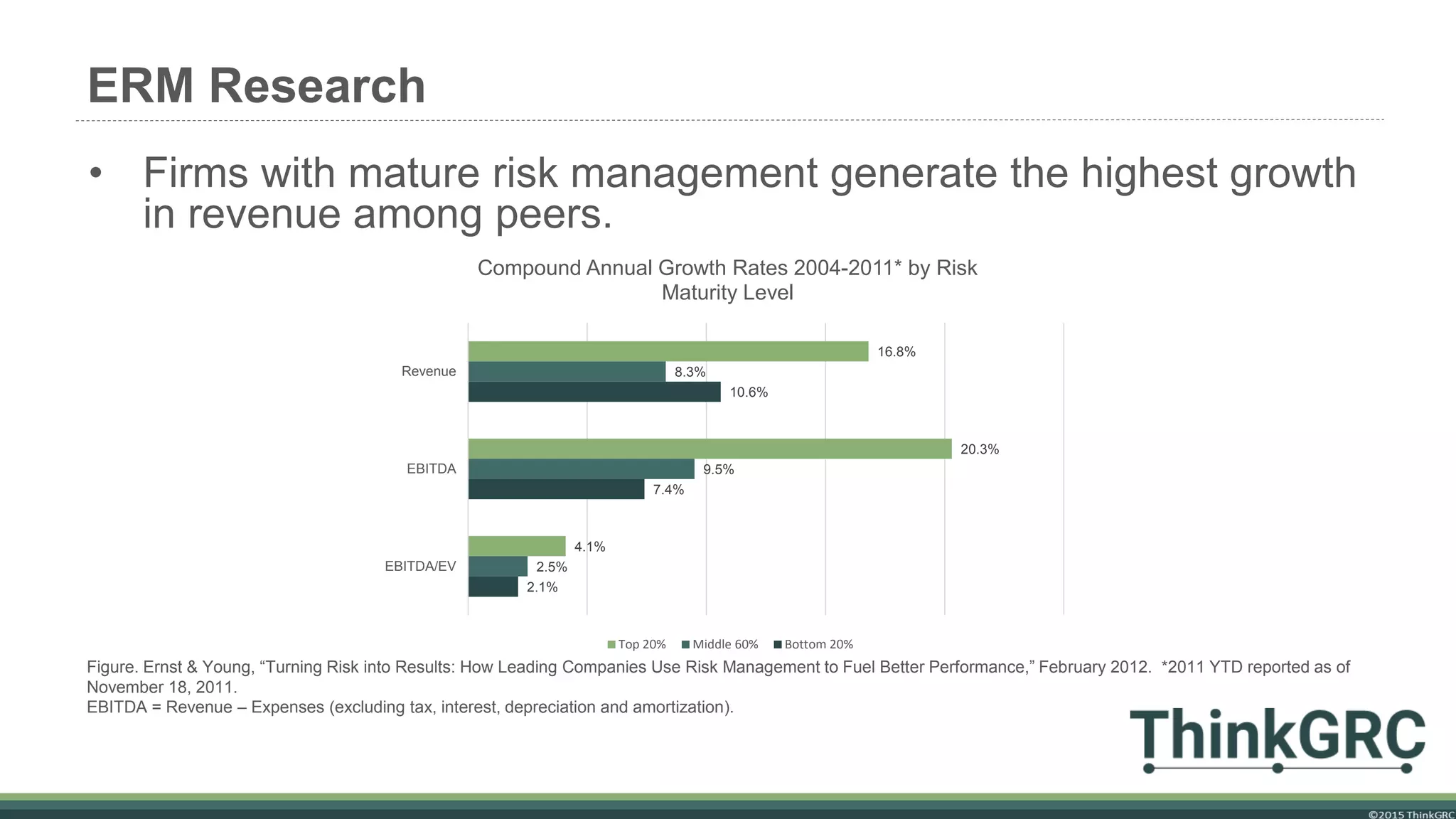
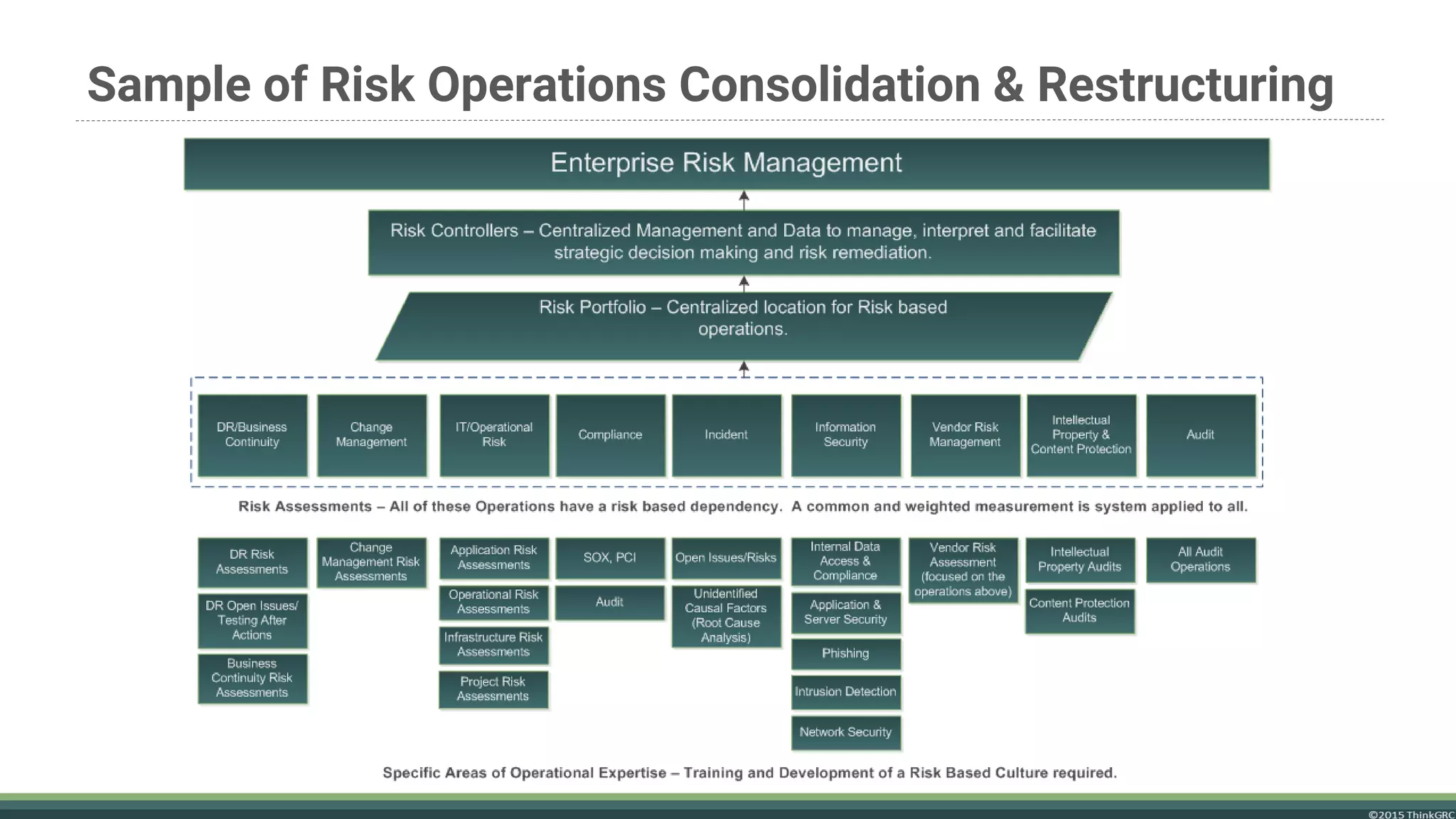
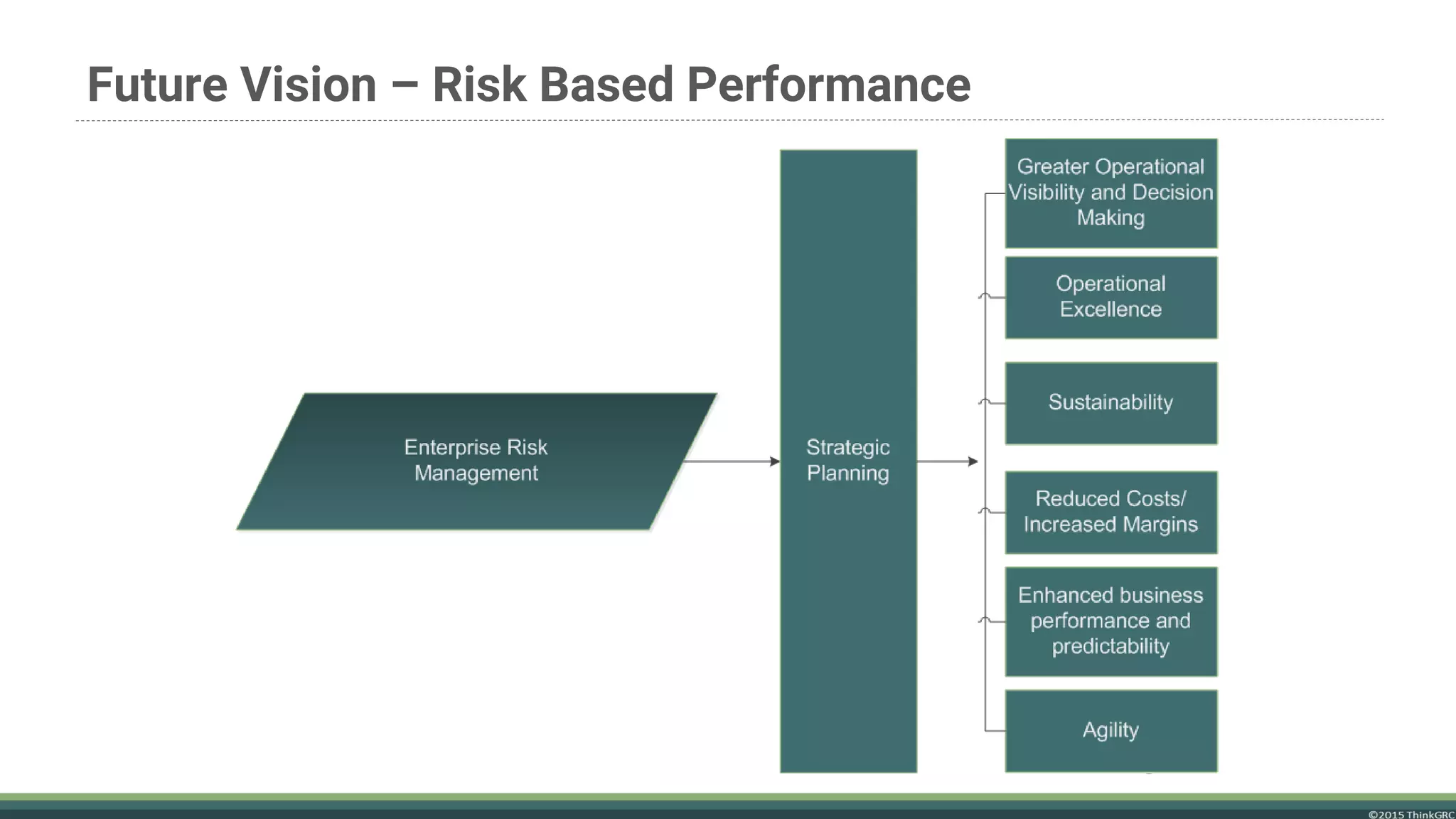
The document advocates for the transition to an Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) model to enhance organizational value and performance amidst challenges such as regulatory pressures and evolving customer needs. It outlines the components of ERM, benefits including improved financial performance and competitive advantage, and emphasizes the importance of a proactive risk management approach. It concludes that implementing ERM requires a focus on strategic planning and the correct use of enabling tools rather than relying solely on software solutions.