and the steps required to design a synchronous counter. It includes detailed steps for creating 2-bit and 3-bit down counters, including determining the number of flip-flops, writing excitation tables, state diagrams, and logic diagrams. Synchronous counters are highlighted for their ability to operate at higher frequencies due to simultaneous clocking of flip-flops, minimizing propagation delay.