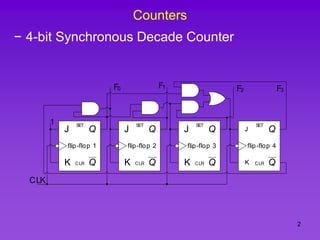
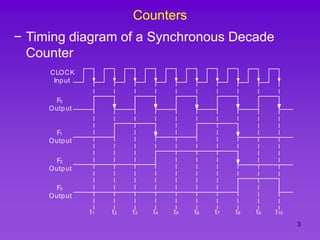
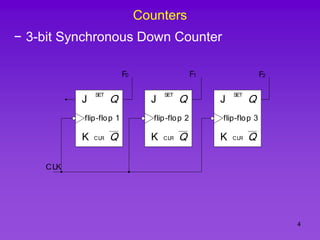
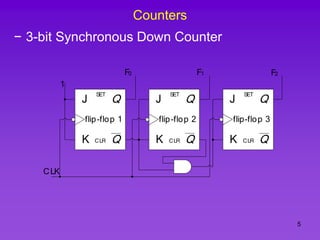
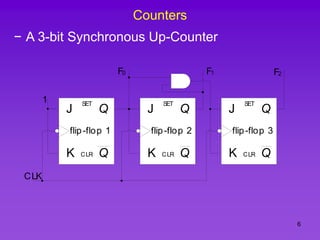
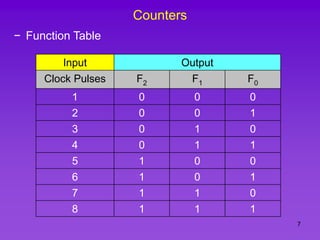
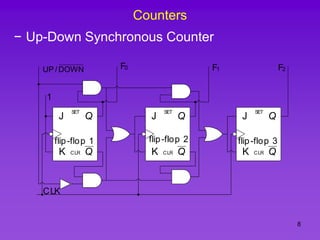
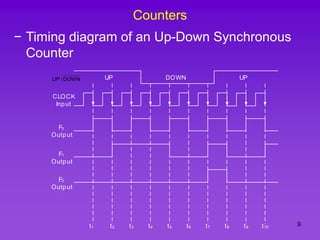
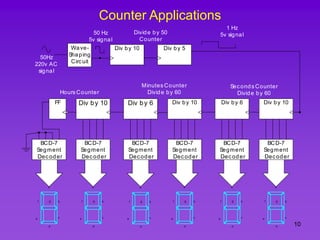
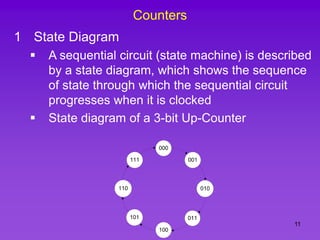
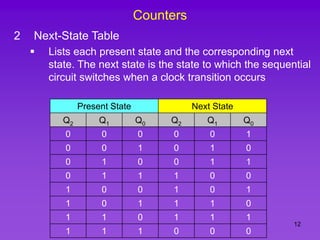
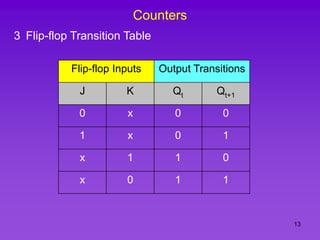
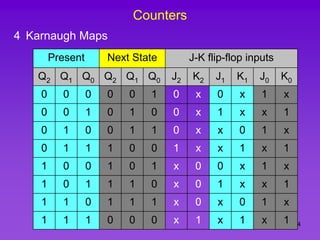
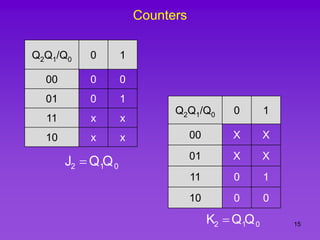
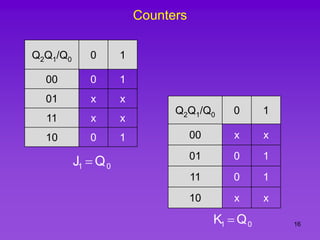
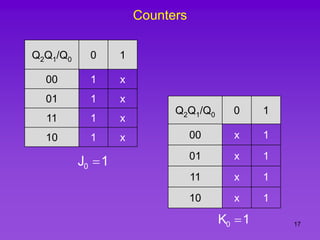
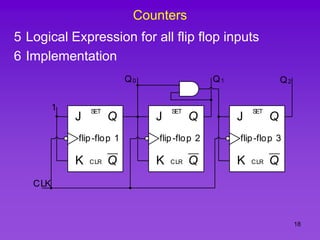
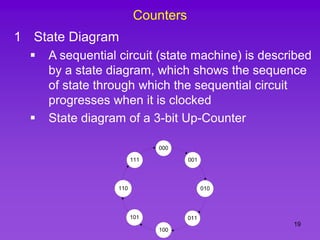
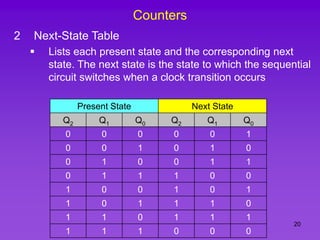
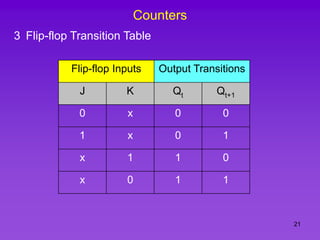
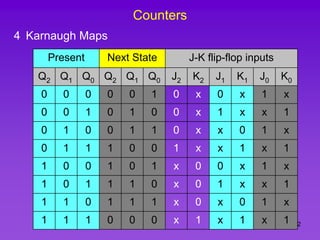
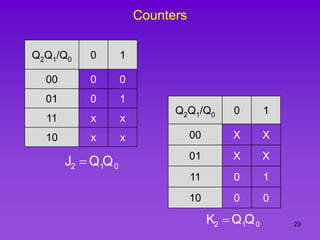
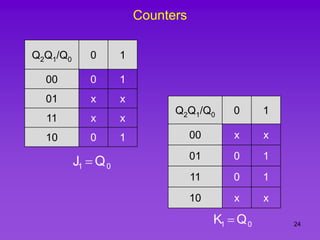
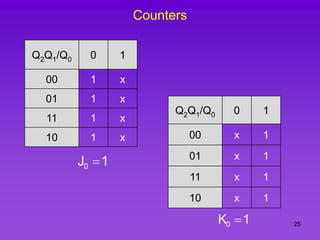
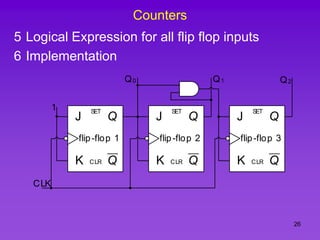
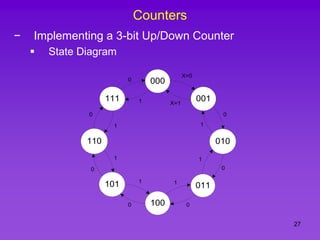
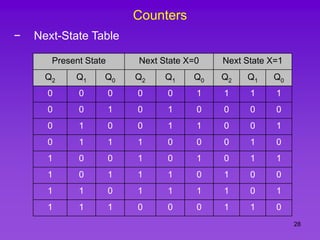
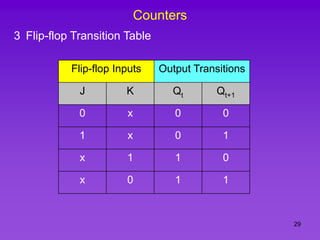
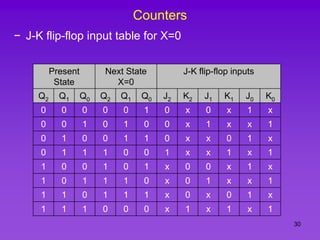
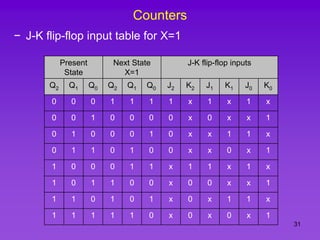
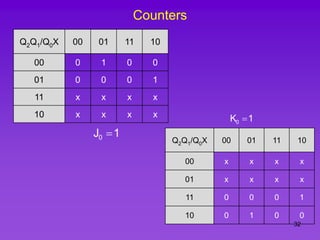
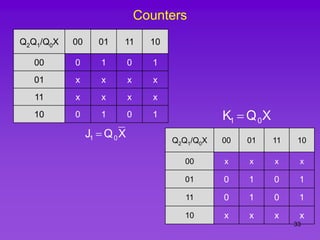
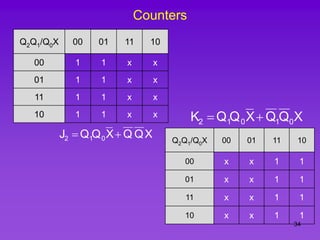
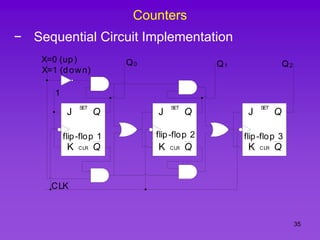
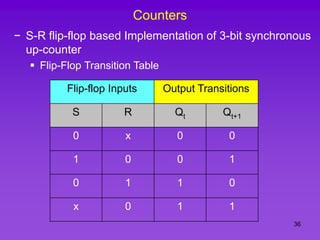
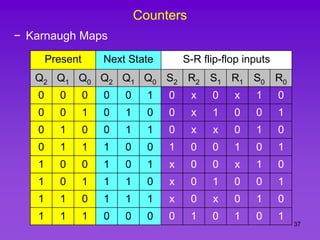
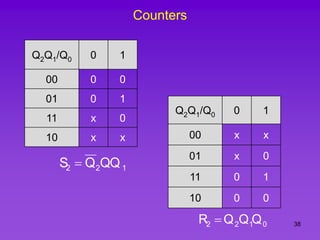
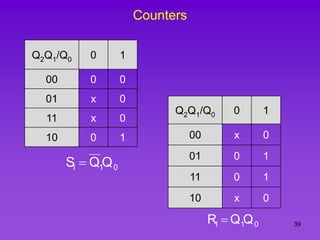
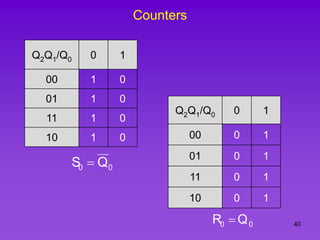
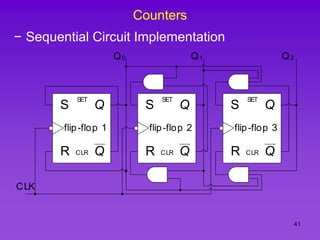
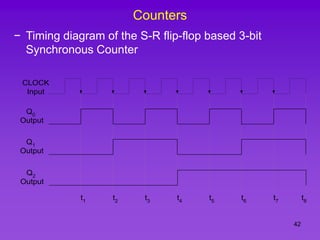
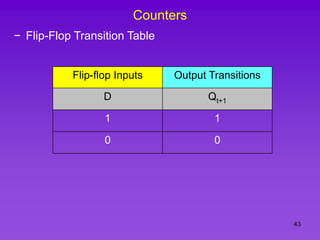
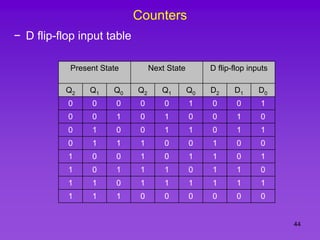
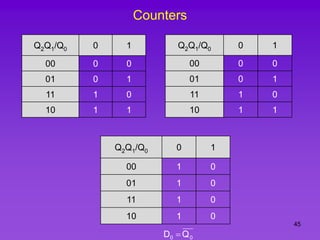
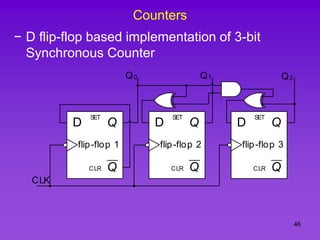
The document provides detailed information on computer logic and design, specifically focusing on various types of counters, including 4-bit synchronous decade counters and 3-bit synchronous up/down counters. It includes timing diagrams, state diagrams, next-state tables, and implementation details using flip-flops, along with Karnaugh maps for logical expressions. The content is structured to aid in understanding the sequential circuit design and applications of these counters in digital systems.