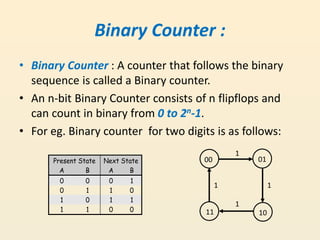
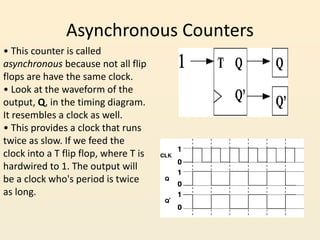
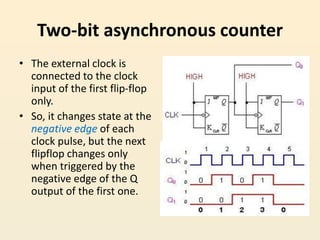
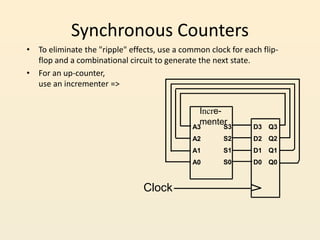
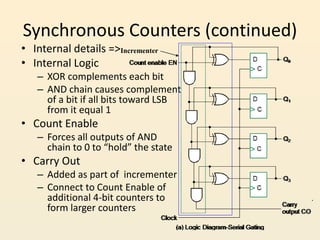
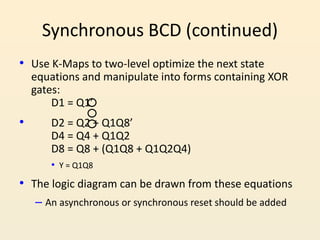
This document discusses different types of counters used in digital circuits. It defines a counter as a sequential circuit that cycles through a sequence of states in response to clock pulses. Binary counters count in binary and can count from 0 to 2n-1 with n flip-flops. Asynchronous counters have flip-flops that are not triggered simultaneously by a clock, while synchronous counters use a common clock for all flip-flops. Other counter types include ring counters, Johnson counters, and decade counters. The document provides examples of binary, asynchronous, and synchronous counters and discusses their applications in areas like timing sequences and addressing memory.