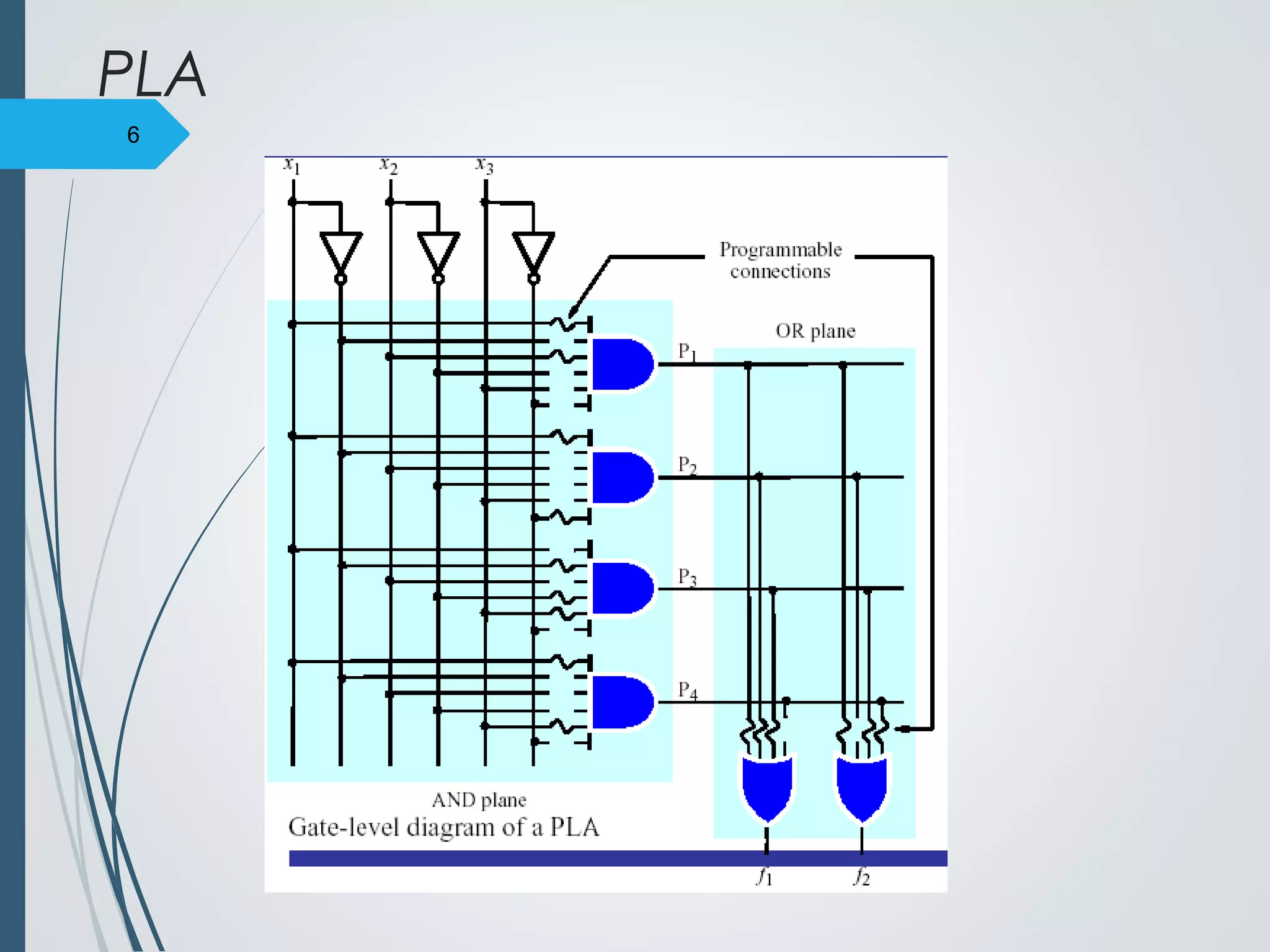
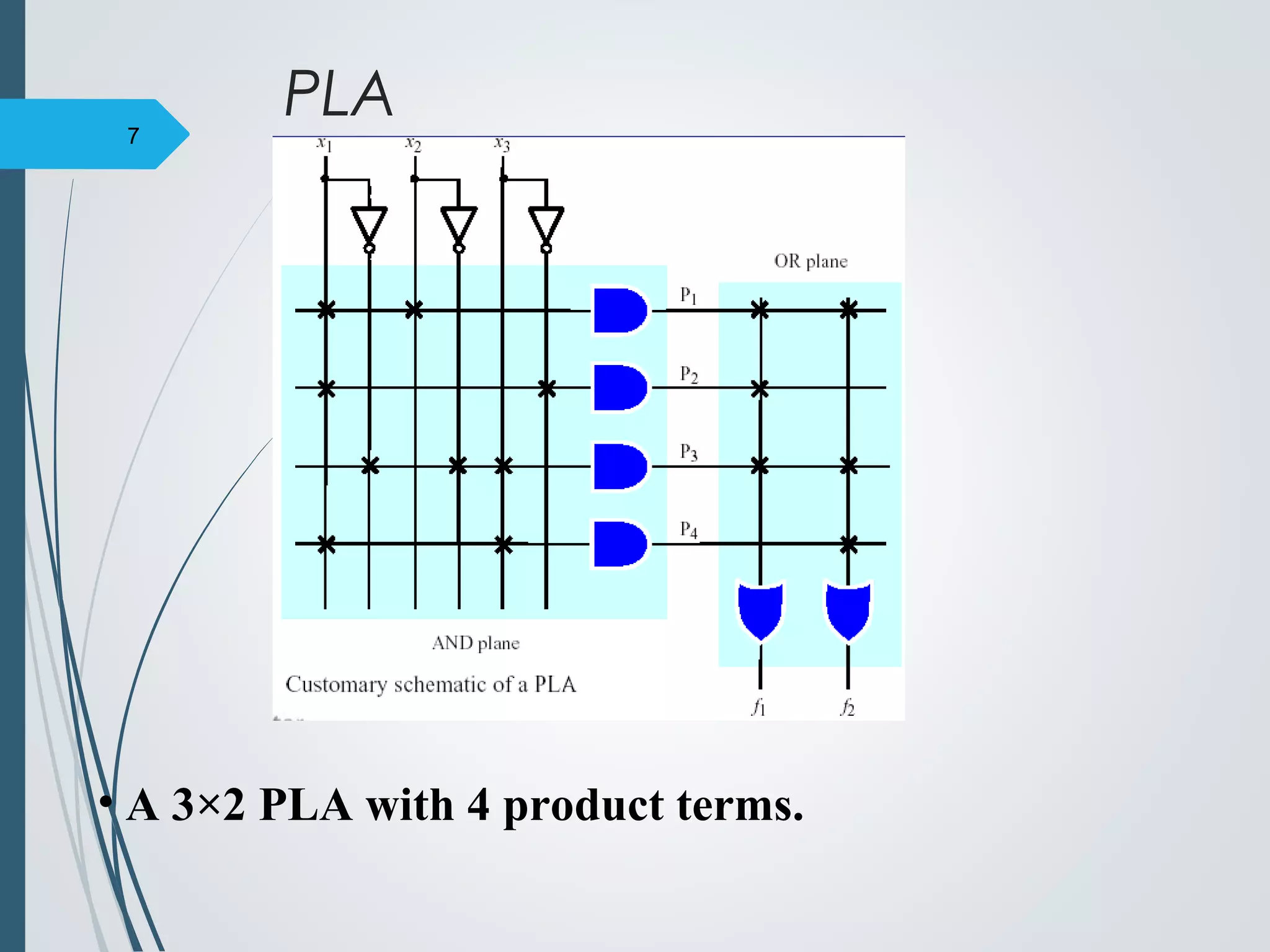
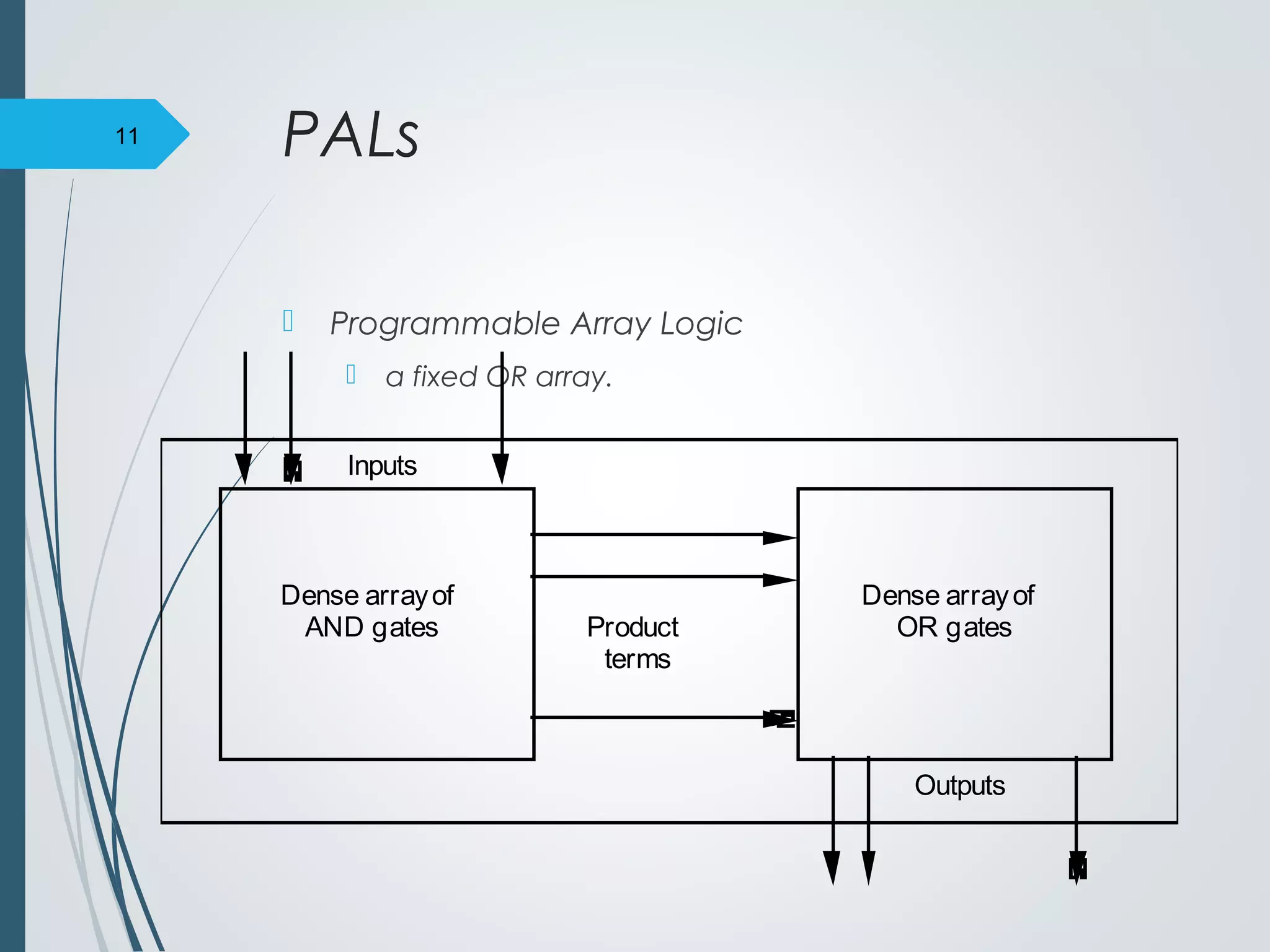
1. Programmable Logic Arrays (PLAs) are pre-fabricated logic blocks containing AND and OR gates that can be personalized by making or breaking connections between gates. This allows them to implement general purpose logic functions.
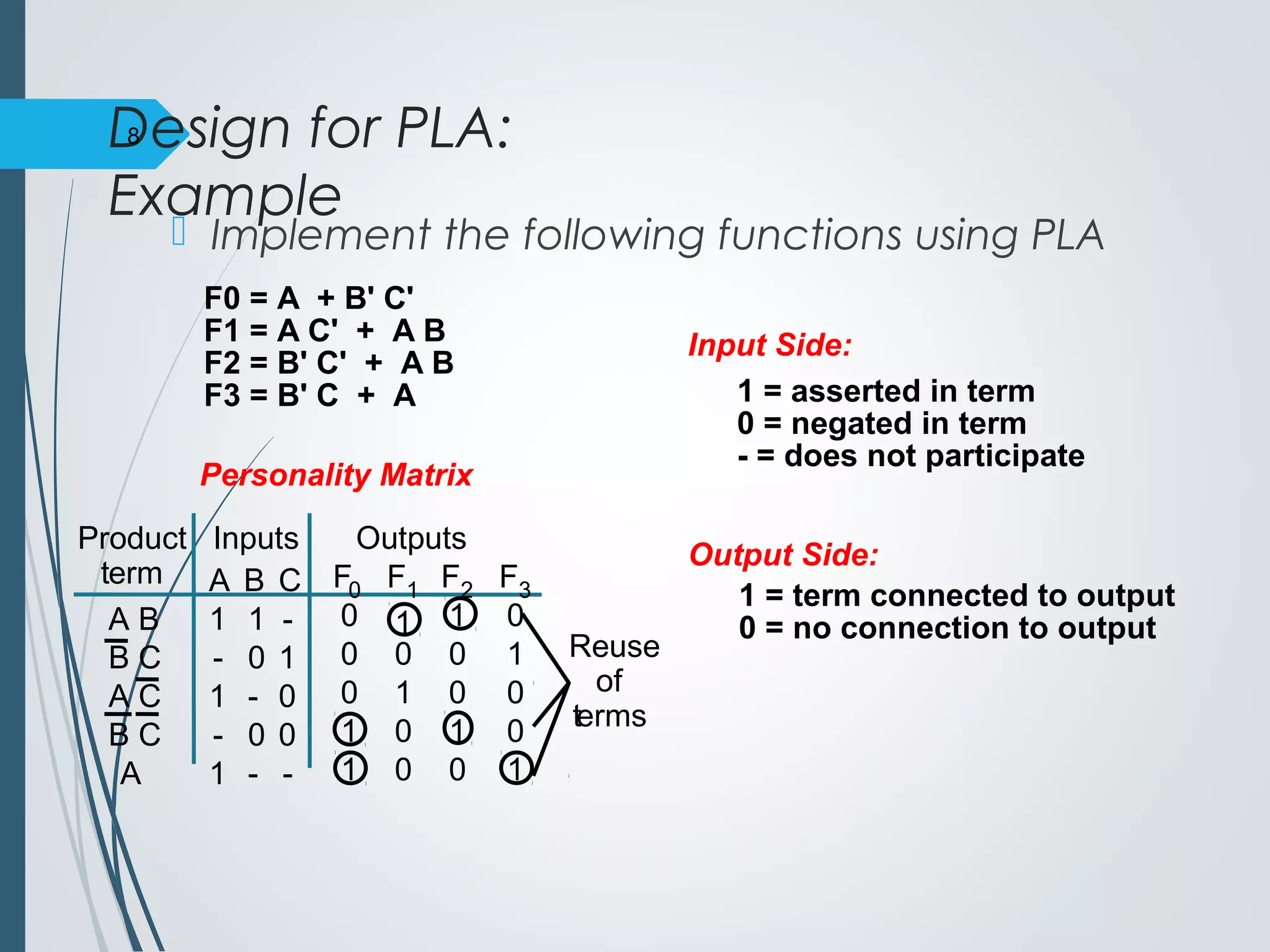
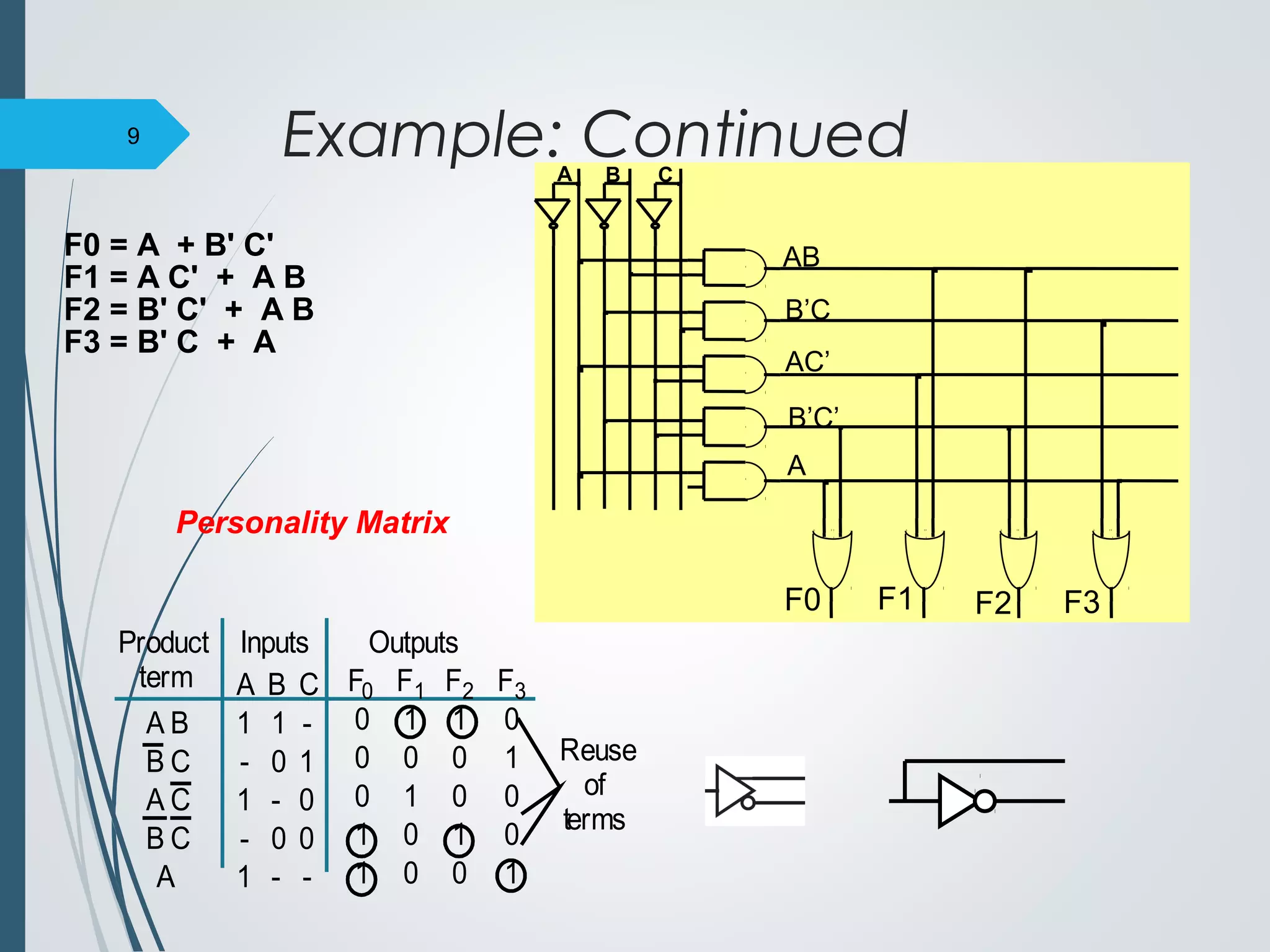
2. An example shows a 3x2 PLA implementing 4 logic functions through a personality matrix that defines which inputs are connected to each product term and which product terms are connected to each output.
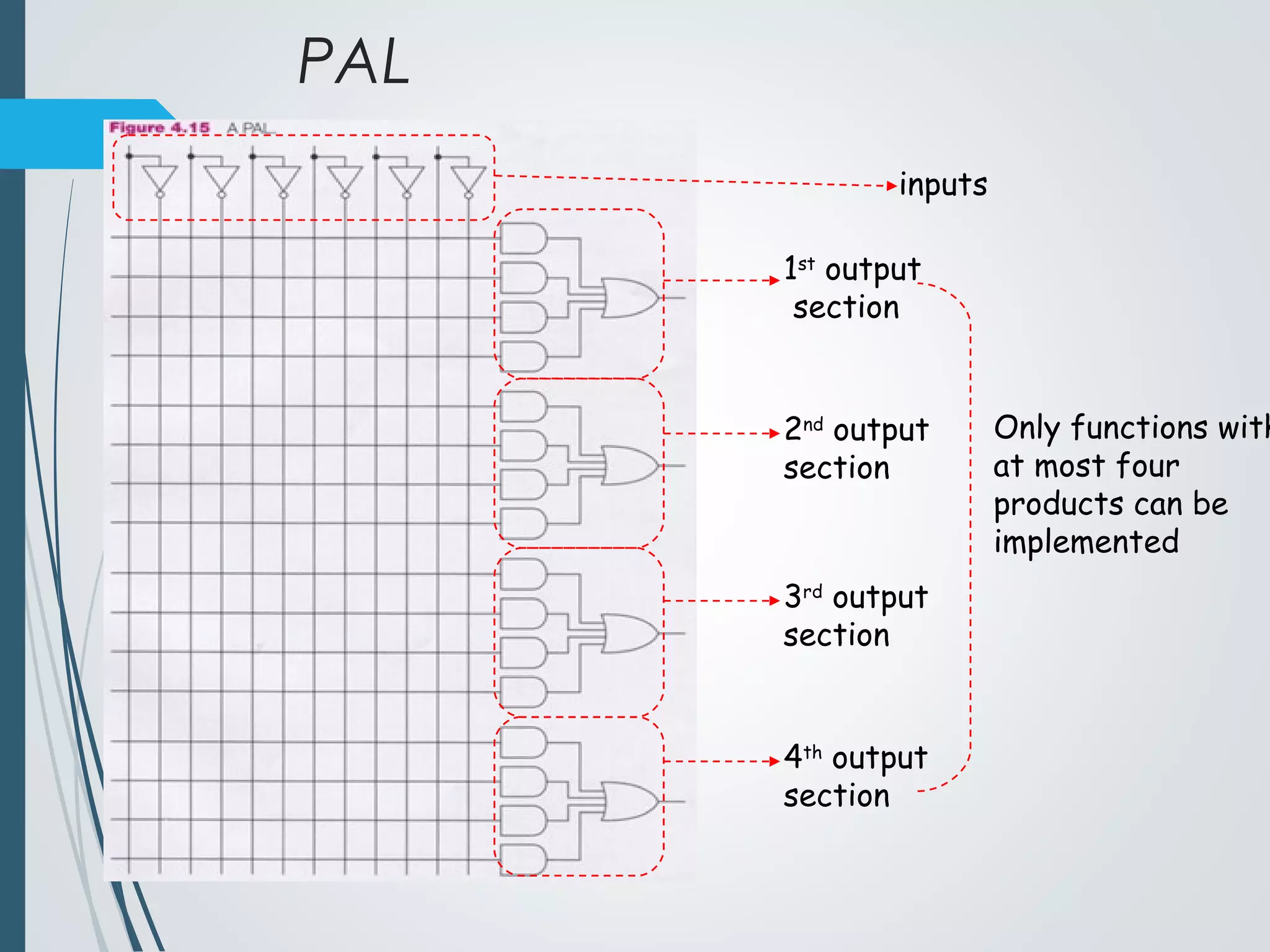
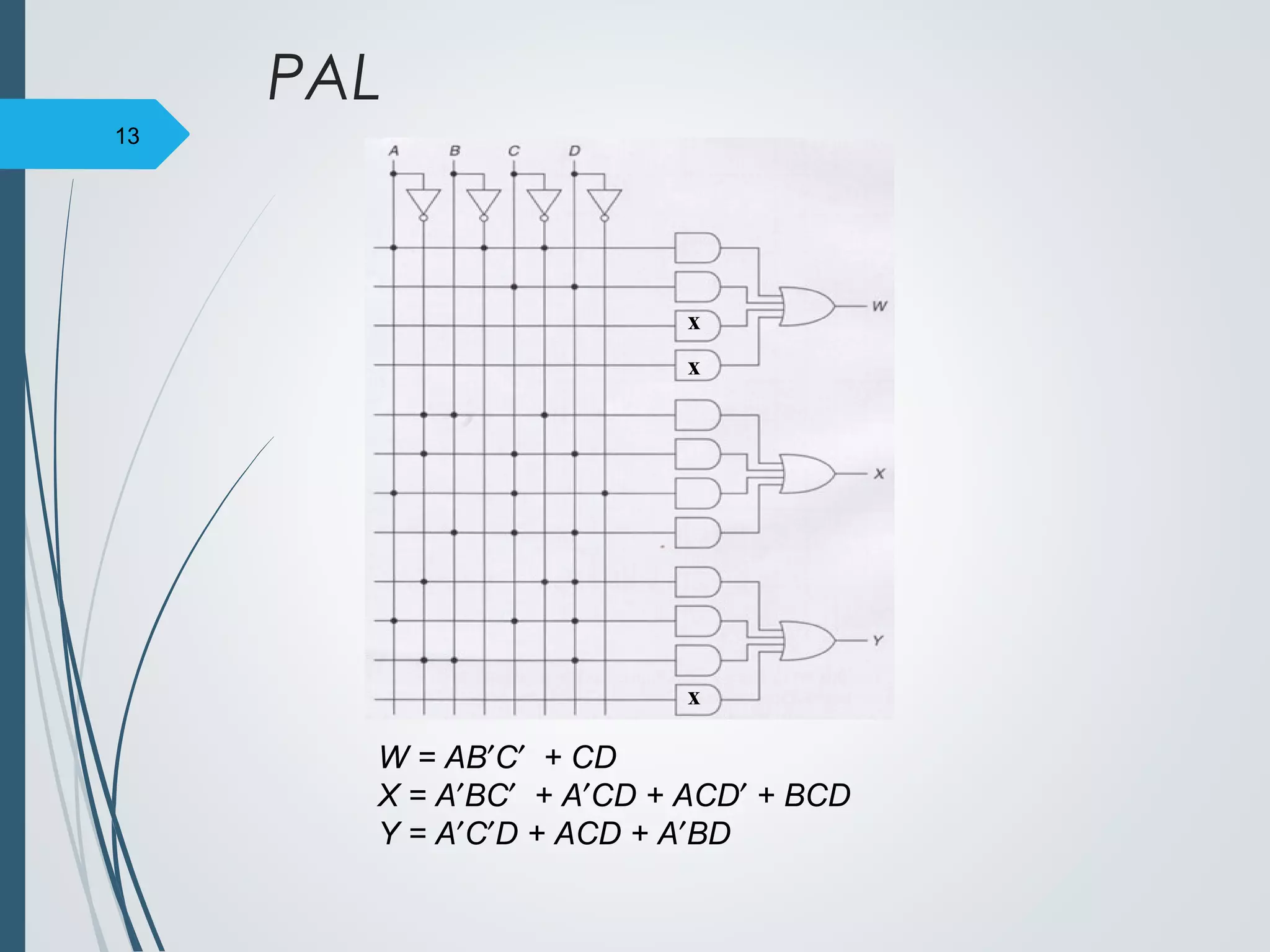
3. PALs (Programmable Array Logic) are similar to PLAs but contain a fixed OR array, limiting them to functions with at most 4 products.